
What is the maximum number of isomers (including stereoisomers) that are possible on monochlorination of methylcyclobutane?
Answer
548.7k+ views
Hint: A stereoisomer is a type of isomers in which molecules have the same molecular formula but arranged in differ in the three dimensional orientations. In methylcyclobutane monochlorination is a single chlorine arranged in different places and forming a new compound.
Complete step by step answer:
To calculate the total number of isomers in monochlorination of methylcyclobutane calculate separately all possible isomers of that compound.
Total numbers of carbon in methylcyclobutane = 5
Total numbers of Hydrogen atom in methylcyclobutane = 10
Total number of chlorine in monochlorination of methylcyclobutane = 1
The structural isomers of the monochlorination of methylcyclobutane are:
(Chloromethyl)cyclobutane
1-Chloro-1-methylcyclobutane
1-chloro-2-methylcyclobutane
1-chloro-3-methylcyclobutane
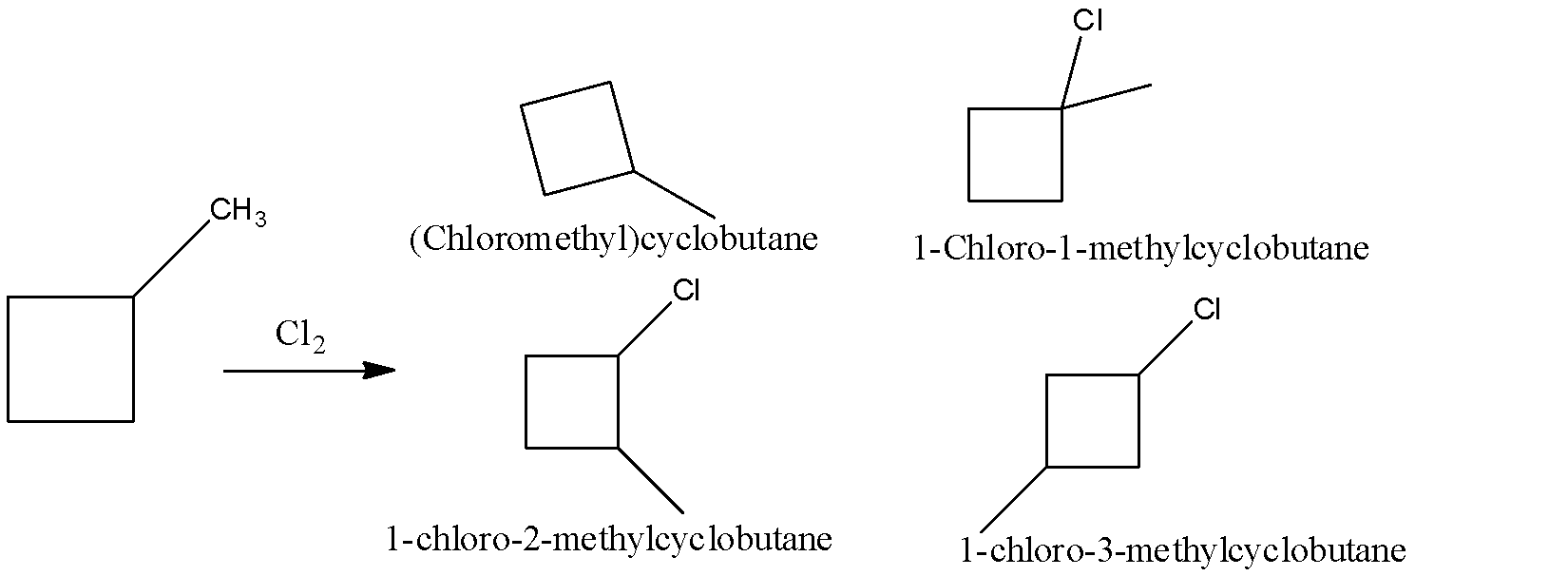
So, there are only 4 structural isomers that can be in the given compound.
