
Let A and B be the two sets such that \[n\left( A-B \right)=60+3x\], \[n\left( B-A \right)=8x\] and \[n\left( A\cap B \right)=x-4\] then draw a Venn diagram to illustrate this information. If \[n\left( A \right)=n\left( B \right)\] then find
(a) The value of \[x\]
(b) \[n\left( A\cup B \right)\]
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: We solve this problem by using the Venn diagrams of sets. The Venn diagrams represent the diagrammatic representation of sets inside the universal set \['\mu '\]
For solving the first part we use the given condition \[n\left( A \right)=n\left( B \right)\] along with the formulas of sets that is
\[\begin{align}
& n\left( A \right)=n\left( A-B \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right) \\
& n\left( B \right)=n\left( B-A \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right) \\
\end{align}\]
For solving second part we use the general formula of sets that is
\[n\left( A\cup B \right)=n\left( A \right)+n\left( B \right)-n\left( A\cap B \right)\]
Complete step-by-step solution
We are given that \[n\left( A-B \right)=60+3x\], \[n\left( B-A \right)=8x\] and \[n\left( A\cap B \right)=x-4\]
Let us draw a Venn diagram that represents the given information then we get
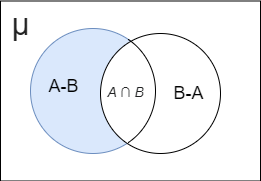
(a) The value of \[x\]
We are given that
\[\Rightarrow n\left( A \right)=n\left( B \right).......equation(i)\]
We know that the formulas of sets that is
\[\begin{align}
& n\left( A \right)=n\left( A-B \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right) \\
& n\left( B \right)=n\left( B-A \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right) \\
\end{align}\]
By using the above formulas to equation (i) we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow n\left( A-B \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right)=n\left( B-A \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right) \\
& \Rightarrow n\left( A-B \right)=n\left( B-A \right) \\
\end{align}\]
By substituting the required values in above equation we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 60+3x=8x \\
& \Rightarrow 5x=60 \\
& \Rightarrow x=12 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the value of \[x\] is 12
(b) \[n\left( A\cup B \right)\]
We know that the direct formula of union of sets that is
\[n\left( A\cup B \right)=n\left( A \right)+n\left( B \right)-n\left( A\cap B \right)\]
By substituting the required values from the formulas we used before in above equation we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow n\left( A\cup B \right)=\left( n\left( A-B \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right) \right)+\left( n\left( B-A \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right) \right)-n\left( A\cap B \right) \\
& \Rightarrow n\left( A\cup B \right)=n\left( A-B \right)+n\left( B-A \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now by substituting the required values in terms of \[x\] in above equation we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow n\left( A\cup B \right)=60+3x+8x+x-4 \\
& \Rightarrow n\left( A\cup B \right)=12x+56 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, by substituting \[x=12\] in above equation we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow n\left( A\cup B \right)=12\times 12+56 \\
& \Rightarrow n\left( A\cup B \right)=200 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the value of \[n\left( A\cup B \right)\] is 200.
Note: Students may make mistakes in the Venn diagram representation.
Venn diagrams are the diagrammatic representation of sets in the universal set \['\mu '\]
So the Venn diagram must be drawn as
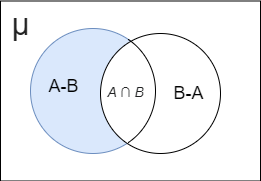
But students may miss the universal set \['\mu '\] and draw the Venn diagram as
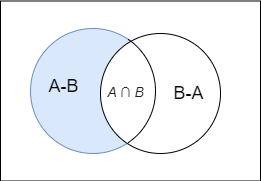
This will be the wrong representation because all the sets are subsets of a universal set \['\mu '\] which is very important to represent in the Venn diagram.
For solving the first part we use the given condition \[n\left( A \right)=n\left( B \right)\] along with the formulas of sets that is
\[\begin{align}
& n\left( A \right)=n\left( A-B \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right) \\
& n\left( B \right)=n\left( B-A \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right) \\
\end{align}\]
For solving second part we use the general formula of sets that is
\[n\left( A\cup B \right)=n\left( A \right)+n\left( B \right)-n\left( A\cap B \right)\]
Complete step-by-step solution
We are given that \[n\left( A-B \right)=60+3x\], \[n\left( B-A \right)=8x\] and \[n\left( A\cap B \right)=x-4\]
Let us draw a Venn diagram that represents the given information then we get

(a) The value of \[x\]
We are given that
\[\Rightarrow n\left( A \right)=n\left( B \right).......equation(i)\]
We know that the formulas of sets that is
\[\begin{align}
& n\left( A \right)=n\left( A-B \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right) \\
& n\left( B \right)=n\left( B-A \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right) \\
\end{align}\]
By using the above formulas to equation (i) we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow n\left( A-B \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right)=n\left( B-A \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right) \\
& \Rightarrow n\left( A-B \right)=n\left( B-A \right) \\
\end{align}\]
By substituting the required values in above equation we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 60+3x=8x \\
& \Rightarrow 5x=60 \\
& \Rightarrow x=12 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the value of \[x\] is 12
(b) \[n\left( A\cup B \right)\]
We know that the direct formula of union of sets that is
\[n\left( A\cup B \right)=n\left( A \right)+n\left( B \right)-n\left( A\cap B \right)\]
By substituting the required values from the formulas we used before in above equation we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow n\left( A\cup B \right)=\left( n\left( A-B \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right) \right)+\left( n\left( B-A \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right) \right)-n\left( A\cap B \right) \\
& \Rightarrow n\left( A\cup B \right)=n\left( A-B \right)+n\left( B-A \right)+n\left( A\cap B \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now by substituting the required values in terms of \[x\] in above equation we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow n\left( A\cup B \right)=60+3x+8x+x-4 \\
& \Rightarrow n\left( A\cup B \right)=12x+56 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, by substituting \[x=12\] in above equation we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow n\left( A\cup B \right)=12\times 12+56 \\
& \Rightarrow n\left( A\cup B \right)=200 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the value of \[n\left( A\cup B \right)\] is 200.
Note: Students may make mistakes in the Venn diagram representation.
Venn diagrams are the diagrammatic representation of sets in the universal set \['\mu '\]
So the Venn diagram must be drawn as

But students may miss the universal set \['\mu '\] and draw the Venn diagram as

This will be the wrong representation because all the sets are subsets of a universal set \['\mu '\] which is very important to represent in the Venn diagram.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




