
What is known as condensation of chromosomes?
Answer
509.1k+ views
Hint: A chromosome is defined as a string of DNA wrapped around associated proteins that give the connected nucleic acid bases a structure and it carries a part of genetic information. Chromosome condensation is the reorganisation of chromatin strands into short chromosomes.
Complete answer:
Chromosome condensation basically explained as one of the major chromatin-remodelling events that occur during Prophase I. It is the longest phase of meiosis where;
- Chromatin condenses into chromosomes.
- The physical contact between homologous chromosomes happens
- The transmission of genetic information between synapsed chromosomes.
Here is an outlook of the condensation of chromosomes.
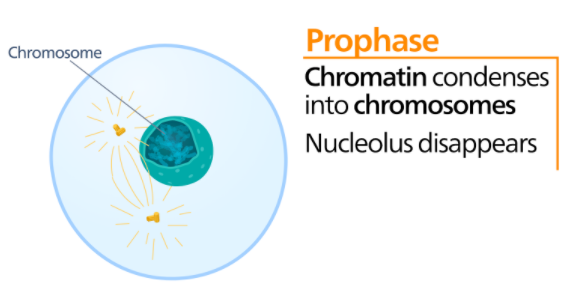
There are five sub-phases under prophase
i) Leptotene: The condensation of chromosomes starts and they attach to the cell membrane through telomeres.
ii) Zygotene: Here pairing of chromosomes starts in this stage and synapsis between homologous chromosomes begin. The paired chromosomes are named bivalents.
iii) Pachytene: Here a chromatid of one pair starts attaching to the chromatid in a homologous chromosome hence the synapse is formed and the crossing over begins. After some time, the crossing over of genetic material between the non-sister chromatids occurs in this phase.
iv) Diplotene: Here, the paired chromosomes separate and become into two pairs of chromatids.
Diakinesis: The chromosomes are highly condensed in this phase. Here the nuclear membrane disintegrates, the nucleolus vanishes and the centrioles move to the equator.
Note: Significance of meiosis is as follows;
- It is responsible for the formation of gametes without which sexual reproduction cannot happen.
- The genetic information for the development of gametes is activated by meiosis and also deactivates the sporophytic information.
- Chromosome numbers are maintained properly by halving the same as the chromosome number doubles after fertilization.
Complete answer:
Chromosome condensation basically explained as one of the major chromatin-remodelling events that occur during Prophase I. It is the longest phase of meiosis where;
- Chromatin condenses into chromosomes.
- The physical contact between homologous chromosomes happens
- The transmission of genetic information between synapsed chromosomes.
Here is an outlook of the condensation of chromosomes.

There are five sub-phases under prophase
i) Leptotene: The condensation of chromosomes starts and they attach to the cell membrane through telomeres.
ii) Zygotene: Here pairing of chromosomes starts in this stage and synapsis between homologous chromosomes begin. The paired chromosomes are named bivalents.
iii) Pachytene: Here a chromatid of one pair starts attaching to the chromatid in a homologous chromosome hence the synapse is formed and the crossing over begins. After some time, the crossing over of genetic material between the non-sister chromatids occurs in this phase.
iv) Diplotene: Here, the paired chromosomes separate and become into two pairs of chromatids.
Diakinesis: The chromosomes are highly condensed in this phase. Here the nuclear membrane disintegrates, the nucleolus vanishes and the centrioles move to the equator.
Note: Significance of meiosis is as follows;
- It is responsible for the formation of gametes without which sexual reproduction cannot happen.
- The genetic information for the development of gametes is activated by meiosis and also deactivates the sporophytic information.
- Chromosome numbers are maintained properly by halving the same as the chromosome number doubles after fertilization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




