
Let z1 and z2 be two complex numbers such that z1 $\ne $ z2 and |z1| = |z2|. If z1 has positive real part and z2 has negative imaginary part, then $\dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{{{z}_{1}}-{{z}_{2}}}$ may be which of the following:
(a) Purely imaginary
(b) Real and positive
(c) Real and negative
(d) None of these
Answer
615.9k+ views
Hint: Consider vectors along the position vector of z1 and z2 in the Argand Plane and with magnitude equal to |z1| and |z2|. A rhombus will be formed as shown in the figure with z1 + z2 and z1 - z2 in the directions of the diagonals. Use the fact that the diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular to each other to get z1 + z2 and z1 - z2 will be perpendicular to each other. This means that $\dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{{{z}_{1}}-{{z}_{2}}}$ will have an argument of $\pm \dfrac{\pi }{2}$ which gives us the final answer.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question, we are given that z1 and z2 are two complex numbers such that z1 $\ne $ z2 and |z1| = |z2|. Also, z1 has a positive real part and z2 has a negative imaginary part.
Using this information, we need to find the nature of $\dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{{{z}_{1}}-{{z}_{2}}}$.
We are given that |z1| = |z2|.
Consider vectors along the position vector of z1 and z2 in the Argand Plane and with magnitude equal to |z1| and |z2|.
A rhombus will be formed. Consider the rhombus formed as shown in the figure below:
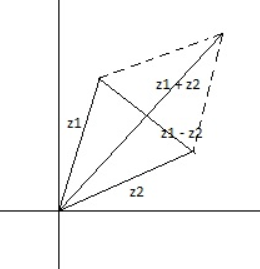
The vector along z1 + z2 will be in the direction of one of the diagonals, while the vector along z1 - z2 will be along the direction of the other diagonal.
We know that the diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular to each other.
Hence, z1 + z2 and z1 - z2 will be perpendicular to each other
So, $\dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{{{z}_{1}}-{{z}_{2}}}$ will have an argument of $\pm \dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Hence, $\dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{{{z}_{1}}-{{z}_{2}}}$ will be purely imaginary.
So, option (a) is correct.
Note: We can solve this question by another lengthy method also. Let z1 = a + bi and z2 = c + di. Now, find $\dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{{{z}_{1}}-{{z}_{2}}}$by substituting these. Simplify this and then use the fact that |z1| = |z2| to get ${{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{c}^{2}}+{{d}^{2}}$. Substitute this in the previous expression to get the answer.Students should remember if z1 + z2 and z1 - z2 are perpendicular to each then $\dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{{{z}_{1}}-{{z}_{2}}}$ will have an argument $\pm \dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
which says the real part is 0 i.e It is purely imaginary.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question, we are given that z1 and z2 are two complex numbers such that z1 $\ne $ z2 and |z1| = |z2|. Also, z1 has a positive real part and z2 has a negative imaginary part.
Using this information, we need to find the nature of $\dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{{{z}_{1}}-{{z}_{2}}}$.
We are given that |z1| = |z2|.
Consider vectors along the position vector of z1 and z2 in the Argand Plane and with magnitude equal to |z1| and |z2|.
A rhombus will be formed. Consider the rhombus formed as shown in the figure below:

The vector along z1 + z2 will be in the direction of one of the diagonals, while the vector along z1 - z2 will be along the direction of the other diagonal.
We know that the diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular to each other.
Hence, z1 + z2 and z1 - z2 will be perpendicular to each other
So, $\dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{{{z}_{1}}-{{z}_{2}}}$ will have an argument of $\pm \dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Hence, $\dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{{{z}_{1}}-{{z}_{2}}}$ will be purely imaginary.
So, option (a) is correct.
Note: We can solve this question by another lengthy method also. Let z1 = a + bi and z2 = c + di. Now, find $\dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{{{z}_{1}}-{{z}_{2}}}$by substituting these. Simplify this and then use the fact that |z1| = |z2| to get ${{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{c}^{2}}+{{d}^{2}}$. Substitute this in the previous expression to get the answer.Students should remember if z1 + z2 and z1 - z2 are perpendicular to each then $\dfrac{{{z}_{1}}+{{z}_{2}}}{{{z}_{1}}-{{z}_{2}}}$ will have an argument $\pm \dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
which says the real part is 0 i.e It is purely imaginary.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




