
What is the Molecular geometry of $CC{l_4}$? Draw its VSPER and Lewis structure?
Answer
471.6k+ views
HINT: The three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that make up a molecule is known as molecular geometry. It provides the molecule's overall shape, as well as bond lengths, bond angles, and other details. To predict molecular geometry, the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory (abbreviated VSEPR) is widely utilized. According to the hypothesis, repulsion between pairs of electrons on a core atom (whether bonding or non-bonding electron pairs) controls the molecule's structure. The valence shell electron pair repulsion hypothesis is a chemical model that predicts a molecule's geometry based on the number of electron pairs surrounding its core atoms.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP ANSWER:
The molecular geometry of $CC{l_4}$ is tetrahedral with bond angles of ${109.5^ \circ }$
Here are the steps that we should follow when drawing a Lewis structure.
$1$ . Determine which atom is the structure's core atom. That will be the atom with the least electronegative charge.
$2$ . Make a skeletal structure with the other atoms single-bonded to the core atom, which is a c atom with four cl atoms linked to it.
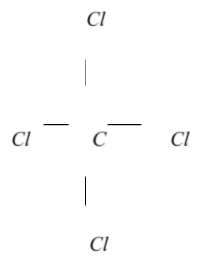
$3$. Make a test structure by wrapping electron pairs around each atom until each one has an octet. (In the trial structure, every atom possesses an octet.)
$4$. Count how many valence electrons there are in your test structure \[\left( {32} \right)\].
$5$. Count the number of valence electrons we have.
$1C$ $ + $ $4Cl$ $ = $ $1 \times 4 + 4 \times 7$ $ = $ $32$
$6$. The number of electrons available in the trial structure is exactly the same as ours.
As a result, the trial structure is the Lewis structure.
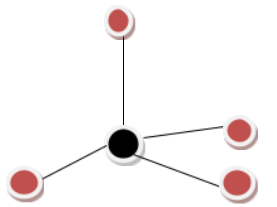
VSEPR Geometry
There are four electron zones around the core carbon atom, according to the Lewis structure.
According to the VSEPR model, the electron zones around an atom expand out to make each region as far apart as possible.
These $CC{l_4}$ clouds will aim towards the corners of a tetrahedron to be as far apart as feasible.
The bonds will radiate from the center atom at ${109.5^ \circ }$ angles to one another.
From the above information, it is confirmed that the structure is Tetrahedral.
Note:
The VSEPR model can be helpful in predicting the structure of almost any molecule or polyatomic ion with a nonmetal central atom, as well as many molecules and polyatomic ions with a central metal atom. The counting process used in VSEPR can accurately predict the three-dimensional structures of a large number of compounds which cannot be predicted using the Lewis electron-pair approach. By focusing exclusively on the number of electron pairs around the core atom, we may use the VSEPR model to predict the geometry of most polyatomic compounds and ions.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP ANSWER:
The molecular geometry of $CC{l_4}$ is tetrahedral with bond angles of ${109.5^ \circ }$
Here are the steps that we should follow when drawing a Lewis structure.
$1$ . Determine which atom is the structure's core atom. That will be the atom with the least electronegative charge.
$2$ . Make a skeletal structure with the other atoms single-bonded to the core atom, which is a c atom with four cl atoms linked to it.
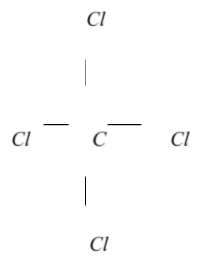
$3$. Make a test structure by wrapping electron pairs around each atom until each one has an octet. (In the trial structure, every atom possesses an octet.)
$4$. Count how many valence electrons there are in your test structure \[\left( {32} \right)\].
$5$. Count the number of valence electrons we have.
$1C$ $ + $ $4Cl$ $ = $ $1 \times 4 + 4 \times 7$ $ = $ $32$
$6$. The number of electrons available in the trial structure is exactly the same as ours.
As a result, the trial structure is the Lewis structure.
VSEPR Geometry
There are four electron zones around the core carbon atom, according to the Lewis structure.
According to the VSEPR model, the electron zones around an atom expand out to make each region as far apart as possible.
These $CC{l_4}$ clouds will aim towards the corners of a tetrahedron to be as far apart as feasible.
The bonds will radiate from the center atom at ${109.5^ \circ }$ angles to one another.
From the above information, it is confirmed that the structure is Tetrahedral.

Note:
The VSEPR model can be helpful in predicting the structure of almost any molecule or polyatomic ion with a nonmetal central atom, as well as many molecules and polyatomic ions with a central metal atom. The counting process used in VSEPR can accurately predict the three-dimensional structures of a large number of compounds which cannot be predicted using the Lewis electron-pair approach. By focusing exclusively on the number of electron pairs around the core atom, we may use the VSEPR model to predict the geometry of most polyatomic compounds and ions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