Now, calculating the isomers of stereoisomers:
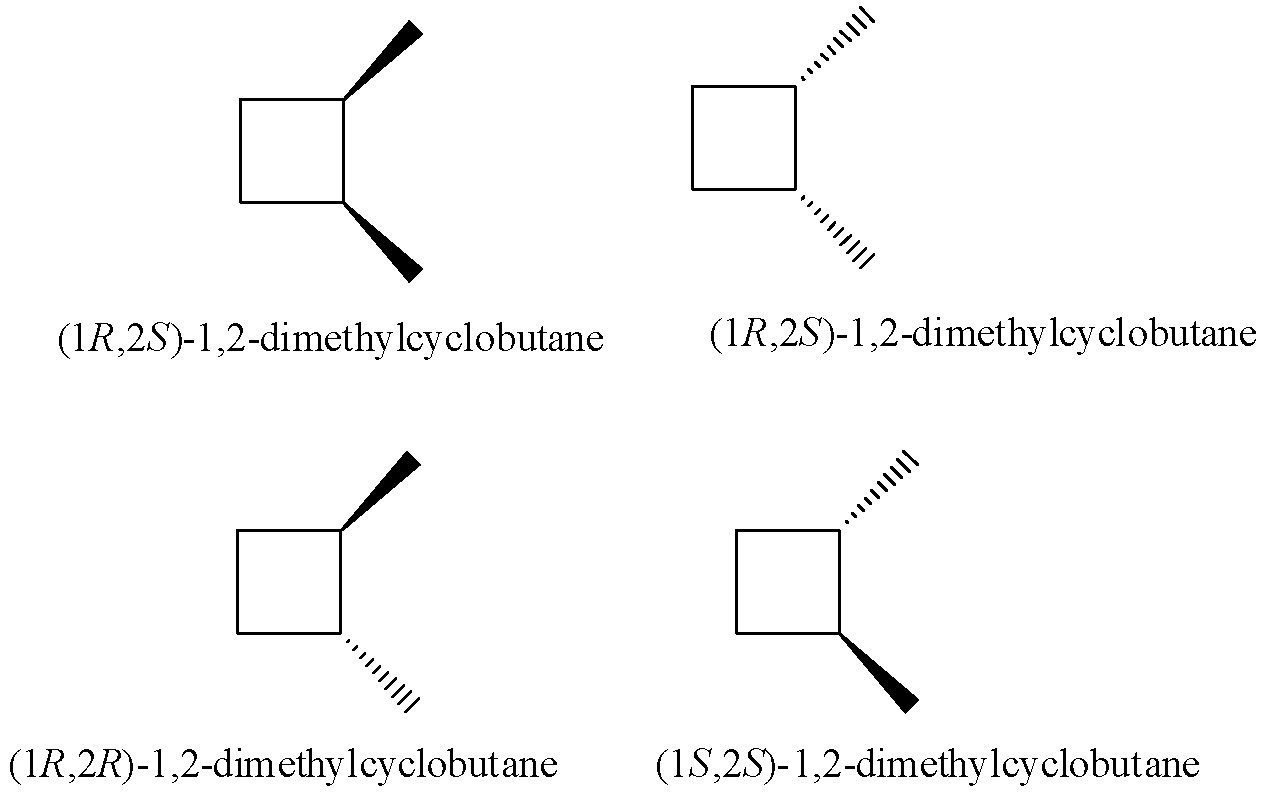
1-chloro-2-methylcyclobutane has two geometrical isomers. Each geometrical isomer has an enantiomer. So there are a total 4 isomers in 1-chloro-2-methylcyclobutane.
1-chloro-3-methylcyclobutane also have two geometrical isomers cis and trans.
