
Lysosomes are practically present in all cells except-
(A) WBC
(B) RBC
(C) Epithelial cells
(D) Goblet cells
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: In many animal cells, a lysosome is a membrane-bound organelle that is located. They are spherical vesicles containing hydrolytic enzymes that can break down biomolecules of several kinds. A lysosome, with both its membrane proteins and its lumenal proteins, has a particular composition. For the enzymes involved in hydrolysis, the pH of the lumen is optimum, similar to stomach activity.
Complete answer: There are no nucleus or cytoplasmic organelles in the mature mammalian red blood cell, such as lysosome and mitochondria, so it can handle a significant volume of haemoglobin to transport oxygen to body cells. RBC does not have a nucleus, since blood is transported to all areas of the body by haemoglobin.
Lysosomes are cellular organelles used for phagocytic activities, and since they do not sustain themselves due to lack of nucleus, RBCs are not even living cells. So I don't think they really need any mechanism, Organelle that offers them a means of digestion and feeding intracellularly. So, well, I guess there are no lysosomes in it.
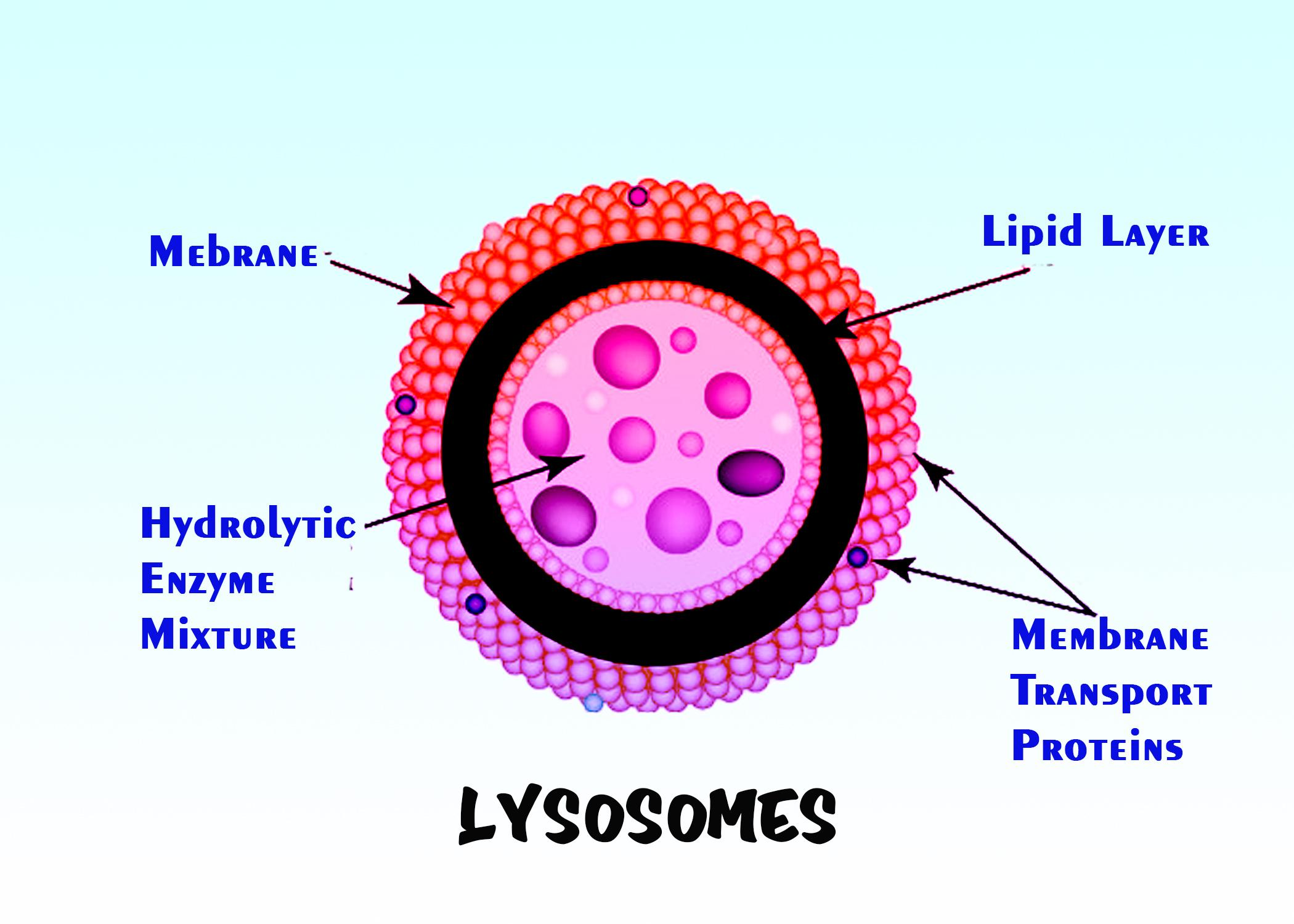
Additional information:
In Neutrophils and agranulocytes (Monocytes), lysosomes are present in a large number. They help to engulf and neutralise the pathogens and chemicals created by them using the digestive enzymes inside them. So, that's why lysosomes in WBCs are present.
With just a few cytoplasmic granules, the goblet cells seemed virtually drained of mucus. They contained dilated rER and some lysosomes in their cytoplasm. Cytoplasmic vacuolations, autophagic vacuoles and swollen degenerated mitochondria were shown by enteroendocrine cells with disintegrated cristaea.
Epithelial Cell Lysosome Dynamics Because lysosomes are called the cytoplasm's "digestion machines," these organelles go to work when nutritional materials are consumed by the cell. The lysosomes bind and release their enzymes once a nutrient cluster is within the cell.
So, the correct answer is ‘RBC’.
