
What is the Lewis structure for bicarbonate?
Answer
531.9k+ views
Hint: To solve this question we first need to know what are Lewis dot structures. The valence electrons of the atoms of a molecule can be represented using the Lewis dot structure. They are a simplified version of the molecular geometry of a compound and can be used to depict the chemical bonding in the molecules.
Complete answer:
Bicarbonate, also known as hydrogen carbonate, is formed when carbonic acid is deprotonated. It is an anion having a formula $HCO_{3}^{-}$.
The Lewis dot structure of a compound can be drawn by the following steps.
1. We first need to know the valence electrons in the atoms of the molecule.
$_{6}C$ has 4 valence electrons, $_{8}O$ has 6 valence electrons, and $_{1}H$ has 1 valence electron.
And the molecule has a negative charge, i.e., 1 electron.
Hence the total number of valence electrons is $1+4+3\times 6+1=24$
2. Identify the least electronegative atom. This atom is the central atom of the molecule.
Carbon is the least electronegative atom in $HCO_{3}^{-}$.
3. Connect the atoms via single bonds to form a skeleton structure.
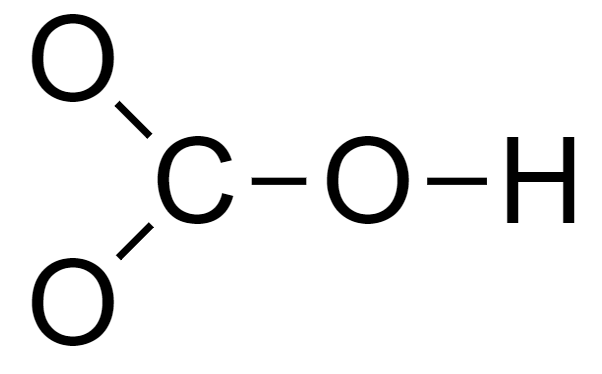
4. Complete the octet of each element.
The two O atoms bonded only to the C atom need 6 electrons each to complete their octet.
The C atom needs 2 electrons to complete its octet.
The O atom bonded to 1 C atom and 1 H atom needs 4 electrons to complete its octet.
The outermost shell of the H atom is complete.
So the total number of electrons required is 18 whereas the available electrons are 16.
Octet can be completed by forming a double bond as follows
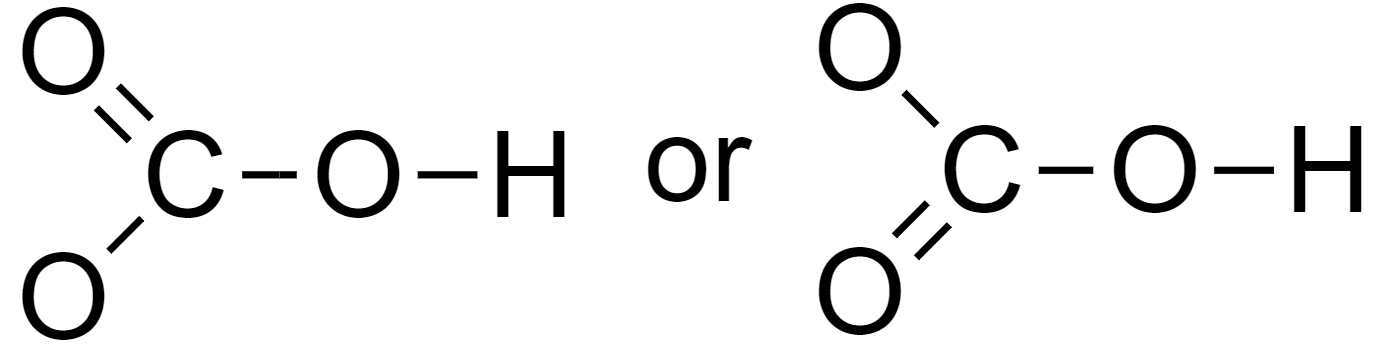
5. Assign lone pairs and the negative charge to the molecules.
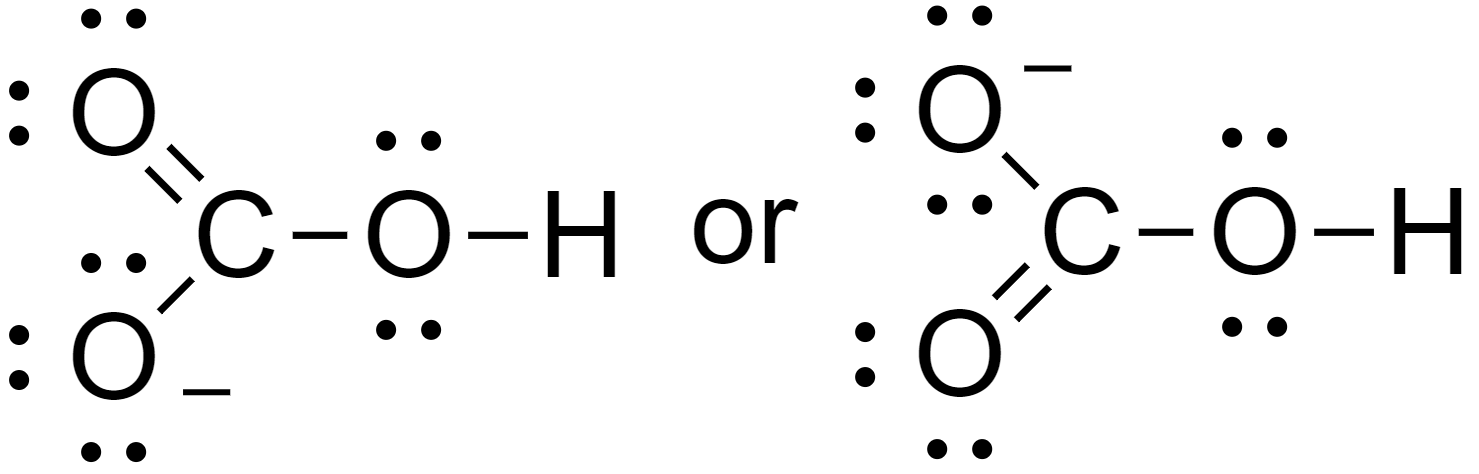
Hence the Lewis structure of bicarbonate is as above.
