
Monocot root differs from the dicot root in
a) presence of more than six xylem vessels
b) well-developed pith
c)absence of secondary growth
d)all of the above
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: monocot root is the fibrous root. It has many small fibers structure arriving from it. They form a wide network. They arise from the base of the stem. The dicot root is the taproot and it has one main root structure from which small fibers arise.
Complete answer:
So, the answer is ‘all of the above’.
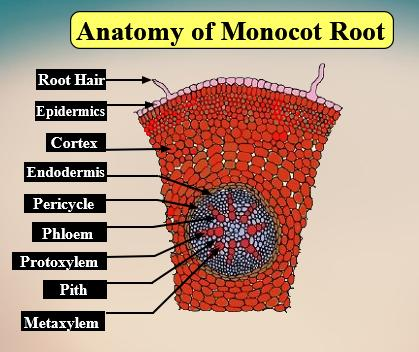
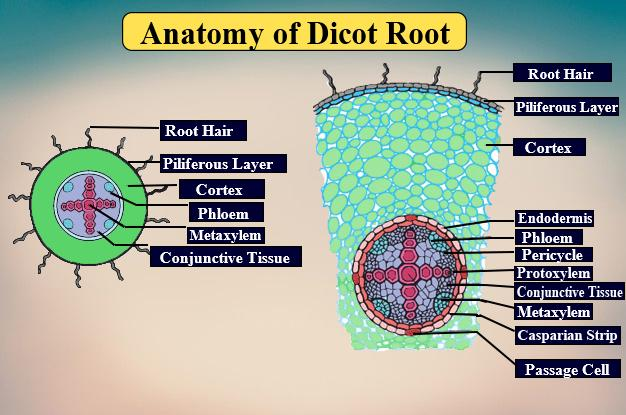
Note: Xylem and phloem bundles are present together and are in the same amount of number in both monocot and dicot root. The best way to differentiate the monocot root from the dicot root is to see whether pith is present or absent.
Complete answer:
| DICOT ROOT | MONOCOT ROOT |
| - In the dicot root the cortex is very narrow | -In the monocot root the cortex is broad and wide. |
| - During the cork formation in the dicot root the epiblema, cortex, and endodermis are peeled off. These layers get replaced by the cork. | -In monocot root cork formation does not take place. The epiblema is peeled off. |
| - Endodermis is not very thick and the Casparian strips are easily visible on the dicot root. The passage cells are absent in it. | -The Casparian strips are only visible in the younger roots and become highly thickened as the roots mature. |
| - Pericycle produces lateral roots, cork cambium, and vascular cambium. Only a part of the vascular cambium is present in the dicot root | - Pericycle produce lateral roots in the plant. |
| -The xylem bundles present are usually 2-5 in number. They are generally arranged angularly to each other. | -Xylem and phloem bundles are numerous. They are usually oval or round in shape. |
| -The conjunctive tissue is parenchymatous in nature and forms the cambium. There is a presence of secondary growth in dicot roots. | -The conjunctive tissue is parenchyma or sclerenchyma in nature and it does not produce cambium. Secondary growth is absent in the sclerenchyma root. |
| -The pith is absent. | -Pith present is well developed. |
So, the answer is ‘all of the above’.


Note: Xylem and phloem bundles are present together and are in the same amount of number in both monocot and dicot root. The best way to differentiate the monocot root from the dicot root is to see whether pith is present or absent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




