
What is meant by the term osmoregulation?
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: Osmoregulation is the dynamic guideline of the osmotic weight of a living being's body liquids, recognized by osmoreceptors, to keep up the homeostasis of the creature's water content; that is, it keeps up the liquid parity and the grouping of electrolytes.
Complete answer:
Osmoregulation: Osmoregulation is typically accomplished by excretory organs that serve likewise for the removal of metabolic squanders. Accordingly, pee is a system of both waste discharge and osmoregulation. Organelles and organs that do osmoregulation incorporate contractile vacuoles, nephritis, antennal organs, and Malpighian tubules of spineless creatures, and salt organs and kidneys of vertebrates.
Contractile vacuoles are organelles in the cells of wipes and freshwater protozoans. In the freshwater Amoeba protest, for instance, the air pocket like contractile vacuole swells with overabundance liquid from the cytoplasm. Its layer at that point siphons important particles back into the cytoplasm, leaving principally water in the vacuole. Contractile proteins encompassing the vacuole at that point unexpectedly pack it, spurting the water out of the cell through a pore in the cell layer. The vacuole at that point gradually starts to top off, rehashing the cycle with a beat hastily taking after a heartbeat.
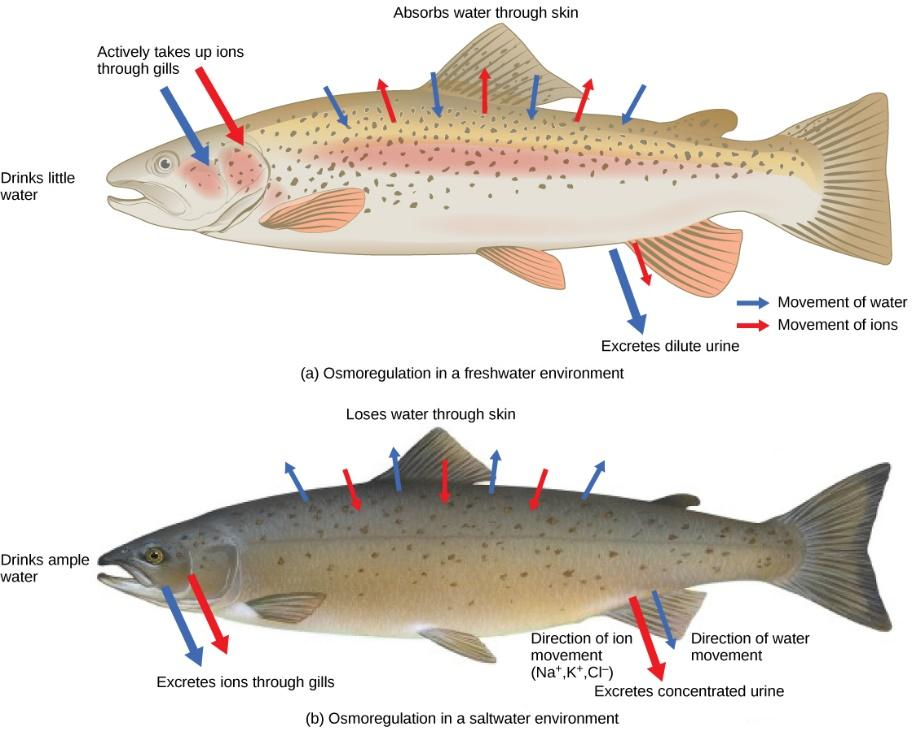
Note: Some marine creatures, for example, the ocean stars are osmoconformers; their body liquids are like seawater in osmolality, so they pick up and lose water at equivalent rates and have no compelling reason to exhaust energy ousting water or salt from the body.
Complete answer:
Osmoregulation: Osmoregulation is typically accomplished by excretory organs that serve likewise for the removal of metabolic squanders. Accordingly, pee is a system of both waste discharge and osmoregulation. Organelles and organs that do osmoregulation incorporate contractile vacuoles, nephritis, antennal organs, and Malpighian tubules of spineless creatures, and salt organs and kidneys of vertebrates.
Contractile vacuoles are organelles in the cells of wipes and freshwater protozoans. In the freshwater Amoeba protest, for instance, the air pocket like contractile vacuole swells with overabundance liquid from the cytoplasm. Its layer at that point siphons important particles back into the cytoplasm, leaving principally water in the vacuole. Contractile proteins encompassing the vacuole at that point unexpectedly pack it, spurting the water out of the cell through a pore in the cell layer. The vacuole at that point gradually starts to top off, rehashing the cycle with a beat hastily taking after a heartbeat.

Note: Some marine creatures, for example, the ocean stars are osmoconformers; their body liquids are like seawater in osmolality, so they pick up and lose water at equivalent rates and have no compelling reason to exhaust energy ousting water or salt from the body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




