
Minimum distance between the curves ${{y}^{2}}=x-1$ and ${{x}^{2}}=y-1$ is equal to :
(a) $\dfrac{3\sqrt{2}}{4}$
(b) $\dfrac{5\sqrt{2}}{4}$
(c) $\dfrac{7\sqrt{2}}{4}$
(d) $\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{4}$
Answer
620.7k+ views
Hint: Here, we will first draw the curves and then we will find the shortest distance between them. If the curves are intersecting then obviously the shortest distance between them is zero. If they are not intersecting then we will find the points on the curves which corresponds to nearest distance and then calculate the distance using the distance formula which states that distance between two points (a, b) and (c, d) is given as $d=\sqrt{{{\left( a-c \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( b-d \right)}^{2}}}$ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
The curves given here are:
${{y}^{2}}=x-1$ and ${{x}^{2}}=y-1$
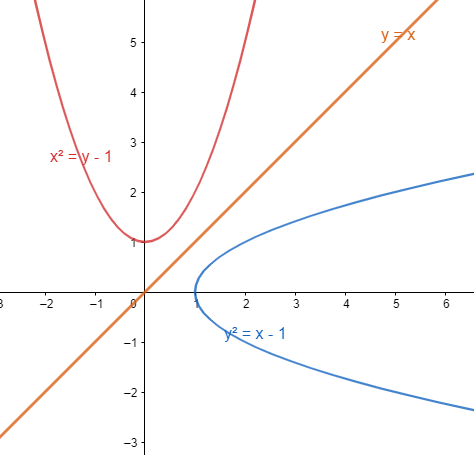
Both of the curves given here are symmetric about the origin. Thus the curves are symmetrical along the line y = x, that is one curve is the mirror image of the other curve along this line.
Now the shortest distance between the two curves is along the common normal to both the curves . The common normal of two non-intersecting curves is a line perpendicular to both the curves . So, the common normal is perpendicular to y = x.
The points on the curve which corresponds to the shortest distance between the curves will have the slope of their tangent equal to that of the line y =x. That is, if tangents are drawn at points corresponding to the shortest distance then these tangents will have a slope equal to 1.
The first curve is: ${{y}^{2}}=x-1$
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get:
$\begin{align}
& 2y.\dfrac{dy}{dx}=1-0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{1}{2y} \\
\end{align}$
But, we have found that the slope of tangent to the curves at the required point is 1.
So, we can write:
$\begin{align}
& 1=\dfrac{1}{2y} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}$
On putting value of y in the first curve, we get:
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}=x-1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{4}+1=x \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Similarly, on differentiating the second curve with respect to x, we get:
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{d\left( {{x}^{2}} \right)}{dx}=\dfrac{d\left( y-1 \right)}{dx} \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=\dfrac{dy}{dx} \\
\end{align}$
Since, we have slope = 1. So:
$\begin{align}
& 1=2x \\
& \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}$
On putting the value of x in second equation, we get:
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}=y-1 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{1}{4}+1=\dfrac{5}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that the distance between two points (a, b) and (c, d) is given as $d=\sqrt{{{\left( a-c \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( b-d \right)}^{2}}}$ . We also know that the distance between the points $\left( \dfrac{5}{4},\dfrac{1}{2} \right)$ and $\left( \dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{5}{4} \right)$ will give the shortest distance between the two curves.
So, the shortest distance is:
\[\begin{align}
& =\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{5}{4} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{5}{4}-\dfrac{1}{2}
\right)}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{2-5}{4} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{5-2}{4} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{\dfrac{9}{16}+\dfrac{9}{16}}=\dfrac{3\sqrt{2}}{4} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, option (a) is the correct answer.
Note: Students should note here that the slope of tangent to a curve is always given as the value of derivative of the curve at that point. The calculations must be done properly to avoid mistakes.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The curves given here are:
${{y}^{2}}=x-1$ and ${{x}^{2}}=y-1$

Both of the curves given here are symmetric about the origin. Thus the curves are symmetrical along the line y = x, that is one curve is the mirror image of the other curve along this line.
Now the shortest distance between the two curves is along the common normal to both the curves . The common normal of two non-intersecting curves is a line perpendicular to both the curves . So, the common normal is perpendicular to y = x.
The points on the curve which corresponds to the shortest distance between the curves will have the slope of their tangent equal to that of the line y =x. That is, if tangents are drawn at points corresponding to the shortest distance then these tangents will have a slope equal to 1.
The first curve is: ${{y}^{2}}=x-1$
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get:
$\begin{align}
& 2y.\dfrac{dy}{dx}=1-0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{1}{2y} \\
\end{align}$
But, we have found that the slope of tangent to the curves at the required point is 1.
So, we can write:
$\begin{align}
& 1=\dfrac{1}{2y} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}$
On putting value of y in the first curve, we get:
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}=x-1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{4}+1=x \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Similarly, on differentiating the second curve with respect to x, we get:
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{d\left( {{x}^{2}} \right)}{dx}=\dfrac{d\left( y-1 \right)}{dx} \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=\dfrac{dy}{dx} \\
\end{align}$
Since, we have slope = 1. So:
$\begin{align}
& 1=2x \\
& \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}$
On putting the value of x in second equation, we get:
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}=y-1 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{1}{4}+1=\dfrac{5}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that the distance between two points (a, b) and (c, d) is given as $d=\sqrt{{{\left( a-c \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( b-d \right)}^{2}}}$ . We also know that the distance between the points $\left( \dfrac{5}{4},\dfrac{1}{2} \right)$ and $\left( \dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{5}{4} \right)$ will give the shortest distance between the two curves.
So, the shortest distance is:
\[\begin{align}
& =\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{5}{4} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{5}{4}-\dfrac{1}{2}
\right)}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{2-5}{4} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{5-2}{4} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{\dfrac{9}{16}+\dfrac{9}{16}}=\dfrac{3\sqrt{2}}{4} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, option (a) is the correct answer.
Note: Students should note here that the slope of tangent to a curve is always given as the value of derivative of the curve at that point. The calculations must be done properly to avoid mistakes.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which country won the ICC Men's ODI World Cup in 2023?

In cricket, how many legal balls are there in a standard over?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

What does "powerplay" mean in limited-overs cricket?

What is the "Powerplay" in T20 cricket?




