
\[MeC \equiv C - COCl\xrightarrow{{{H_2} + {\text{Lindlar's catalyst}}}}(A)\] The product (A) is:
(A) \[Me - C \equiv C - CHO\]
(B)
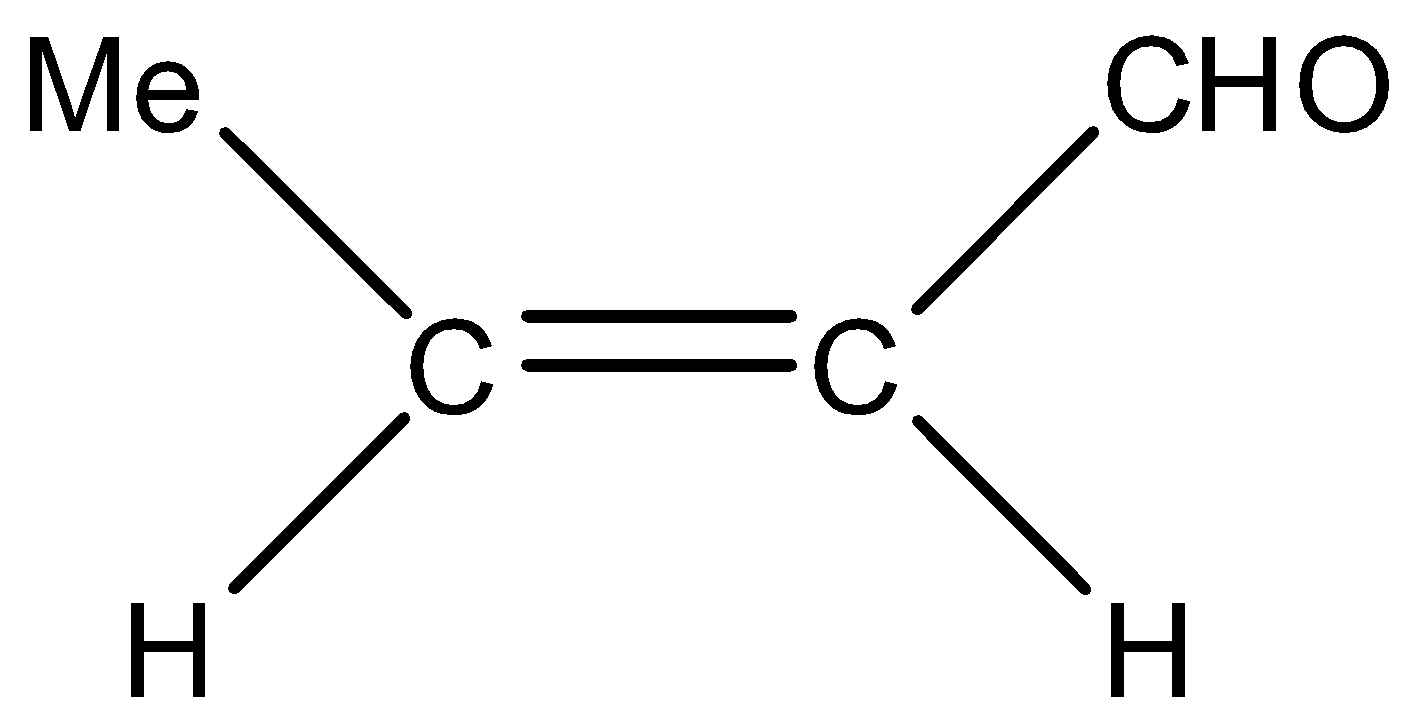
(C)
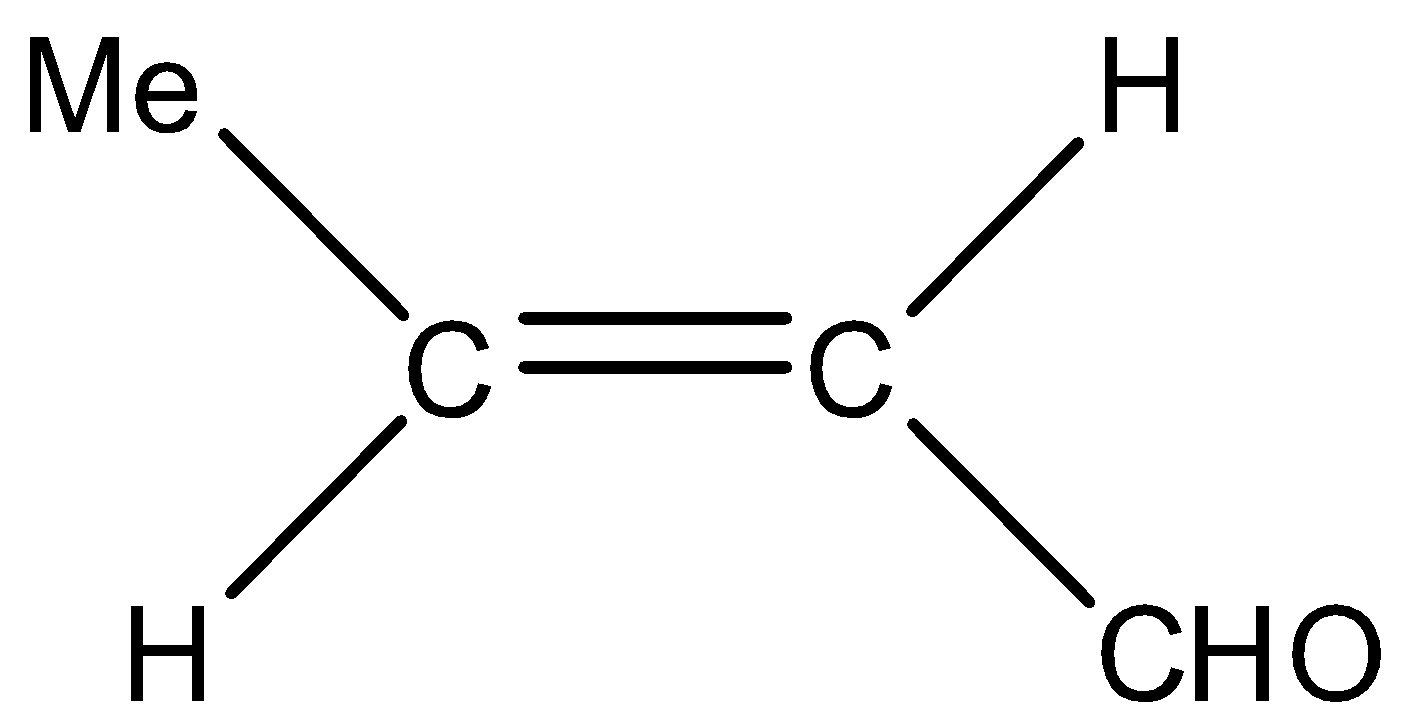
(D)
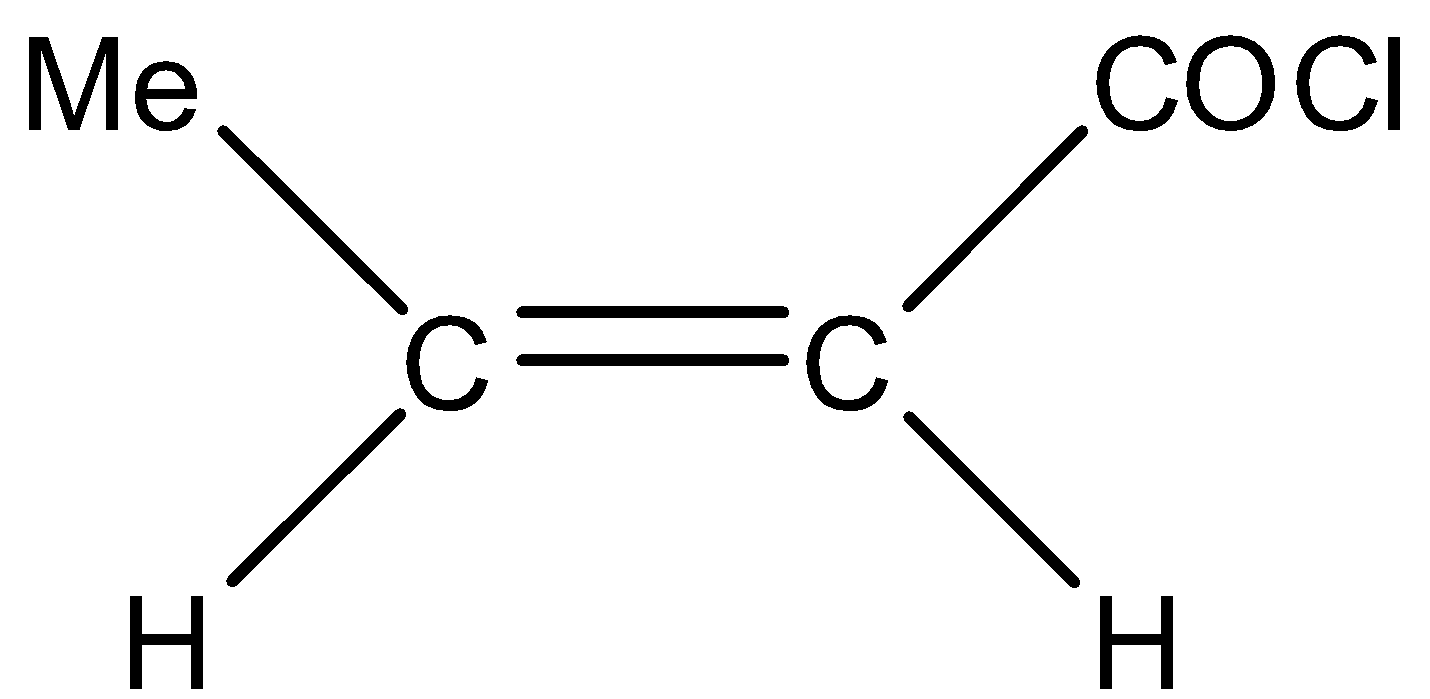



Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: Lindlar’s catalyst is Palladium metal deposited on solid calcium carbonate. It is useful for reduction of specific functional groups when it is allowed to react with reactant and hydrogen gas. The final product has Z-configuration.
