
Most covalent bonds involve sharing of ………………. Electrons?
(A) $ 3 $
(B) $ 2 $
(C) $ 4 $
(D) $ 6 $
Answer
520.5k+ views
Hint :Chemical bonds are the force which holds the atoms together to form compounds. The classification of the bonds depends on the state of electrons. If the bond is formed by donating and accepting the electrons, it is an ionic bond and if it is formed by sharing of electrons then it is a covalent bond.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Covalent compounds are formed by mutual sharing of electrons to fulfill their orbits in order to be stable. For elements like carbon donating electrons from the valence shell or accepting it, becomes difficult as carbon has four electrons to be either removed or more four to be added to be stable which is quite difficult.
In order to overcome the problem these types of atoms share electrons with other atoms with similar ones.
Single covalent bond: In single covalent bond one electron of each atom is shared. We can say a pair of electrons is shared. Single covalent bond forms a sigma bond in which the orbitals overlap head-on and electron density is concentrated in the middle of two nuclei.
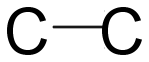
Double covalent bond: In this two electrons from each atom involved in bonding i.e. two pairs of electrons are shared. One of the bonds is sigma and the other is pi bond. Pi bond is formed by overlapping of orbitals laterally.
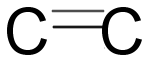
Triple covalent bond: In this bond three electrons from each atom are involved in sharing i.e. three pairs of electrons. In which one is sigma and one is Pi bond.
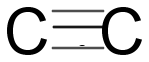
Thus, options (A) $ 3 $ and (B) $ 2 $ are the correct choice.
Note :
The strength of double and triple covalent bonds are more than single covalent bonds. Double and triple bonds also restrict the geometry and hence increases the stability of covalent compounds.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Covalent compounds are formed by mutual sharing of electrons to fulfill their orbits in order to be stable. For elements like carbon donating electrons from the valence shell or accepting it, becomes difficult as carbon has four electrons to be either removed or more four to be added to be stable which is quite difficult.
In order to overcome the problem these types of atoms share electrons with other atoms with similar ones.
Single covalent bond: In single covalent bond one electron of each atom is shared. We can say a pair of electrons is shared. Single covalent bond forms a sigma bond in which the orbitals overlap head-on and electron density is concentrated in the middle of two nuclei.
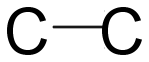
Double covalent bond: In this two electrons from each atom involved in bonding i.e. two pairs of electrons are shared. One of the bonds is sigma and the other is pi bond. Pi bond is formed by overlapping of orbitals laterally.
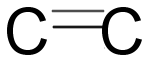
Triple covalent bond: In this bond three electrons from each atom are involved in sharing i.e. three pairs of electrons. In which one is sigma and one is Pi bond.
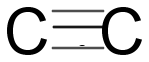
Thus, options (A) $ 3 $ and (B) $ 2 $ are the correct choice.
Note :
The strength of double and triple covalent bonds are more than single covalent bonds. Double and triple bonds also restrict the geometry and hence increases the stability of covalent compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




