
Let $f(x) = {\mathop{\rm sgn}} ({\mathop{\rm sgn}} (x))$ . Then $\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 0} f(x)$ is:-
A) 1
B) 2
C) 0
D) Does not exist
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: Here in this question the concept of signum function and limit will get used. Definition of signum function and limit existence is as follows:-
Signum function or sign function is defined as f(x) = $\dfrac{{\left| x \right|}}{x};x \ne 0$
$f(x) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 1,x < 0}\\
{0,x = 0}\\
{1,x > 0}
\end{array}} \right\}$ is called a signum function.
Limit of a function exists when $\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ - }} f(x)\mathop { = \lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ + }} f(x) = L$ which is left hand side limit and right hand side limit and $L = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 0} f(x)$
Complete step-by-step answer:
As the given function is $f(x) = {\mathop{\rm sgn}} ({\mathop{\rm sgn}} (x))$ so, first of all we will find the left hand side limit.
$ \Rightarrow \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ - }} f(x) = {\mathop{\rm sgn}} ({\mathop{\rm sgn}} ({0^ - }))$
Now from the definition of signum function we know that ${\mathop{\rm sgn}} (x) = - 1$ when $x < 0$therefore we will get,
$ \Rightarrow \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ - }} f(x) = {\mathop{\rm sgn}} ( - 1)$
For all values less than 0 signum functions will give -1
$ \Rightarrow \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ - }} f(x) = - 1$
Now we will find the right hand side limit.
$ \Rightarrow \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ + }} f(x) = {\mathop{\rm sgn}} ({\mathop{\rm sgn}} ({0^ + }))$
Now from the definition of signum function we know that ${\mathop{\rm sgn}} (x) = 1$ when $x > 0$therefore we will get,
$ \Rightarrow \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ + }} f(x) = {\mathop{\rm sgn}} (1)$
For all values greater than 0 signum function will give +1
$ \Rightarrow \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ + }} f(x) = 1$
As we can see that left hand limit is not equal to the right hand limit therefore limit does not exist so the correct option is (D)
Note: Students may likely to make mistake while putting value of signum function so here below graphical approach for signum function is mentioned:-
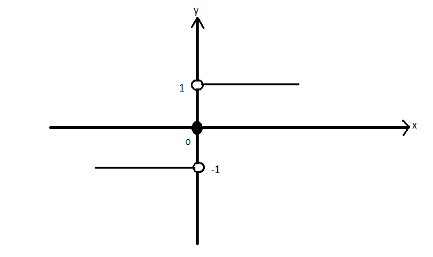
Here we can see that for x greater than zero the value of the function is 1 and for x less than zero the value of function is -1 and at x equal to zero value is zero. Also at points 1 and -1 there is a point of discontinuity as the graph breaks at these points.
Signum function or sign function is defined as f(x) = $\dfrac{{\left| x \right|}}{x};x \ne 0$
$f(x) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ - 1,x < 0}\\
{0,x = 0}\\
{1,x > 0}
\end{array}} \right\}$ is called a signum function.
Limit of a function exists when $\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ - }} f(x)\mathop { = \lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ + }} f(x) = L$ which is left hand side limit and right hand side limit and $L = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 0} f(x)$
Complete step-by-step answer:
As the given function is $f(x) = {\mathop{\rm sgn}} ({\mathop{\rm sgn}} (x))$ so, first of all we will find the left hand side limit.
$ \Rightarrow \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ - }} f(x) = {\mathop{\rm sgn}} ({\mathop{\rm sgn}} ({0^ - }))$
Now from the definition of signum function we know that ${\mathop{\rm sgn}} (x) = - 1$ when $x < 0$therefore we will get,
$ \Rightarrow \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ - }} f(x) = {\mathop{\rm sgn}} ( - 1)$
For all values less than 0 signum functions will give -1
$ \Rightarrow \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ - }} f(x) = - 1$
Now we will find the right hand side limit.
$ \Rightarrow \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ + }} f(x) = {\mathop{\rm sgn}} ({\mathop{\rm sgn}} ({0^ + }))$
Now from the definition of signum function we know that ${\mathop{\rm sgn}} (x) = 1$ when $x > 0$therefore we will get,
$ \Rightarrow \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ + }} f(x) = {\mathop{\rm sgn}} (1)$
For all values greater than 0 signum function will give +1
$ \Rightarrow \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ + }} f(x) = 1$
As we can see that left hand limit is not equal to the right hand limit therefore limit does not exist so the correct option is (D)
Note: Students may likely to make mistake while putting value of signum function so here below graphical approach for signum function is mentioned:-

Here we can see that for x greater than zero the value of the function is 1 and for x less than zero the value of function is -1 and at x equal to zero value is zero. Also at points 1 and -1 there is a point of discontinuity as the graph breaks at these points.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