Complete Step-by-Step answer:
We are given a compound which has both alkyne and acid chloride functionality. This compound is allowed to react with hydrogen gas and Lindlar’s catalyst. Let’s see which compounds make Lindlar’s catalyst.
- Lindlar’s catalyst is Palladium metal deposited on calcium carbonate solid. Let’s see what kinf of reaction it can give.
- Hydrogen gas and Lindlar’s catalyst can reduce the alkyne functional group and gives cis-alkene as the exclusive product. Here, trans-alkene is not formed at all. Let’s see what will happen in our reaction.
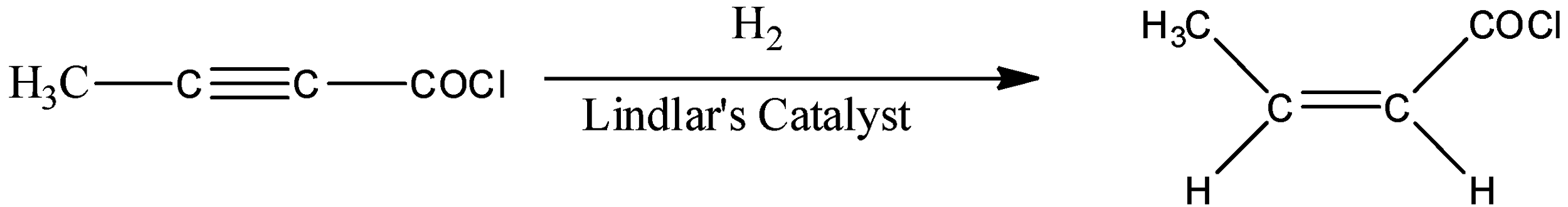
- Remember that hydrogen gas cannot react with acid chloride in presence of Lindlar’s catalyst.
- In option (A), the alkyne is not reduced, in option (B) and (C), acid chloride functional group is reduced to aldehyde, so all of them are not correct.
Hence, correct option is (D)
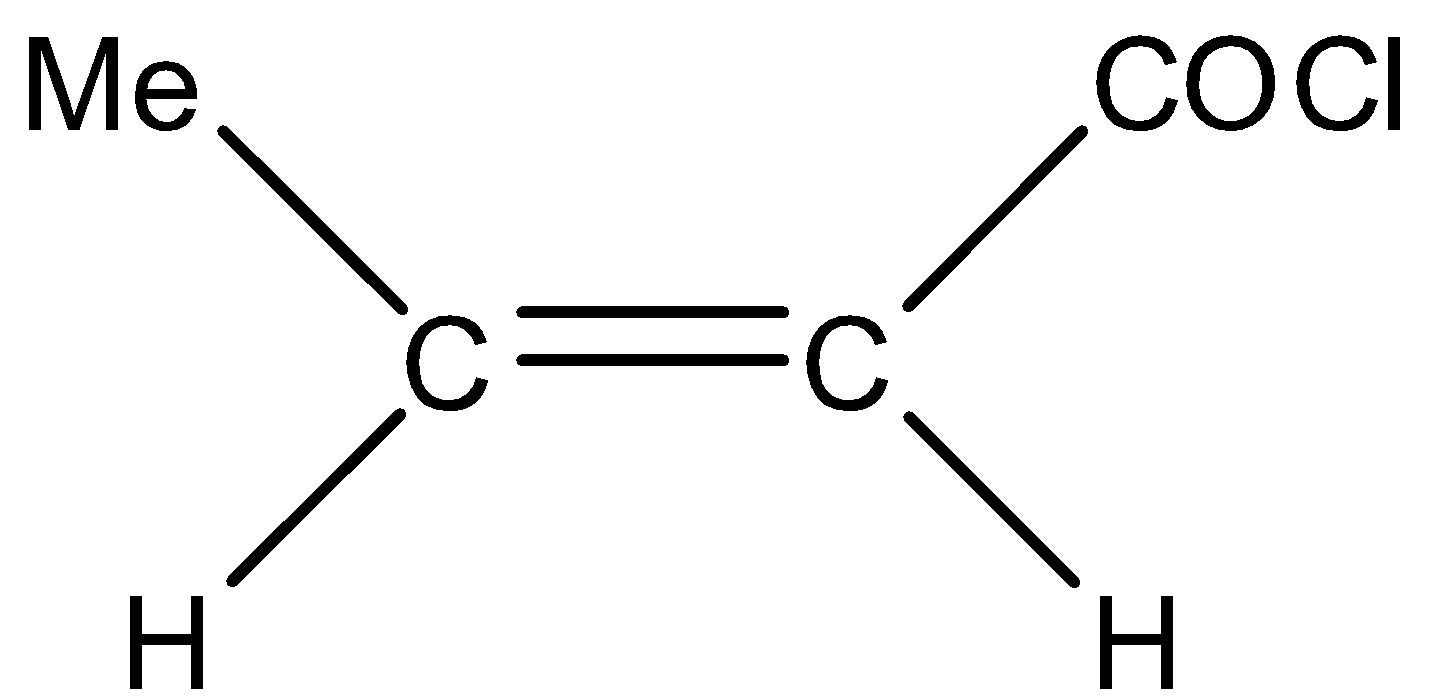 .
.
Note:
- Note that the final product after reduction by Lindlar’s catalyst will always be having cis-configuration at the reduction center.
- Remember that hydrogen gas and Lindlar’s catalyst will not reduce the acid chloride functional group. Actually, the reagents used for reduction of acid chloride functional group are Palladium metal on barium sulfate as catalyst and hydrogen gas but this reagent is specific for reduction of the acid chloride group. This reaction is called Rosenmund reduction. The final reaction can be given as below.
\[R - COCl\xrightarrow[{Pd/BaS{O_4}}]{{{H_2}}}R - CHO\]
