
Light does not bend while travelling from rarer to denser medium.
(A). True
(B). False
Answer
614.1k+ views
- Hint: In order to deal with this question first we will state the Snell's law and according to this law we will make a diagram also we will study the concept behind the bending of light when it travels from one medium to another and we will observe the required result.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Snell's law is defined as "The sine ratio of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant, for the light of a given color and for the given media pair".
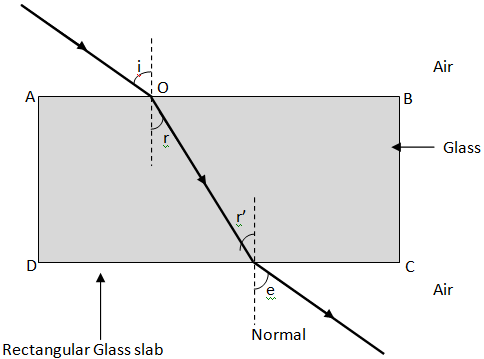
Where “i” is incidence angle and "r" is refraction angle.
We know that when a ray of light travels from rarer to denser medium, it bends towards the normal
This is clear from the above picture. The reason behind the bending of light when it travels from one medium to another is the change in the speed of light in the medium as it crosses the boundary of one medium. For example, the speed of light in air is higher than the speed of light in water. So when the light travels from air to water, it experiences a sudden change in the speed which is reflected by the bending at the edge of two mediums. This ratio of speed of light in one medium to another is also called refractive index of one medium with respect to another.
Hence, light always bend while travelling from rarer to denser medium.
So, the statement is false and the correct answer is option B.
Note- Material refractive index is a dimensionless number which defines how easily light passes through the material. It is defined as where c is the vacuum velocity of light, and v is the medium phase velocity of light. The refractive index has a multitude of applications. It is often used to classify a given substance, to validate its purity or to quantify its concentration. Generally it is used to measure the concentration of a solute in an aqueous solution.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Snell's law is defined as "The sine ratio of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant, for the light of a given color and for the given media pair".

Where “i” is incidence angle and "r" is refraction angle.
We know that when a ray of light travels from rarer to denser medium, it bends towards the normal
This is clear from the above picture. The reason behind the bending of light when it travels from one medium to another is the change in the speed of light in the medium as it crosses the boundary of one medium. For example, the speed of light in air is higher than the speed of light in water. So when the light travels from air to water, it experiences a sudden change in the speed which is reflected by the bending at the edge of two mediums. This ratio of speed of light in one medium to another is also called refractive index of one medium with respect to another.
Hence, light always bend while travelling from rarer to denser medium.
So, the statement is false and the correct answer is option B.
Note- Material refractive index is a dimensionless number which defines how easily light passes through the material. It is defined as where c is the vacuum velocity of light, and v is the medium phase velocity of light. The refractive index has a multitude of applications. It is often used to classify a given substance, to validate its purity or to quantify its concentration. Generally it is used to measure the concentration of a solute in an aqueous solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




