
What is the major difference between cyclic hemiacetal and cyclic acetal?
Answer
527.1k+ views
Hint: To determine the difference, we first need to know what are acetals and hemiacetals. Acetals are functional groups in which the carbon atom is attached to 2 -OR groups, 1 -R alkyl group, and 1 -H hydrogen. Hemiacetals are compounds in which a carbon atom is attached to 1 -OR group, 1 -OH group, 1 -H group, and 1 -R alkyl group.
Complete answer:
Now a hemiacetal is formed upon the addition of an alcohol to aldehyde. When the protonation of the hydroxyl group in the hemiacetal takes place, water is lost and acetal is formed.

Now, when an organic diol is added to an aldehyde, a cyclic acetal is formed. The carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde is attacked twice in a nucleophilic reaction and an intramolecular ring formation occurs.
For example, the addition of ethanediol to acetaldehyde results in the formation of an acetal 2-methyl-1,3-dioxolane.
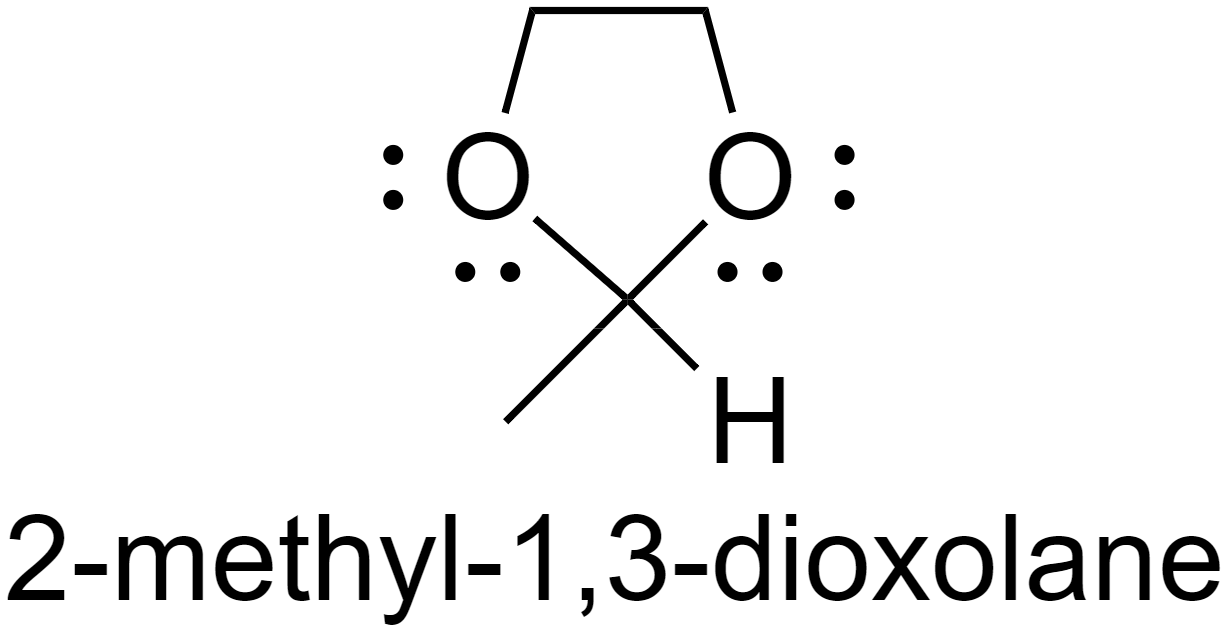
Whereas when a hydroxyl group-containing aldehyde is protonated a hemiacetal is formed. The hydroxyl group is far away from the aldehyde group and hence intramolecular ring formation takes place but only by one nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon.
For example, tetrahydrofuran-2-ol is formed when the protonated hydroxyl group attacks the carbonyl carbon atom and forms a ring.

So, the main difference between cyclic acetal and cyclic hemiacetal compound is that the protonated hydroxyl group attacks the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde in a nucleophilic reaction once while the formation of cyclic hemiacetal and twice during the formation of the cyclic acetal compound.
Note:
It should be noted that hemiacetals (also known as lactols) are not usually stable compounds. However, a few stable 5- and 6- membered cyclic hemiacetal compounds can be readily formed and are stable. Aldoses like glucose exist as cyclic hemiacetals.
Complete answer:
Now a hemiacetal is formed upon the addition of an alcohol to aldehyde. When the protonation of the hydroxyl group in the hemiacetal takes place, water is lost and acetal is formed.

Now, when an organic diol is added to an aldehyde, a cyclic acetal is formed. The carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde is attacked twice in a nucleophilic reaction and an intramolecular ring formation occurs.
For example, the addition of ethanediol to acetaldehyde results in the formation of an acetal 2-methyl-1,3-dioxolane.

Whereas when a hydroxyl group-containing aldehyde is protonated a hemiacetal is formed. The hydroxyl group is far away from the aldehyde group and hence intramolecular ring formation takes place but only by one nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon.
For example, tetrahydrofuran-2-ol is formed when the protonated hydroxyl group attacks the carbonyl carbon atom and forms a ring.

So, the main difference between cyclic acetal and cyclic hemiacetal compound is that the protonated hydroxyl group attacks the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde in a nucleophilic reaction once while the formation of cyclic hemiacetal and twice during the formation of the cyclic acetal compound.
Note:
It should be noted that hemiacetals (also known as lactols) are not usually stable compounds. However, a few stable 5- and 6- membered cyclic hemiacetal compounds can be readily formed and are stable. Aldoses like glucose exist as cyclic hemiacetals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




