
Let O be the origin and A be the point (64, 0). If P and Q divide OA in the ratio $1:2:3$, find the coordinate of the point P.
(a) $\left( \dfrac{32}{3},0 \right)$
(b) $\left( 32,0 \right)$
(c) $\left( \dfrac{64}{3},0 \right)$
(d) $\left( 16,0 \right)$
(e) $\left( \dfrac{16}{3},0 \right)$
Answer
623.7k+ views
Hint: To find the coordinate of the point P by using the section formula. Section formula is used to determine the coordinate of a point that divides a line into two parts such that the ratio of their length is m: n.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Let O be the origin and the coordinate of the point A is (64, 0). The points P and Q divide the line OA in the ratio 1:2:3 as shown in the below figure.
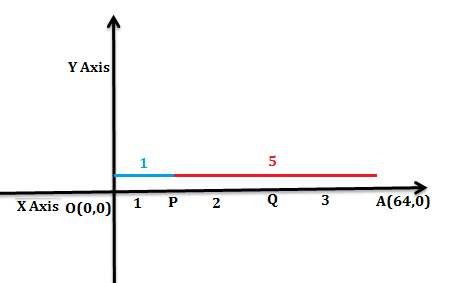
Here, O and A be the given two points $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)=\left( 0,0 \right)$ and $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)=\left( 64,0 \right)$ respectively and P be the point dividing the line-segment OA internally in the ratio m:n = 1:5, then from the sectional formula for determining the coordinate for a point P is given as
$P(x,y)=\left( \dfrac{m{{x}_{2}}+n{{x}_{1}}}{m+n},\dfrac{m{{y}_{2}}+n{{y}_{1}}}{m+n} \right)................(1)$
Now put all the values in the equation (1), we get
$P(x,y)=\left( \dfrac{1\times 64+5\times 0}{1+5},\dfrac{1\times 0+5\times 0}{1+5} \right)$
\[P(x,y)=\left( \dfrac{64+0}{6},\dfrac{0+0}{6} \right)\]
\[P(x,y)=\left( \dfrac{64}{6},0 \right)\]
\[P(x,y)=\left( \dfrac{32}{3},0 \right)\]
Hence the coordinate of the point P is \[\left( \dfrac{32}{3},0 \right)\]
Therefore the correct option for the given question is option (a).
Note: The possibility for the mistake is that you might get confused about the difference between an internal and an external division of a line segment. When the point P lies on the external part of the line segment, we use the section formula for the external division for its coordinates. On the contrary, when the point P lies on the internal part of the line segment, we use the section formula for the internal division for its coordinates.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Let O be the origin and the coordinate of the point A is (64, 0). The points P and Q divide the line OA in the ratio 1:2:3 as shown in the below figure.

Here, O and A be the given two points $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)=\left( 0,0 \right)$ and $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)=\left( 64,0 \right)$ respectively and P be the point dividing the line-segment OA internally in the ratio m:n = 1:5, then from the sectional formula for determining the coordinate for a point P is given as
$P(x,y)=\left( \dfrac{m{{x}_{2}}+n{{x}_{1}}}{m+n},\dfrac{m{{y}_{2}}+n{{y}_{1}}}{m+n} \right)................(1)$
Now put all the values in the equation (1), we get
$P(x,y)=\left( \dfrac{1\times 64+5\times 0}{1+5},\dfrac{1\times 0+5\times 0}{1+5} \right)$
\[P(x,y)=\left( \dfrac{64+0}{6},\dfrac{0+0}{6} \right)\]
\[P(x,y)=\left( \dfrac{64}{6},0 \right)\]
\[P(x,y)=\left( \dfrac{32}{3},0 \right)\]
Hence the coordinate of the point P is \[\left( \dfrac{32}{3},0 \right)\]
Therefore the correct option for the given question is option (a).
Note: The possibility for the mistake is that you might get confused about the difference between an internal and an external division of a line segment. When the point P lies on the external part of the line segment, we use the section formula for the external division for its coordinates. On the contrary, when the point P lies on the internal part of the line segment, we use the section formula for the internal division for its coordinates.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




