
What is the mechanism of aromatization?
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint:Aromatization is a chemical reaction during which a single non-aromatic precursor is used to form an aromatic system.
An aromatic compound is the one which is planer, cyclic, has conjugation, and has (4n+2) pi electrons i.e., obeys Huckel’s rule.
There are many pathways for aromatization but the most common one is dehydrogenation.
Complete step by step answer:
Aromatization can be done using various pathways, some of them are described below:
Dehydrogenation of cyclic compounds:
E.g. dehydrogenation of cyclohexane in the presence of Platinum and heat will yield benzene.
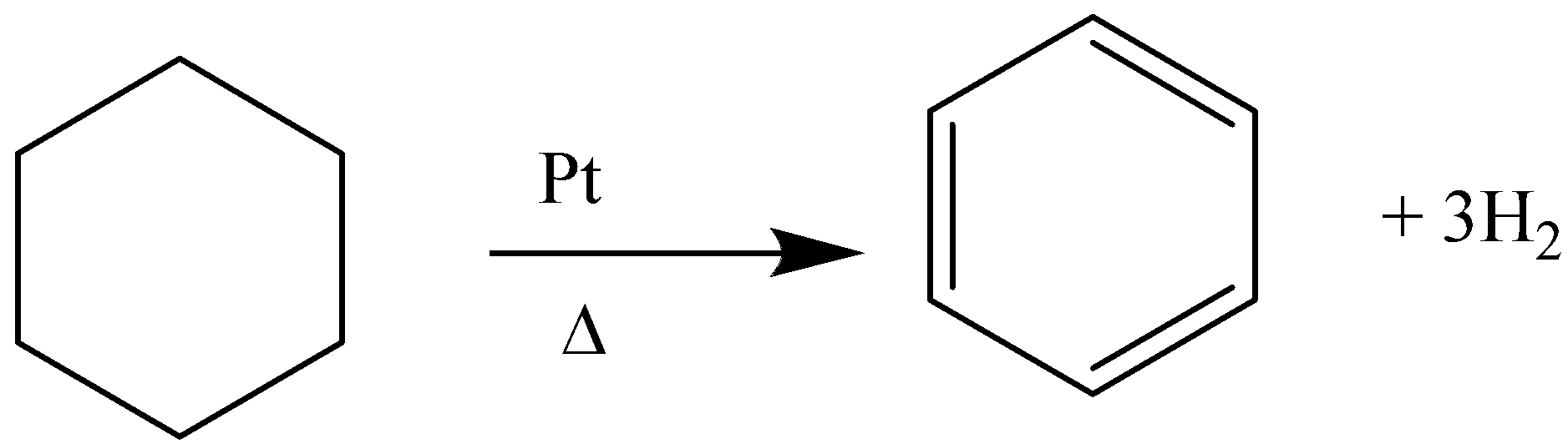
Similarly, cyclohex-1-ene, cyclohex-1,4-diene will also give benzene as a product. As the degree of unsaturation of the precursor (reactant) increases the rate of the reaction also increases.
From Acyclic precursor:
Benzene can also be formed when 3 molecules of ethyne are heated at high temperatures in the presence of Zn dust which acts as a catalyst.
There are many more pathways to carry out aromatization but dehydrogenation remains the most widely used. Dehydrogenation, as the name suggests, is the removal of hydrogen from a molecule.
Aromatization also happens inside the biological system in various biological compounds. The difference is in a biological system the catalysts for the reaction are enzymes. The enzyme responsible for the aromatization of biologically active compounds is known as Aromatase.
Note: Aromatic compounds are called so because each aromatic compound has a distinct aroma (odour). They are known for their high stability and undergo any chemical change under drastic conditions. These are highly conjugated systems and undergo resonance.
An aromatic compound is the one which is planer, cyclic, has conjugation, and has (4n+2) pi electrons i.e., obeys Huckel’s rule.
There are many pathways for aromatization but the most common one is dehydrogenation.
Complete step by step answer:
Aromatization can be done using various pathways, some of them are described below:
Dehydrogenation of cyclic compounds:
E.g. dehydrogenation of cyclohexane in the presence of Platinum and heat will yield benzene.

Similarly, cyclohex-1-ene, cyclohex-1,4-diene will also give benzene as a product. As the degree of unsaturation of the precursor (reactant) increases the rate of the reaction also increases.
From Acyclic precursor:
Benzene can also be formed when 3 molecules of ethyne are heated at high temperatures in the presence of Zn dust which acts as a catalyst.
There are many more pathways to carry out aromatization but dehydrogenation remains the most widely used. Dehydrogenation, as the name suggests, is the removal of hydrogen from a molecule.
Aromatization also happens inside the biological system in various biological compounds. The difference is in a biological system the catalysts for the reaction are enzymes. The enzyme responsible for the aromatization of biologically active compounds is known as Aromatase.
Note: Aromatic compounds are called so because each aromatic compound has a distinct aroma (odour). They are known for their high stability and undergo any chemical change under drastic conditions. These are highly conjugated systems and undergo resonance.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




