
Label the diagram of the taproot system and write its significance.

Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Most dicotyledonous plants, such as grams, dandelions, etc. possess taproots. They can also be modified for support or food storage as seen in carrots, beets, etc.
Complete answer:
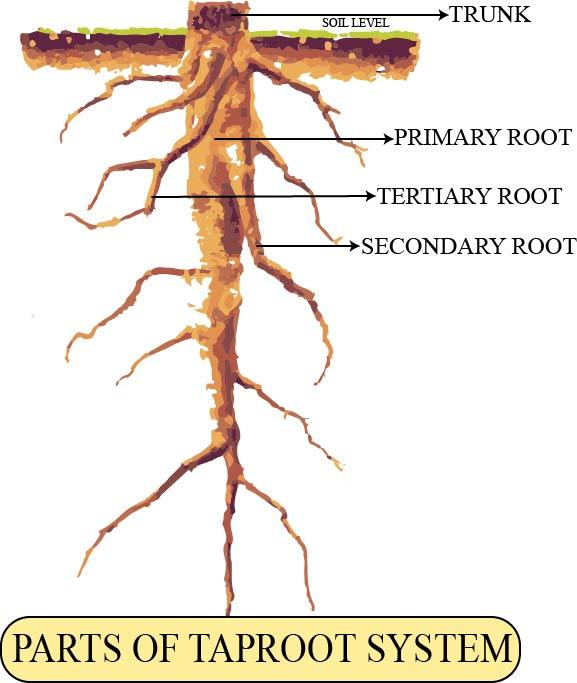
‘The taproot system’ consists of a primary root or tap root, secondary root (lateral branches of the primary root), tertiary root, root hairs, and root cap.
-The primary root in the taproot system develops from the radicle of the cotyledon. It grows into a straight, slender, and very thick mass. As it grows deep into the soil, it starts tapering to a much smaller diameter.
-The lateral roots growing from the primary taproot i.e. Secondary root and Tertiary root provide support to the plant.
-The root tip remains covered by a root cap that protects the young, tender root as it penetrates into the soil.
-The root hairs help in the absorption of water and minerals from the soil.
-The taproots growing deep down into the soil not only provide stability to the plant but also by holding the soil together prevents its erosion. In certain plants, the taps roots also play a critical role in storing the food (carrots, beetroot, etc.).
-Since the roots can grow deep into the soil the plants with a taproot system will have better sustenance under drought conditions.
Note: The formation of root takes place in acropetal succession i.e. the youngest or the newer part is found near the growing point and the oldest towards the base of the parent root. In orientation the taproot is vertical, secondary roots are horizontal or oblique while the tertiary roots run in different directions. Rootlets are the ultimate root branches. Root hairs arise from the epidermis of the primary root.
Complete answer:

‘The taproot system’ consists of a primary root or tap root, secondary root (lateral branches of the primary root), tertiary root, root hairs, and root cap.
-The primary root in the taproot system develops from the radicle of the cotyledon. It grows into a straight, slender, and very thick mass. As it grows deep into the soil, it starts tapering to a much smaller diameter.
-The lateral roots growing from the primary taproot i.e. Secondary root and Tertiary root provide support to the plant.
-The root tip remains covered by a root cap that protects the young, tender root as it penetrates into the soil.
-The root hairs help in the absorption of water and minerals from the soil.
-The taproots growing deep down into the soil not only provide stability to the plant but also by holding the soil together prevents its erosion. In certain plants, the taps roots also play a critical role in storing the food (carrots, beetroot, etc.).
-Since the roots can grow deep into the soil the plants with a taproot system will have better sustenance under drought conditions.
Note: The formation of root takes place in acropetal succession i.e. the youngest or the newer part is found near the growing point and the oldest towards the base of the parent root. In orientation the taproot is vertical, secondary roots are horizontal or oblique while the tertiary roots run in different directions. Rootlets are the ultimate root branches. Root hairs arise from the epidermis of the primary root.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




