
What is methane? Draw its electron dot structure. Name the type of bonds formed in this compound. Why are such compounds?
(i) Are poor conductors of electricity and
(ii) Have low melting and boiling points? What happens when this compound burns in oxygen?
Answer
524.9k+ views
Hint: To answer this question we should be aware of the chemical formula of methane, Lewis dot structure and the type of bond formed. This information will help us to account for poor conductivity, low boiling and melting point.
Complete answer:
Methane is the simplest hydrocarbon. The chemical formula of methane is $C{{H}_{4}}$. It is a gas that exists abundantly in nature.
Now, let's know its structure:
Lewis dot structure is a representation of the arrangement of electrons around each atom of a compound or a molecule. This is why it is also known as electron dot structure.
The electronic configuration of carbon = $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{2}}$
The valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell which takes part in chemical bonding with other atoms. The number of valence electrons in a carbon atom is 4.
The electronic configuration in hydrogen = $1{{s}^{1}}$
The number of valence electrons in hydrogen is 1.
The Lewis dot structure of methane:
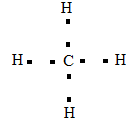
The type of bond formed in methane is covalent bond.
(i) The compounds where the electrons are bonded by covalent bonds have poor conductivity. As covalent compounds have no free electrons or ions. So, methane is a poor conductor of electricity.
(ii) Methane has low melting and boiling point as it is a covalent compound. Covalent compounds have weak intermolecular forces. The bonds between the atoms break easy only with less amount of energy such as heat. Thus, has a very low melting point and boiling point.
When the methane is burnt in presence of oxygen, carbon dioxide and water is been released:
\[C{{H}_{4}}+{{O}_{2}}\to C{{O}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O\]
Note:
The Lewis dot structure that is nothing but the electron dot structure failed to find the shape of methane. The valence electrons take part in chemical bonding with other atoms. Methane exists as a gaseous form in nature. Normally the gas has poor electricity conductivity as it does not have any free atoms or ions. It forms a tetrahedral shape.
Complete answer:
Methane is the simplest hydrocarbon. The chemical formula of methane is $C{{H}_{4}}$. It is a gas that exists abundantly in nature.
Now, let's know its structure:
Lewis dot structure is a representation of the arrangement of electrons around each atom of a compound or a molecule. This is why it is also known as electron dot structure.
The electronic configuration of carbon = $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{2}}$
The valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell which takes part in chemical bonding with other atoms. The number of valence electrons in a carbon atom is 4.
The electronic configuration in hydrogen = $1{{s}^{1}}$
The number of valence electrons in hydrogen is 1.
The Lewis dot structure of methane:


The type of bond formed in methane is covalent bond.
(i) The compounds where the electrons are bonded by covalent bonds have poor conductivity. As covalent compounds have no free electrons or ions. So, methane is a poor conductor of electricity.
(ii) Methane has low melting and boiling point as it is a covalent compound. Covalent compounds have weak intermolecular forces. The bonds between the atoms break easy only with less amount of energy such as heat. Thus, has a very low melting point and boiling point.
When the methane is burnt in presence of oxygen, carbon dioxide and water is been released:
\[C{{H}_{4}}+{{O}_{2}}\to C{{O}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O\]
Note:
The Lewis dot structure that is nothing but the electron dot structure failed to find the shape of methane. The valence electrons take part in chemical bonding with other atoms. Methane exists as a gaseous form in nature. Normally the gas has poor electricity conductivity as it does not have any free atoms or ions. It forms a tetrahedral shape.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




