
Mention the technique used to separate DNA fragments in rDNA technology.
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: According to sizes like DNA, RNA, and proteins, a technique that is commonly used in the lab to separate charged molecules called electrophoresis involves running a current through a gel containing the molecules of interest. The molecules will travel based on their size and charge, through the gel in different directions or at different speeds, allowing them to be separated from one another.
Complete step by step answer:
By the combination of DNA from two or more sources, recombinant DNA (or rDNA) is done, which often involves combining the DNA of different organisms. This process of gel electrophoresis depends on the ability to cut and rejoin DNA molecules at points that are identified by specific sequences of nucleotide bases called restriction sites. Here, DNA fragments are cut out of their normal position in the chromosome using restriction enzymes (also called restriction endonucleases) and then inserted into other chromosomes or DNA molecules using enzymes called ligases. The gene and the plasmid are extracted from the cells in rDNA technology. By using the agarose gel electrophoresis technique the DNA fragments can be separated. A technique used to separate DNA fragments according to their size is called gel electrophoresis where DNA samples are loaded into wells (indentations) at one end of a gel, then to pull them an electric current is applied through the gel. As we know, DNA fragments are negatively charged, so they move towards the positive electrode. As a result, separation of the DNA fragments based on their size when there is an external supply of electric charge.
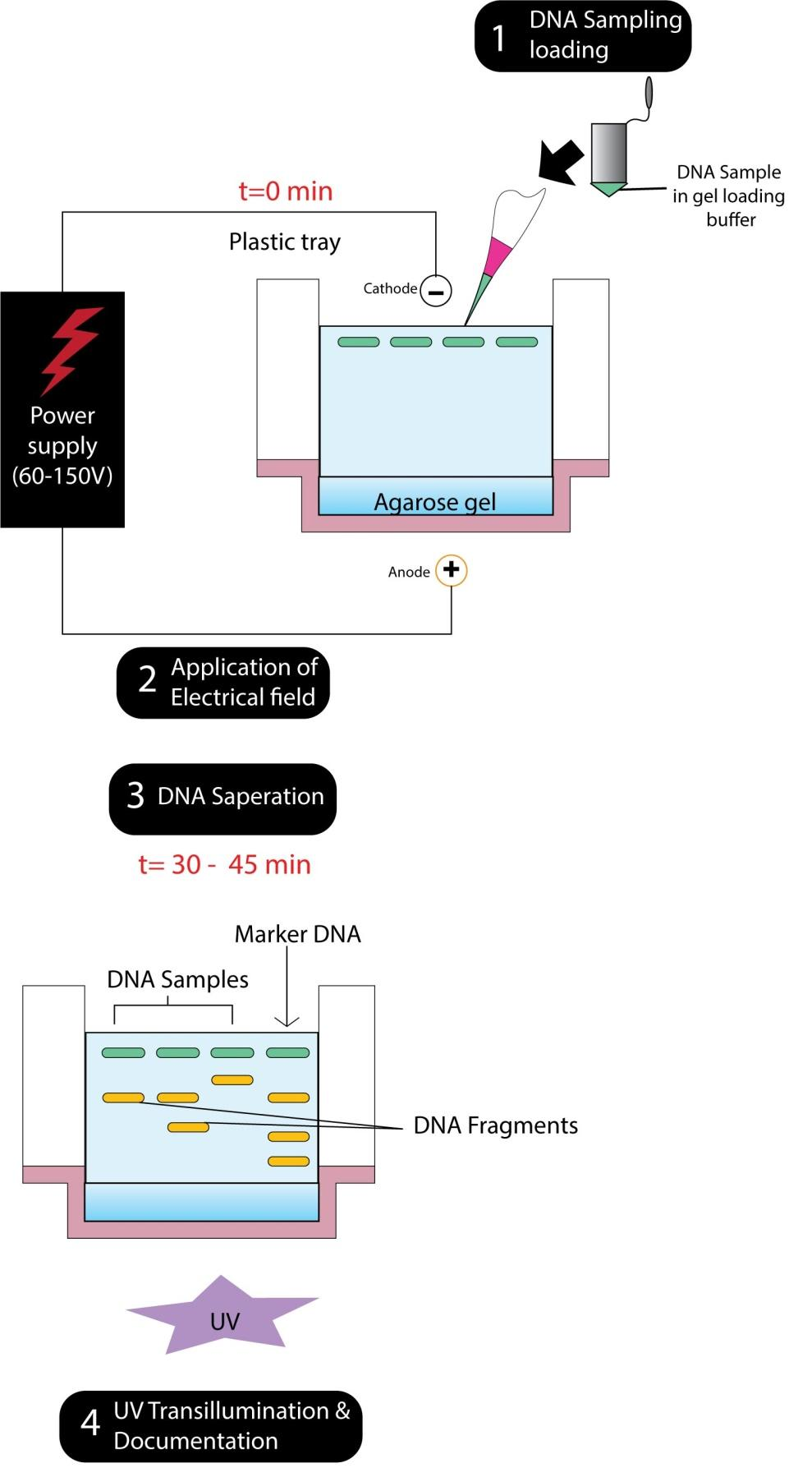
So, the correct answer is, ‘gel electrophoresis’.
