
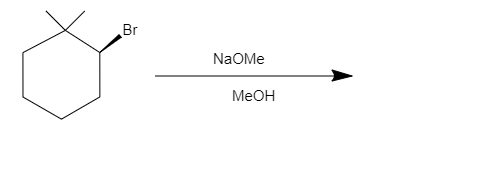
What is the major product in the following reaction?

Answer
511.8k+ views
Hint: Elimination reactions is a very vast area of organic reactions. Elimination reactions involve removal of pairs of atoms or groups of atoms usually through action of bases, acids etc. It leads to transformation of organic compounds containing single carbon-carbon bonds to double or triple carbon-carbon bonds.
Complete answer:
These elimination reactions are majorly classified into ${E_1}$ (unimolecular elimination) and ${E_2}$ (bimolecular elimination).
${E_2}$ mechanism is a one step mechanism. In alkyl halides the carbon-halogen and carbon-hydrogen bond breaks in a single step forming a double bond. It is a second order reaction in which the rate depends upon both substrate and eliminating agent. The base usually abstracts the proton from the substrate and the leaving group (halogen mostly) leaves forming double bonded organic compounds. The important point to note is that the leaving group and the $\beta - H$ (that the base abstracts) should be antiperiplanar to each other.
The most common mechanism for dehydrohalogenation is the ${E_2}$ mechanism.
Now, coming to our question;
The given reaction is a dehydrohalogenation. It undergoes elimination via ${E_2}$ mechanism. Where bromide $\left( {Br} \right)$ is a leaving group and the base present $\left( {NaOMe} \right)$ will abstract the $\beta - H$ forming $3,3 - Dimethylcyclohexene$ .
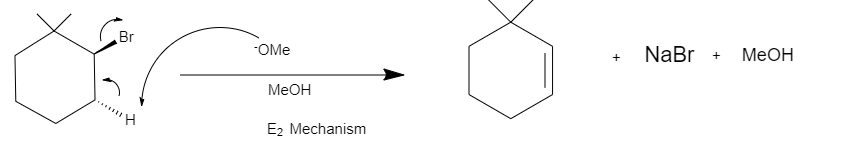
We can clearly see that the leaving group bromide and the $\beta - H$ are antiperiplanar. Thus, the reaction takes place via the ${E_2}$ mechanism.
Note:
We should know about the ${E_1}$ mechanism as well. It takes place via two steps. There is a formation of carbocation as an intermediate in the ${E_1}$ mechanism. The reaction rate is proportional to only the concentration of substrate. It exhibits first-order kinetics. ${E_1}$ mechanism shows similar features as the $S{N_1}$ reaction.
Complete answer:
These elimination reactions are majorly classified into ${E_1}$ (unimolecular elimination) and ${E_2}$ (bimolecular elimination).
${E_2}$ mechanism is a one step mechanism. In alkyl halides the carbon-halogen and carbon-hydrogen bond breaks in a single step forming a double bond. It is a second order reaction in which the rate depends upon both substrate and eliminating agent. The base usually abstracts the proton from the substrate and the leaving group (halogen mostly) leaves forming double bonded organic compounds. The important point to note is that the leaving group and the $\beta - H$ (that the base abstracts) should be antiperiplanar to each other.
The most common mechanism for dehydrohalogenation is the ${E_2}$ mechanism.
Now, coming to our question;
The given reaction is a dehydrohalogenation. It undergoes elimination via ${E_2}$ mechanism. Where bromide $\left( {Br} \right)$ is a leaving group and the base present $\left( {NaOMe} \right)$ will abstract the $\beta - H$ forming $3,3 - Dimethylcyclohexene$ .

We can clearly see that the leaving group bromide and the $\beta - H$ are antiperiplanar. Thus, the reaction takes place via the ${E_2}$ mechanism.
Note:
We should know about the ${E_1}$ mechanism as well. It takes place via two steps. There is a formation of carbocation as an intermediate in the ${E_1}$ mechanism. The reaction rate is proportional to only the concentration of substrate. It exhibits first-order kinetics. ${E_1}$ mechanism shows similar features as the $S{N_1}$ reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




