
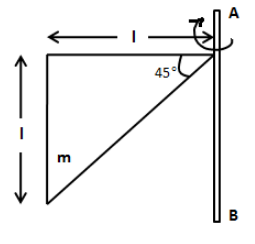
Moment of inertia of a triangle plane of mass M shown in the figure, about axis AB is:

Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint:The centre of mass of a right angle triangle is \[\dfrac{2}{3}l\] from the axis. According to the parallel axes theorem, the moment of inertia of the body is the sum of the moment of inertia of the body about the axis passing through the centre of the body and the product of the mass of the body and square of the distance between the two axes. The moment of inertia of the triangle about the axis passing through the centre is \[{I_C} = \dfrac{{M{l^2}}}{{18}}\].
Formula used:
Parallel axes theorem, \[I = {I_C} + M{R^2}\]
Here, \[{I_C}\] is the moment of inertia about the centre of mass, M is the mass of the body and R is the distance between the two parallel axes.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that the base and height of the triangle is l. Also, the mass of the triangle is M. We know that the centre of mass of a right angle triangle is \[\dfrac{2}{3}l\] from the axis. Here, l is the base length of the triangle.
We have from the parallel axis theorem, the moment of inertia of the body is the sum of the moment of inertia of the body about the axis passing through the centre of the body and the product of the mass of the body and square of the distance between the two axes. Therefore, we can express the moment of inertia of this triangle about the axis AB as,
\[{I_{AB}} = {I_C} + M{R^2}\]
Here, R is the distance between the two axes and it is equal to \[\dfrac{2}{3}l\]. Therefore, the above equation becomes,
\[{I_{AB}} = {I_C} + M{\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}l} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {I_{AB}} = {I_C} + \dfrac{4}{9}M{l^2}\] …… (1)
We know the moment of inertia of the triangle about the axis passing through the centre is,
\[{I_C} = \dfrac{{M{l^2}}}{{18}}\]
Substituting the above equation in equation (1), we get,
\[ \Rightarrow {I_{AB}} = \dfrac{{M{l^2}}}{{18}} + \dfrac{4}{9}M{l^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {I_{AB}} = M{l^2}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{18}} + \dfrac{4}{9}} \right)\]
\[ \therefore {I_{AB}} = \dfrac{{M{l^2}}}{2}\]
Thus, the moment of inertia of the triangle about the axis AB is \[\dfrac{{M{l^2}}}{2}\].
Note: To derive the expression for the centre of mass of a triangle requires a lot of calculations. To avoid this, students can memorize the expression for centre of mass of the right angle triangle, \[{\text{COM}} = \dfrac{2}{3}l\]. Whether the triangle moves clockwise or counter clockwise, the moment of inertia of the triangle will not change.
Formula used:
Parallel axes theorem, \[I = {I_C} + M{R^2}\]
Here, \[{I_C}\] is the moment of inertia about the centre of mass, M is the mass of the body and R is the distance between the two parallel axes.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that the base and height of the triangle is l. Also, the mass of the triangle is M. We know that the centre of mass of a right angle triangle is \[\dfrac{2}{3}l\] from the axis. Here, l is the base length of the triangle.
We have from the parallel axis theorem, the moment of inertia of the body is the sum of the moment of inertia of the body about the axis passing through the centre of the body and the product of the mass of the body and square of the distance between the two axes. Therefore, we can express the moment of inertia of this triangle about the axis AB as,
\[{I_{AB}} = {I_C} + M{R^2}\]
Here, R is the distance between the two axes and it is equal to \[\dfrac{2}{3}l\]. Therefore, the above equation becomes,
\[{I_{AB}} = {I_C} + M{\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}l} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {I_{AB}} = {I_C} + \dfrac{4}{9}M{l^2}\] …… (1)
We know the moment of inertia of the triangle about the axis passing through the centre is,
\[{I_C} = \dfrac{{M{l^2}}}{{18}}\]
Substituting the above equation in equation (1), we get,
\[ \Rightarrow {I_{AB}} = \dfrac{{M{l^2}}}{{18}} + \dfrac{4}{9}M{l^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {I_{AB}} = M{l^2}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{18}} + \dfrac{4}{9}} \right)\]
\[ \therefore {I_{AB}} = \dfrac{{M{l^2}}}{2}\]
Thus, the moment of inertia of the triangle about the axis AB is \[\dfrac{{M{l^2}}}{2}\].
Note: To derive the expression for the centre of mass of a triangle requires a lot of calculations. To avoid this, students can memorize the expression for centre of mass of the right angle triangle, \[{\text{COM}} = \dfrac{2}{3}l\]. Whether the triangle moves clockwise or counter clockwise, the moment of inertia of the triangle will not change.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




