
Methylamine $[C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}}]$ is a bidentate ligand.
If true enter 1, else enter 0.
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: Ligands are molecules that are attached to the central metal atom in the coordination compound. In bidentate ligand, there are two sites for attaching to the central metal atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Coordination compounds are the compounds in which the central metal atom is linked to several ions or neutral molecules by coordinate bonds, i.e., by donation of lone pairs of electrons by these ions or neutral molecules to the central metal atoms.
The donor atoms, molecules, or anions that donate a pair of electrons to the metal atom or ions and form a coordinate bond with it are called ligands. The metal atom or ion to which these ligands are attached is called the central metal atom or ion.
The number of coordinating or ligating groups present in a ligand is called the denticity of that ligand.
Monodentate ligand has one donor atom, the bidentate ligand has 2 donor atoms, tridentate has 3 donor atoms, and so on.
For example, Ammonia ($N{{H}_{3}}$ ), water (${{H}_{2}}O$ ) are examples of the monodentate ligand.
Oxalate ion ($2CO{{O}^{-}}$ ): is a bidentate ligand because it has 2 oxygen donor atoms.
The structure of Oxalate ion is:
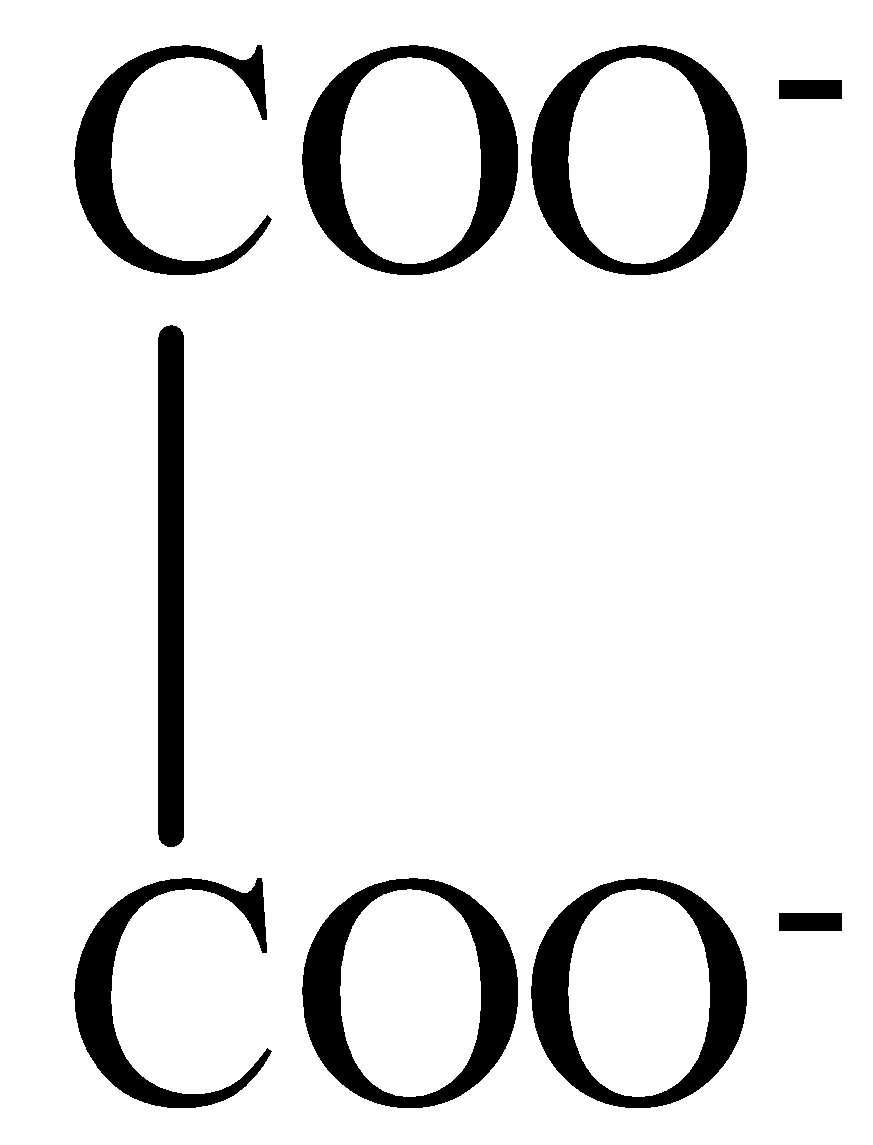
So, in Methylamine $[C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}}]$, has one donor atom, i.e., nitrogen. Hence, it is a monodentate ligand.
Hence, Methylamine $[C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}}]$ is a bidentate ligand is false.
Note: Ligands are classified as negative, positive, and neutral ligands. The negative ligand has a negative charge, the positive ligand has a positive charge and the neutral ligand has zero charges. Methylamine $[C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}}]$ is a neutral ligand.