Additional information:
1) Paul Berg, a Stanford researcher, ligated DNA fragments of two viruses for the first time in 1972. He was awarded Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1980 due to his significant contributions to deciphering nucleic acids biochemistry concerning recombinant DNA technology.
2) Some other scientists named Boyer and Cohen introduced antibacterial resistance recombinant DNA molecules they created in E.coli bacteria.
3) The first organism containing recombinant DNA molecules was engineered by Herb Boyer (UCSF) and Stanley Cohen (Stanford University) later in 1973.
Note:
Regarding GMOs, there are many ethical issues to be considered, and these are highly argued upon. Some of the issues are mentioned below:
1) Introducing a new genetically modified species in the environment can disturb the natural ecosystem; for example, it is being argued that resistant plants may give rise to resistant weed, which can be difficult to control.
2) Another argument of the anti-GMO community is cross-contamination and horizontal gene transfer between organisms.
3) Recombinant organisms lack genetic variability as they are clones, so when one disease or pest attacks it can wipe out the whole GMO population.
Complete step by step answer:
By the combination of DNA from two or more sources, recombinant DNA (or rDNA) is done, which often involves combining the DNA of different organisms. This process of gel electrophoresis depends on the ability to cut and rejoin DNA molecules at points that are identified by specific sequences of nucleotide bases called restriction sites. Here, DNA fragments are cut out of their normal position in the chromosome using restriction enzymes (also called restriction endonucleases) and then inserted into other chromosomes or DNA molecules using enzymes called ligases. The gene and the plasmid are extracted from the cells in rDNA technology. By using the agarose gel electrophoresis technique the DNA fragments can be separated. A technique used to separate DNA fragments according to their size is called gel electrophoresis where DNA samples are loaded into wells (indentations) at one end of a gel, then to pull them an electric current is applied through the gel. As we know, DNA fragments are negatively charged, so they move towards the positive electrode. As a result, separation of the DNA fragments based on their size when there is an external supply of electric charge.

So, the correct answer is, ‘gel electrophoresis’.
Additional information:
1) Paul Berg, a Stanford researcher, ligated DNA fragments of two viruses for the first time in 1972. He was awarded Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1980 due to his significant contributions to deciphering nucleic acids biochemistry concerning recombinant DNA technology.
2) Some other scientists named Boyer and Cohen introduced antibacterial resistance recombinant DNA molecules they created in E.coli bacteria.
3) The first organism containing recombinant DNA molecules was engineered by Herb Boyer (UCSF) and Stanley Cohen (Stanford University) later in 1973.
Note:
Regarding GMOs, there are many ethical issues to be considered, and these are highly argued upon. Some of the issues are mentioned below:
1) Introducing a new genetically modified species in the environment can disturb the natural ecosystem; for example, it is being argued that resistant plants may give rise to resistant weed, which can be difficult to control.
2) Another argument of the anti-GMO community is cross-contamination and horizontal gene transfer between organisms.
3) Recombinant organisms lack genetic variability as they are clones, so when one disease or pest attacks it can wipe out the whole GMO population.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




