
What is meant by zero error of Vernier calipers?
Answer
602.7k+ views
Hint – In this question use the concept that a Vernier caliper has two scales that is the scale of Vernier caliper and the main scale of Vernier caliper, so if the scale of the Vernier caliper does not exactly coincides with the main scale than the Vernier caliper has the zero error.
Step by Step Answer:
Before performing the experiment we have to calibrate the instrument and calculate its zero error.
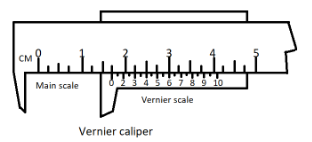
So if the pointer of the instrument indicates below zero then it is called a negative zero error and we have to add the magnitude of this error in the measured reading of the instrument.
Therefore true reading = measured reading + magnitude of negative zero error.
Now if the pointer of the instrument indicates above zero then it is called a positive zero error and we have to subtract the magnitude of this error in the measured reading of the instrument.
Therefore true reading = measured reading – magnitude of positive zero error.
Now if the pointer of the instrument indicates exactly at zero then it is called a null zero error and in this case measured reading is equal to the true reading of the instrument.
So in general we can say if the scale of the Vernier caliper does not exactly coincides with the main scale than the Vernier caliper has the zero error, it can be positive or negative i.e. if the scale of the Vernier caliper is on right side of the main scale than the zeroth error is called as positive zeroth error otherwise negative zeroth error.
Note – Vernier caliper plays a major role in measurement of the outer dimensions of an object or even the inner dimensions of it. It can also be used to measure the depth. In general a Vernier scale has the length of 9 mains scale divisions and these are further divided into 10 more divisions. The least count is equal to the difference of 1 main scale division to that of 1 Vernier scale division.
Step by Step Answer:
Before performing the experiment we have to calibrate the instrument and calculate its zero error.

So if the pointer of the instrument indicates below zero then it is called a negative zero error and we have to add the magnitude of this error in the measured reading of the instrument.
Therefore true reading = measured reading + magnitude of negative zero error.
Now if the pointer of the instrument indicates above zero then it is called a positive zero error and we have to subtract the magnitude of this error in the measured reading of the instrument.
Therefore true reading = measured reading – magnitude of positive zero error.
Now if the pointer of the instrument indicates exactly at zero then it is called a null zero error and in this case measured reading is equal to the true reading of the instrument.
So in general we can say if the scale of the Vernier caliper does not exactly coincides with the main scale than the Vernier caliper has the zero error, it can be positive or negative i.e. if the scale of the Vernier caliper is on right side of the main scale than the zeroth error is called as positive zeroth error otherwise negative zeroth error.
Note – Vernier caliper plays a major role in measurement of the outer dimensions of an object or even the inner dimensions of it. It can also be used to measure the depth. In general a Vernier scale has the length of 9 mains scale divisions and these are further divided into 10 more divisions. The least count is equal to the difference of 1 main scale division to that of 1 Vernier scale division.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




