
Let the function $ f\left( x \right)={{\left[ x \right]}^{2}}+\left[ x+1 \right]-3 $ where [.] denotes the greatest integer function. Then
A. $ f\left( x \right)\ne 0 $ for all real values of x.
B. $ f\left( x \right)=0 $ for only two real values of x.
C. $ f\left( x \right)=0 $ for infinite value of x.
D. $ f\left( x \right)=0 $ for no real value of x.
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: For this question, we will first use $ \left[ x+I \right]=\left[ x \right]+I $ to find quadratic function in the form of [x]. Then we will suppose [x] as y and solve the quadratic equation. Then we will use the value to find the value of [x]. After that, we will use the definition of the greatest integer function to find the range of x. Using that, we will find our answer.
Complete step by step answer:
Here we are given the function f(x) as $ f\left( x \right)={{\left[ x \right]}^{2}}+\left[ x+1 \right]-3 $ where [.] denotes the greatest integer function. We need to find the number of values of x when f(x) = 0.
Let us first simplify our given function.
$ f\left( x \right)={{\left[ x \right]}^{2}}+\left[ x+1 \right]-3 $ .
We know that for a greatest integer function, $ \left[ x+I \right]=\left[ x \right]+I $ where I is any integer.
Therefore, let us change [x+1] into above form, we get $ f\left( x \right)={{\left[ x \right]}^{2}}+\left[ x \right]+1-3 $ .
Simplifying we get $ f\left( x \right)={{\left[ x \right]}^{2}}+\left[ x \right]-2 $ .
Now let us put f(x) = 0 to evaluate the value of x. We get, $ {{\left[ x \right]}^{2}}+\left[ x \right]-2=0 $ .
To avoid confusion let us suppose [x] as y, we get $ {{y}^{2}}+y-2=0 $ .
Using splitting the middle term method, we see that $ -2=\left( 2 \right)\left( -1 \right)\text{ and }1=2+\left( -1 \right) $ so we get,
\[\begin{align}
& {{y}^{2}}+\left( 2-1 \right)y-2=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}+2y-y-2=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y\left( y+2 \right)-1\left( y+2 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( y-1 \right)\left( y+2 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}\].
This implies that $ y-1=0\text{ and }y+2=0 $ or we can say y = 1, y = -2.
Putting values of y as [x], we get $ \left[ x \right]=1,\left[ x \right]=-2 $ .
Now according to the greatest integer function, [x] returns the largest integer less than or equal to x. So for [x] = 1, x should lie between 1 and 2 where it can be equal to 1 but not equal to 2. Therefore, for $ \left[ x \right]=1,1\le x\text{ }<\text{ }2\Rightarrow x\in \left[ 1,2 \right) $ .
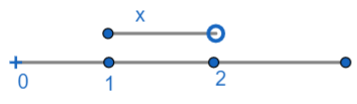
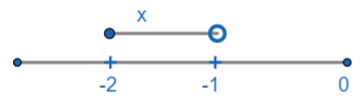
For $ \left[ x \right]=-2 $ .
x should lie between -1 and -2 where it can be equal to -2 but not equal to -1.
Therefore, for $ \left[ x \right]=-2,-2\le x\le -1\Rightarrow x\in \left[ -2,-1 \right) $ .
Combining both ranges of x, we get that $ x\in \left[ -2,-1 \right)\cup \left[ 1,2 \right) $ .
Now let us analyze our given options.
A. As we can see, there are real values for which $ f\left( x \right)=0 $ so option A is not correct.
B. In the interval [-2,-1) and [1,2) there exist infinite real numbers and not just two, so option B is not correct.
C. Option C is correct because there lies infinite values between found intervals for which $ f\left( x \right)=0 $ .
D. 1,2 are some examples of real values for which $ f\left( x \right)=0 $ so option D is not correct.
Hence option C is the correct answer.
Note:
Students should note that, while applying the definition of the greatest integer function on [x] = 1 make sure that 2 is not included and for [x] = -2, make sure that -1 is not included. Take care of signs while solving quadratic equations.
Complete step by step answer:
Here we are given the function f(x) as $ f\left( x \right)={{\left[ x \right]}^{2}}+\left[ x+1 \right]-3 $ where [.] denotes the greatest integer function. We need to find the number of values of x when f(x) = 0.
Let us first simplify our given function.
$ f\left( x \right)={{\left[ x \right]}^{2}}+\left[ x+1 \right]-3 $ .
We know that for a greatest integer function, $ \left[ x+I \right]=\left[ x \right]+I $ where I is any integer.
Therefore, let us change [x+1] into above form, we get $ f\left( x \right)={{\left[ x \right]}^{2}}+\left[ x \right]+1-3 $ .
Simplifying we get $ f\left( x \right)={{\left[ x \right]}^{2}}+\left[ x \right]-2 $ .
Now let us put f(x) = 0 to evaluate the value of x. We get, $ {{\left[ x \right]}^{2}}+\left[ x \right]-2=0 $ .
To avoid confusion let us suppose [x] as y, we get $ {{y}^{2}}+y-2=0 $ .
Using splitting the middle term method, we see that $ -2=\left( 2 \right)\left( -1 \right)\text{ and }1=2+\left( -1 \right) $ so we get,
\[\begin{align}
& {{y}^{2}}+\left( 2-1 \right)y-2=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}+2y-y-2=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y\left( y+2 \right)-1\left( y+2 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( y-1 \right)\left( y+2 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}\].
This implies that $ y-1=0\text{ and }y+2=0 $ or we can say y = 1, y = -2.
Putting values of y as [x], we get $ \left[ x \right]=1,\left[ x \right]=-2 $ .
Now according to the greatest integer function, [x] returns the largest integer less than or equal to x. So for [x] = 1, x should lie between 1 and 2 where it can be equal to 1 but not equal to 2. Therefore, for $ \left[ x \right]=1,1\le x\text{ }<\text{ }2\Rightarrow x\in \left[ 1,2 \right) $ .

For $ \left[ x \right]=-2 $ .
x should lie between -1 and -2 where it can be equal to -2 but not equal to -1.
Therefore, for $ \left[ x \right]=-2,-2\le x\le -1\Rightarrow x\in \left[ -2,-1 \right) $ .

Combining both ranges of x, we get that $ x\in \left[ -2,-1 \right)\cup \left[ 1,2 \right) $ .
Now let us analyze our given options.
A. As we can see, there are real values for which $ f\left( x \right)=0 $ so option A is not correct.
B. In the interval [-2,-1) and [1,2) there exist infinite real numbers and not just two, so option B is not correct.
C. Option C is correct because there lies infinite values between found intervals for which $ f\left( x \right)=0 $ .
D. 1,2 are some examples of real values for which $ f\left( x \right)=0 $ so option D is not correct.
Hence option C is the correct answer.
Note:
Students should note that, while applying the definition of the greatest integer function on [x] = 1 make sure that 2 is not included and for [x] = -2, make sure that -1 is not included. Take care of signs while solving quadratic equations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