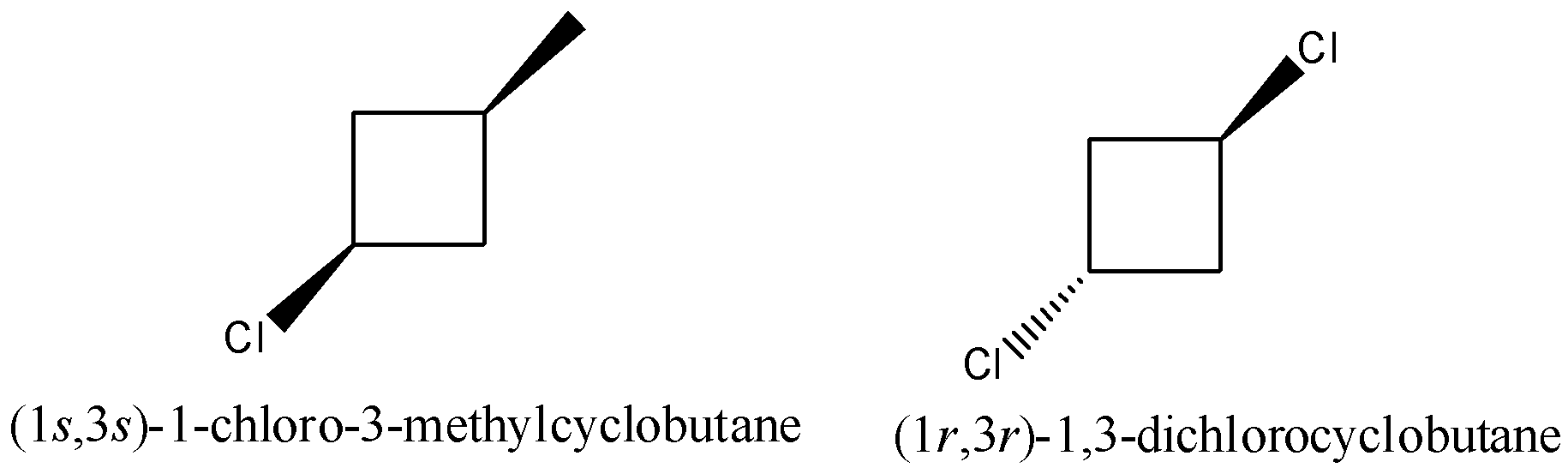
So, maximum number of isomers can be of monochlorination of methylcyclobutane are 4+2+2=8
Hence, the correct answer is 8
Note: Cis: If two alkyl groups R- are on the same side of the C=C.
Trans: IF the two alkyl groups R- on the opposite side of the C=C.
Optical isomers: If the two compounds have the same number of atoms and bonds.
Isomers can be found simply by arranging the atoms in different chains and cycles. After looking this see the geometrical isomers cis and trans that is form which have same double bond or not. Finally if the compound is optically then each compound will form dextro -rotatory and leavo-rotatory. One which is on the left and another on the right. Using this find the isomers of the compound in chains or cycling.
Complete step by step answer:
To calculate the total number of isomers in monochlorination of methylcyclobutane calculate separately all possible isomers of that compound.
Total numbers of carbon in methylcyclobutane = 5
Total numbers of Hydrogen atom in methylcyclobutane = 10
Total number of chlorine in monochlorination of methylcyclobutane = 1
The structural isomers of the monochlorination of methylcyclobutane are:
(Chloromethyl)cyclobutane
1-Chloro-1-methylcyclobutane
1-chloro-2-methylcyclobutane
1-chloro-3-methylcyclobutane

So, there are only 4 structural isomers that can be in the given compound.
Now, calculating the isomers of stereoisomers:
1-chloro-2-methylcyclobutane has two geometrical isomers. Each geometrical isomer has an enantiomer. So there are a total 4 isomers in 1-chloro-2-methylcyclobutane.

1-chloro-3-methylcyclobutane also have two geometrical isomers cis and trans.

So, maximum number of isomers can be of monochlorination of methylcyclobutane are 4+2+2=8
Hence, the correct answer is 8
Note: Cis: If two alkyl groups R- are on the same side of the C=C.
Trans: IF the two alkyl groups R- on the opposite side of the C=C.
Optical isomers: If the two compounds have the same number of atoms and bonds.
Isomers can be found simply by arranging the atoms in different chains and cycles. After looking this see the geometrical isomers cis and trans that is form which have same double bond or not. Finally if the compound is optically then each compound will form dextro -rotatory and leavo-rotatory. One which is on the left and another on the right. Using this find the isomers of the compound in chains or cycling.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