Complete Step-by-Step answer:
We are given a compound which has both alkyne and acid chloride functionality. This compound is allowed to react with hydrogen gas and Lindlar’s catalyst. Let’s see which compounds make Lindlar’s catalyst.
- Lindlar’s catalyst is Palladium metal deposited on calcium carbonate solid. Let’s see what kinf of reaction it can give.
- Hydrogen gas and Lindlar’s catalyst can reduce the alkyne functional group and gives cis-alkene as the exclusive product. Here, trans-alkene is not formed at all. Let’s see what will happen in our reaction.
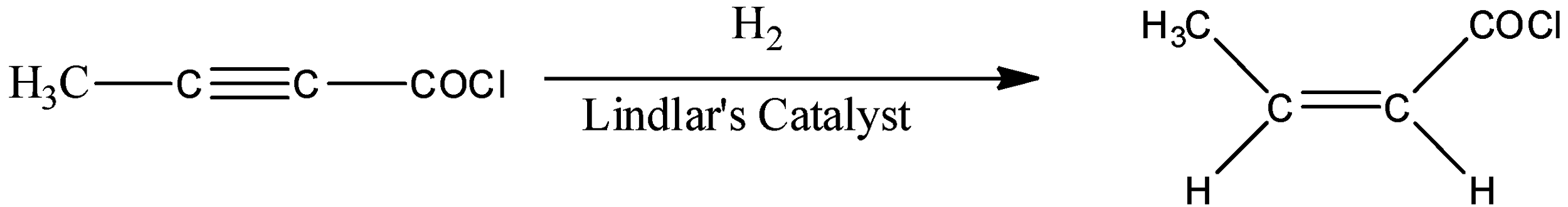
- Remember that hydrogen gas cannot react with acid chloride in presence of Lindlar’s catalyst.
- In option (A), the alkyne is not reduced, in option (B) and (C), acid chloride functional group is reduced to aldehyde, so all of them are not correct.
Hence, correct option is (D)

Note:
- Note that the final product after reduction by Lindlar’s catalyst will always be having cis-configuration at the reduction center.
- Remember that hydrogen gas and Lindlar’s catalyst will not reduce the acid chloride functional group. Actually, the reagents used for reduction of acid chloride functional group are Palladium metal on barium sulfate as catalyst and hydrogen gas but this reagent is specific for reduction of the acid chloride group. This reaction is called Rosenmund reduction. The final reaction can be given as below.
\[R - COCl\xrightarrow[{Pd/BaS{O_4}}]{{{H_2}}}R - CHO\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




