
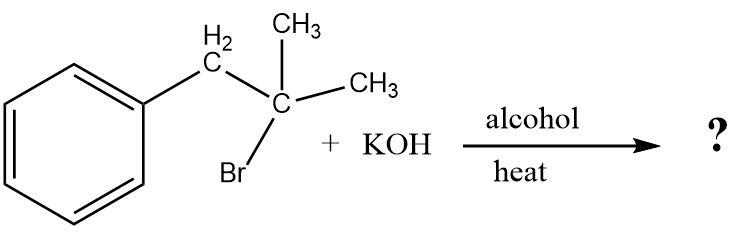
What is the major product of the following reaction?

Answer
504.6k+ views
Hint: The potassium hydroxide is alkaline in nature and a very strong base used in organic synthesis. But when potassium hydroxide is present in an alcoholic medium its properties and functions are different from that of aqueous potassium hydroxide.
Complete answer:
The given reaction has the ability to process in two directions which is either a nucleophilic substitution or an elimination reaction.
If a nucleophilic substitution reaction takes place then the hydroxide ions supplied by potassium hydroxide would act as nucleophiles and replace the bromine substituent attached to the tertiary carbon atom resulting in the formation of a tertiary alcohol.
But if an elimination reaction takes place then a dehydrohalogenation will occur resulting in the formation of an alkene.
The alcoholic potassium hydroxide facilitates the elimination reaction. Another factor that supports elimination over substitution is that the reactant is a tertiary bromide.
The elimination reaction occurs according to Saytzeff's rule which results in the formation of a more substituted and stable alkene. The double bond is formed from the removal of the bromine atom and the hydrogen atom that is attached to the secondary carbon atom and not the primary carbon atom.
Hence, a conjugated alkene is formed as the final product of the elimination reaction.
Note:
The final alkene product formed in the reaction is not only stable because of being more substituted (due to hyperconjugation) but also due to the fact that the double bond is formed adjacent to the benzene ring resulting is a conjugated system i.e. a resonance stabilized system.
Complete answer:
The given reaction has the ability to process in two directions which is either a nucleophilic substitution or an elimination reaction.
If a nucleophilic substitution reaction takes place then the hydroxide ions supplied by potassium hydroxide would act as nucleophiles and replace the bromine substituent attached to the tertiary carbon atom resulting in the formation of a tertiary alcohol.
But if an elimination reaction takes place then a dehydrohalogenation will occur resulting in the formation of an alkene.
The alcoholic potassium hydroxide facilitates the elimination reaction. Another factor that supports elimination over substitution is that the reactant is a tertiary bromide.
The elimination reaction occurs according to Saytzeff's rule which results in the formation of a more substituted and stable alkene. The double bond is formed from the removal of the bromine atom and the hydrogen atom that is attached to the secondary carbon atom and not the primary carbon atom.
Hence, a conjugated alkene is formed as the final product of the elimination reaction.

Note:
The final alkene product formed in the reaction is not only stable because of being more substituted (due to hyperconjugation) but also due to the fact that the double bond is formed adjacent to the benzene ring resulting is a conjugated system i.e. a resonance stabilized system.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