Note: Lysosomes serve as the cell's waste disposal mechanism by digesting products from both within and outside the cell in the cytoplasm. Material is taken up through endocytosis from outside the cell, while material is digested by autophagy from the inside of the cell. The sizes of the organelles differ substantially, and the larger ones may be more than 10 times the size of the smaller ones. The Belgian biologist Christian de Duve found them and named them.
Complete answer: There are no nucleus or cytoplasmic organelles in the mature mammalian red blood cell, such as lysosome and mitochondria, so it can handle a significant volume of haemoglobin to transport oxygen to body cells. RBC does not have a nucleus, since blood is transported to all areas of the body by haemoglobin.
Lysosomes are cellular organelles used for phagocytic activities, and since they do not sustain themselves due to lack of nucleus, RBCs are not even living cells. So I don't think they really need any mechanism, Organelle that offers them a means of digestion and feeding intracellularly. So, well, I guess there are no lysosomes in it.

Additional information:
In Neutrophils and agranulocytes (Monocytes), lysosomes are present in a large number. They help to engulf and neutralise the pathogens and chemicals created by them using the digestive enzymes inside them. So, that's why lysosomes in WBCs are present.
With just a few cytoplasmic granules, the goblet cells seemed virtually drained of mucus. They contained dilated rER and some lysosomes in their cytoplasm. Cytoplasmic vacuolations, autophagic vacuoles and swollen degenerated mitochondria were shown by enteroendocrine cells with disintegrated cristaea.
Epithelial Cell Lysosome Dynamics Because lysosomes are called the cytoplasm's "digestion machines," these organelles go to work when nutritional materials are consumed by the cell. The lysosomes bind and release their enzymes once a nutrient cluster is within the cell.
So, the correct answer is ‘RBC’.
Note: Lysosomes serve as the cell's waste disposal mechanism by digesting products from both within and outside the cell in the cytoplasm. Material is taken up through endocytosis from outside the cell, while material is digested by autophagy from the inside of the cell. The sizes of the organelles differ substantially, and the larger ones may be more than 10 times the size of the smaller ones. The Belgian biologist Christian de Duve found them and named them.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