Complete step by step answer:
Coordination compounds are the compounds in which the central metal atom is linked to several ions or neutral molecules by coordinate bonds, i.e., by donation of lone pairs of electrons by these ions or neutral molecules to the central metal atoms.
The donor atoms, molecules, or anions that donate a pair of electrons to the metal atom or ions and form a coordinate bond with it are called ligands. The metal atom or ion to which these ligands are attached is called the central metal atom or ion.
The number of coordinating or ligating groups present in a ligand is called the denticity of that ligand.
Monodentate ligand has one donor atom, the bidentate ligand has 2 donor atoms, tridentate has 3 donor atoms, and so on.
For example, Ammonia ($N{{H}_{3}}$ ), water (${{H}_{2}}O$ ) are examples of the monodentate ligand.
Oxalate ion ($2CO{{O}^{-}}$ ): is a bidentate ligand because it has 2 oxygen donor atoms.
The structure of Oxalate ion is:
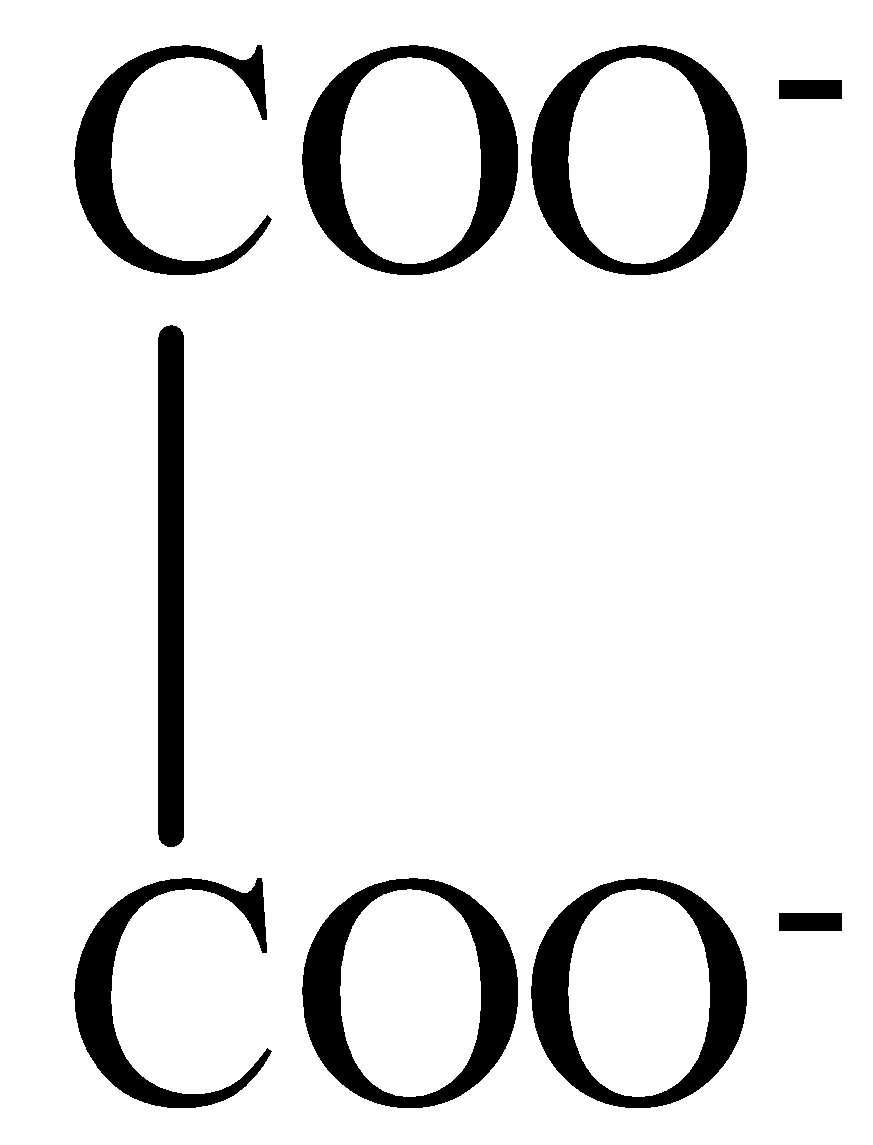
So, in Methylamine $[C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}}]$, has one donor atom, i.e., nitrogen. Hence, it is a monodentate ligand.
Hence, Methylamine $[C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}}]$ is a bidentate ligand is false.
Note: Ligands are classified as negative, positive, and neutral ligands. The negative ligand has a negative charge, the positive ligand has a positive charge and the neutral ligand has zero charges. Methylamine $[C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}}]$ is a neutral ligand.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




