
Justify the importance of decomposers in an ecosystem.
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Decomposers, the name only suggests that these are the organisms that decompose, or break down, organic material such as the remains of dead organisms. Examples of decomposers are bacteria and fungi.
Complete answer:
Decomposers mostly prey on dead things: dead plant materials like leaf litter and wood, animal carcasses, and feces. Decomposers perform a valuable service as Earth’s cleanup member. Without decomposers, dead leaves, dead insects, and dead animals would compile everywhere. Imagine what the planet would look like.
-The other important function is that decomposers make vital nutrients available to an ecosystem’s primary producers—usually plants and algae. Decomposers break a part of complex organic materials into simpler substances: water and CO2, plus simple compounds containing nitrogen, phosphorus, and calcium. All of those components are substances that plants get to grow.
-Some decomposers are specialized and break down only a particular quite dead organism. Others are generalists that prey on many different materials. Because of decomposers, nutrients get added back to the soil or water, therefore the producers can use them to grow and reproduce.
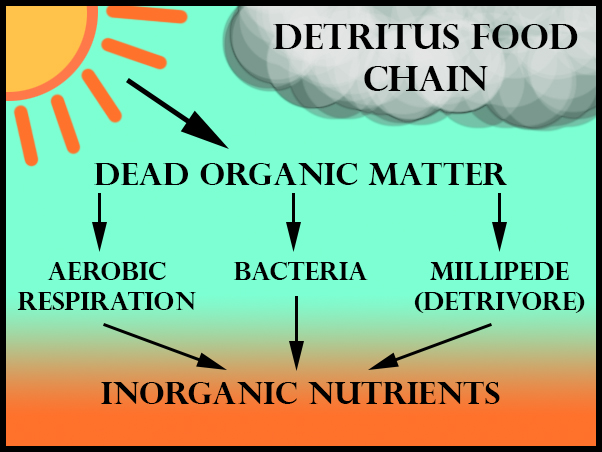
Most decomposers that are present are microscopic organisms, including protozoa and bacteria. Other decomposers are large enough to ascertain without a microscope. They include fungi alongside invertebrate organisms sometimes called detritivores, which include earthworms, termites, and millipedes.
Note: Fungi are important decomposers, especially in forests. Some sorts of fungi, like mushrooms, appear as if plants. But fungi don't contain chlorophyll, the pigment that green plants use to form their food with the energy of sunlight. The fungi get all their nutrients from dead materials that they break down with special enzymes.
Complete answer:
Decomposers mostly prey on dead things: dead plant materials like leaf litter and wood, animal carcasses, and feces. Decomposers perform a valuable service as Earth’s cleanup member. Without decomposers, dead leaves, dead insects, and dead animals would compile everywhere. Imagine what the planet would look like.
-The other important function is that decomposers make vital nutrients available to an ecosystem’s primary producers—usually plants and algae. Decomposers break a part of complex organic materials into simpler substances: water and CO2, plus simple compounds containing nitrogen, phosphorus, and calcium. All of those components are substances that plants get to grow.
-Some decomposers are specialized and break down only a particular quite dead organism. Others are generalists that prey on many different materials. Because of decomposers, nutrients get added back to the soil or water, therefore the producers can use them to grow and reproduce.
Most decomposers that are present are microscopic organisms, including protozoa and bacteria. Other decomposers are large enough to ascertain without a microscope. They include fungi alongside invertebrate organisms sometimes called detritivores, which include earthworms, termites, and millipedes.
Note: Fungi are important decomposers, especially in forests. Some sorts of fungi, like mushrooms, appear as if plants. But fungi don't contain chlorophyll, the pigment that green plants use to form their food with the energy of sunlight. The fungi get all their nutrients from dead materials that they break down with special enzymes.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




