
What is meant by photophosphorylation? Discuss the cyclic photophosphorylation.
Answer
575.1k+ views
Hint: This process takes place during photosynthesis. In this process, ADP is phosphorylated to ATP in the presence of sunlight. Cyclic photophosphorylation occurs on the stroma lamellae.
Complete Answer:
Photophosphorylation is a very important step of photosynthesis. It is the process of conversion (phosphorylation) of ADP to ATP using the energy from sunlight. All organisms produce ATP which is the source of energy. In photosynthesis, this phosphorylation takes place by the flow of electrons which is generated by the photolysis of water. It occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. There are two types of photophosphorylation- cyclic and non cyclic.
Cyclic photophosphorylation- Cyclic photophosphorylation uses light directly to generate ATP. This type of photophosphorylation occurs in Green and purple sulphur bacteria. It happens when there is low oxygen present. Photosystem 1 is involved in this process. The sunlight generates electrons. This electron is passed through several electron acceptors like ferredoxin. As the electron transfers from the electron acceptor, it loses some energy. When the electron contains the correct amount of energy, ATP is synthesised. This ATP diffuses from the thylakoid to stroma where this energy is used for making glucose. The electron now moves back to the chlorophyll from where it originated and will further continue the same process. Thus the process is known as cyclic photophosphorylation.
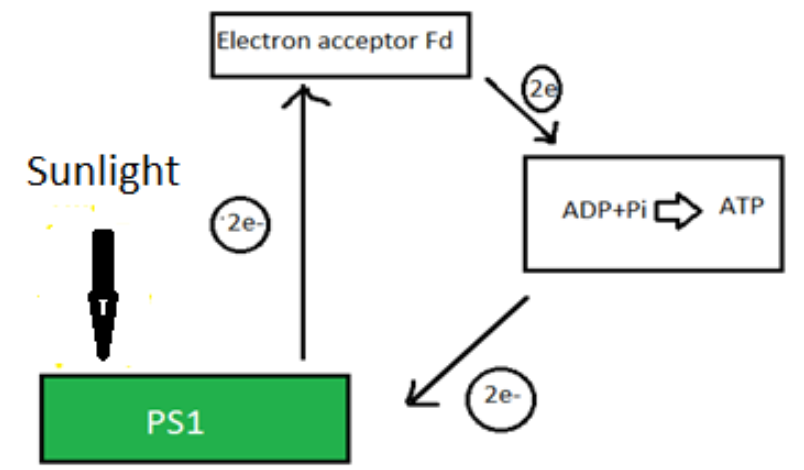
Note: The cyclic photophosphorylation occurs in C4 plants. It does not liberate oxygen and involves only PS1. Non- cyclic photophosphorylation involves both PSI and PSII. It takes place in the presence of sunlight and oxygen and sufficient carbon dioxide. It involves photolysis of water and produces ATP and NADPH along with oxygen.
Complete Answer:
Photophosphorylation is a very important step of photosynthesis. It is the process of conversion (phosphorylation) of ADP to ATP using the energy from sunlight. All organisms produce ATP which is the source of energy. In photosynthesis, this phosphorylation takes place by the flow of electrons which is generated by the photolysis of water. It occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. There are two types of photophosphorylation- cyclic and non cyclic.
Cyclic photophosphorylation- Cyclic photophosphorylation uses light directly to generate ATP. This type of photophosphorylation occurs in Green and purple sulphur bacteria. It happens when there is low oxygen present. Photosystem 1 is involved in this process. The sunlight generates electrons. This electron is passed through several electron acceptors like ferredoxin. As the electron transfers from the electron acceptor, it loses some energy. When the electron contains the correct amount of energy, ATP is synthesised. This ATP diffuses from the thylakoid to stroma where this energy is used for making glucose. The electron now moves back to the chlorophyll from where it originated and will further continue the same process. Thus the process is known as cyclic photophosphorylation.

Note: The cyclic photophosphorylation occurs in C4 plants. It does not liberate oxygen and involves only PS1. Non- cyclic photophosphorylation involves both PSI and PSII. It takes place in the presence of sunlight and oxygen and sufficient carbon dioxide. It involves photolysis of water and produces ATP and NADPH along with oxygen.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE




