
What is the lattice energy of Calcium Chloride?
Answer
514.5k+ views
Hint :The Born-Haber cycle is a very useful method in calculating the lattice enthalpy of any compound. To find out the lattice enthalpy we need the total ionization energy when the compound is prepared from its constituent atoms or ions. We also need sublimation energy, dissociation energy, ionization energy and electron affinity values.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us first consider the Born-Haber Cycle of $ CaC{l_2} $ . Only by seeing this we can calculate the lattice energy of the compound.
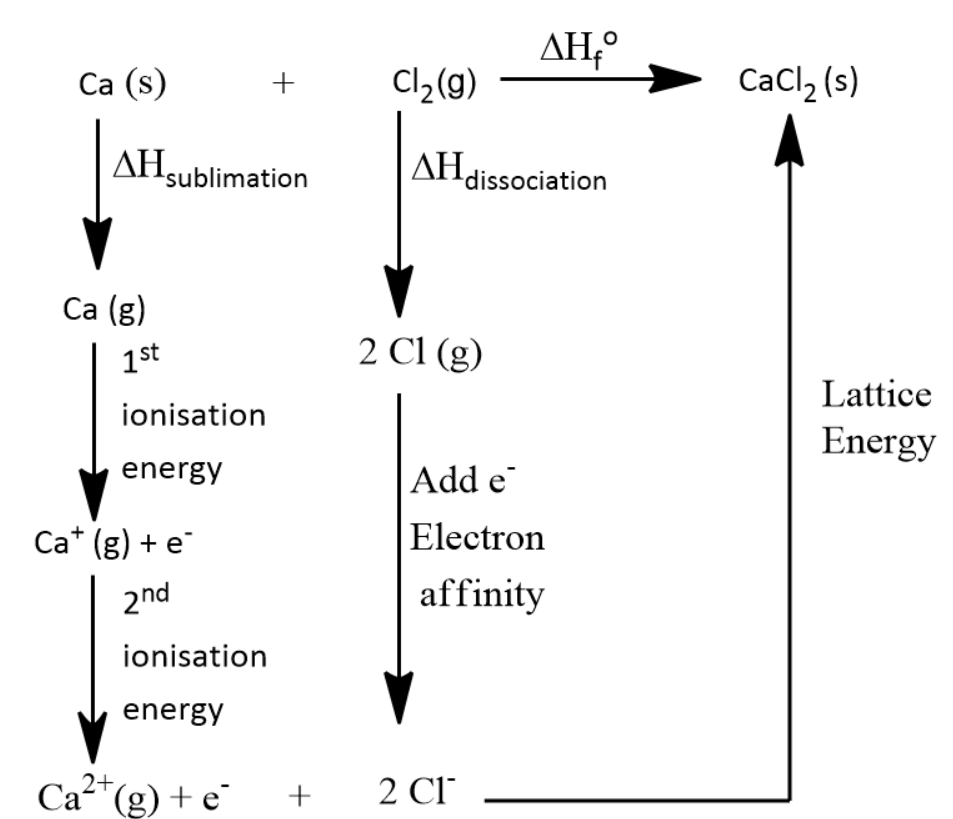
By the above diagram we can say that
Standard enthalpy of formation ( $ \Delta H_f^o $ ) = lattice energy + (2 $ \times $ Electron affinity for chlorine) + Bond Energy of Chlorine gas + first and second ionisation energy of calcium + Sublimation energy of Calcium solid.
$ \Delta {H_{{\text{sublimation}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}121{\text{ }}kJ $
1st Ionization Energy of Ca = 589.5 $ kJ $
2nd Ionization Energy of Ca = 1145 $ kJ $
Bond Energy of Cl2 = 242.7 $ kJ $
Electron Affinity for chlorine = 2 $ \times $ (−349 $ kJ $ )
Standard Enthalpy of Formation of CaCl2 (s) = −795 $ kJ $
We can substitute these values in the equation to find out the lattice energy
$ \Rightarrow - 795{\text{ }}kJ{\text{ }} = {\text{ Lattice Energy }} + {\text{ }}2 \times \left( { - 349{\text{ }}kJ} \right){\text{ }} + {\text{ }}242.4{\text{ }}kJ{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}1145{\text{ }}kJ{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}589.5{\text{ }}kJ{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}121{\text{ }}kJ $
$ \Rightarrow {\text{Lattice Energy = }} - 795{\text{ }}kJ - 2 \times \left( { - 349{\text{ }}kJ} \right) - 242.4{\text{ }}kJ - 1145{\text{ }}kJ - 589.5{\text{ }}kJ - 121{\text{ }}kJ $
$ \Rightarrow {\text{Lattice Energy}} = - 2195.2{\text{ }}kJ/mol $
This is how we find the lattice energy of calcium chloride by using Born-Haber cycle.
Note :
We can also use another method to find out the lattice energy of a compound
This method is by using the Born-Lande Equation, given by
$ Lattice{\text{ }}Energy = \dfrac{{{N_A} \times M \times {z^ + } \times {z^ - } \times {e^2}}}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _o}r}}\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{n}} \right) $
Where $ {N_A} $ is the Avogadro number
$ M $ is the Madelung Constant
$ {z^ + },{z^ - } $ are the charges of cation and anion respectively
$ e $ is the electronic charge
$ {\varepsilon _o} $ is permittivity of free space
$ r $ is the radial distance
$ n $ is the born exponent.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us first consider the Born-Haber Cycle of $ CaC{l_2} $ . Only by seeing this we can calculate the lattice energy of the compound.

By the above diagram we can say that
Standard enthalpy of formation ( $ \Delta H_f^o $ ) = lattice energy + (2 $ \times $ Electron affinity for chlorine) + Bond Energy of Chlorine gas + first and second ionisation energy of calcium + Sublimation energy of Calcium solid.
$ \Delta {H_{{\text{sublimation}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}121{\text{ }}kJ $
1st Ionization Energy of Ca = 589.5 $ kJ $
2nd Ionization Energy of Ca = 1145 $ kJ $
Bond Energy of Cl2 = 242.7 $ kJ $
Electron Affinity for chlorine = 2 $ \times $ (−349 $ kJ $ )
Standard Enthalpy of Formation of CaCl2 (s) = −795 $ kJ $
We can substitute these values in the equation to find out the lattice energy
$ \Rightarrow - 795{\text{ }}kJ{\text{ }} = {\text{ Lattice Energy }} + {\text{ }}2 \times \left( { - 349{\text{ }}kJ} \right){\text{ }} + {\text{ }}242.4{\text{ }}kJ{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}1145{\text{ }}kJ{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}589.5{\text{ }}kJ{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}121{\text{ }}kJ $
$ \Rightarrow {\text{Lattice Energy = }} - 795{\text{ }}kJ - 2 \times \left( { - 349{\text{ }}kJ} \right) - 242.4{\text{ }}kJ - 1145{\text{ }}kJ - 589.5{\text{ }}kJ - 121{\text{ }}kJ $
$ \Rightarrow {\text{Lattice Energy}} = - 2195.2{\text{ }}kJ/mol $
This is how we find the lattice energy of calcium chloride by using Born-Haber cycle.
Note :
We can also use another method to find out the lattice energy of a compound
This method is by using the Born-Lande Equation, given by
$ Lattice{\text{ }}Energy = \dfrac{{{N_A} \times M \times {z^ + } \times {z^ - } \times {e^2}}}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _o}r}}\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{n}} \right) $
Where $ {N_A} $ is the Avogadro number
$ M $ is the Madelung Constant
$ {z^ + },{z^ - } $ are the charges of cation and anion respectively
$ e $ is the electronic charge
$ {\varepsilon _o} $ is permittivity of free space
$ r $ is the radial distance
$ n $ is the born exponent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