Note:
It should be noted that in sodium hydrogen carbonate, the hydrogen atom is attached to one of the oxygen atoms. Hence, we can assume that in hydrogen carbonate $HCO_{3}^{-}$, the hydrogen atom will also be bonded to the oxygen atom.
Complete answer:
Bicarbonate, also known as hydrogen carbonate, is formed when carbonic acid is deprotonated. It is an anion having a formula $HCO_{3}^{-}$.
The Lewis dot structure of a compound can be drawn by the following steps.
1. We first need to know the valence electrons in the atoms of the molecule.
$_{6}C$ has 4 valence electrons, $_{8}O$ has 6 valence electrons, and $_{1}H$ has 1 valence electron.
And the molecule has a negative charge, i.e., 1 electron.
Hence the total number of valence electrons is $1+4+3\times 6+1=24$
2. Identify the least electronegative atom. This atom is the central atom of the molecule.
Carbon is the least electronegative atom in $HCO_{3}^{-}$.
3. Connect the atoms via single bonds to form a skeleton structure.
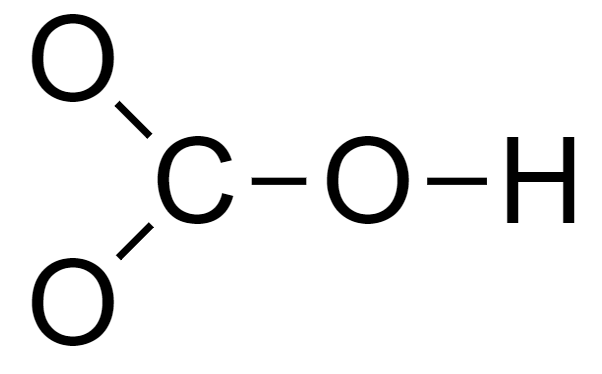
4. Complete the octet of each element.
The two O atoms bonded only to the C atom need 6 electrons each to complete their octet.
The C atom needs 2 electrons to complete its octet.
The O atom bonded to 1 C atom and 1 H atom needs 4 electrons to complete its octet.
The outermost shell of the H atom is complete.
So the total number of electrons required is 18 whereas the available electrons are 16.
Octet can be completed by forming a double bond as follows
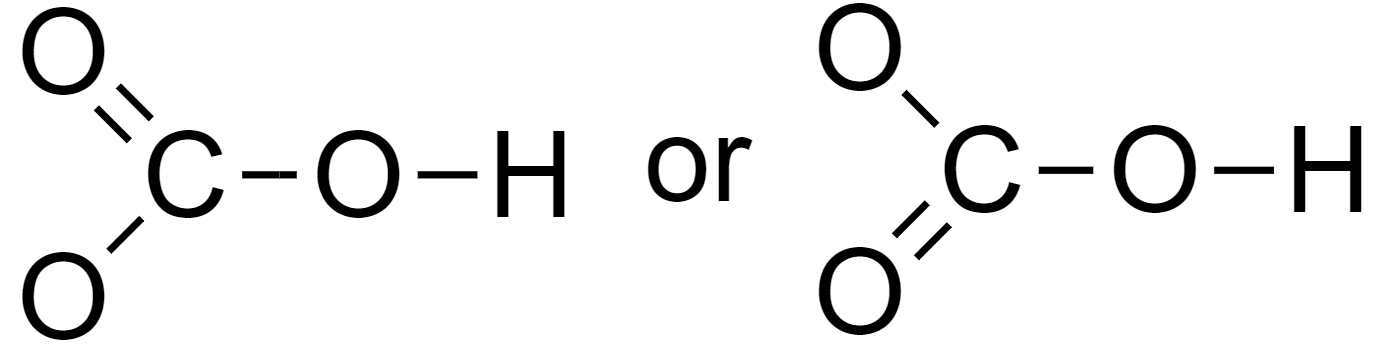
5. Assign lone pairs and the negative charge to the molecules.

Hence the Lewis structure of bicarbonate is as above.
Note:
It should be noted that in sodium hydrogen carbonate, the hydrogen atom is attached to one of the oxygen atoms. Hence, we can assume that in hydrogen carbonate $HCO_{3}^{-}$, the hydrogen atom will also be bonded to the oxygen atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




