
What is jump discontinuity in math?
Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: We first need to understand the meaning of the word ‘discontinuity’. In mathematical terms, a discontinuity is any point in the domain of the function where the function is not defined or any point where the left-hand limit and right-hand limit of the function are not equal. We need to be aware about the types of discontinuity in mathematics.
Complete step by step solution:
In this question we will find the limits of the given function. Now by limits we mean that we will find the left-hand limit and right-hand limit of the function and then we will compare the limits. We say that it is a jump discontinuity in maths if we see that after finding the left-hand limit and right-hand limit of the function that they are not equal. When this case appears then we say that it is a jump discontinuity.
We can see jump discontinuity from the graph of the function given below:
\[f\left(x\right) = \begin{cases}
x+1 & x> 0 \\
-x & x\leq 0
\end{cases}\]
The graph of the function is as follows, and the jump discontinuity can clearly be seen here:
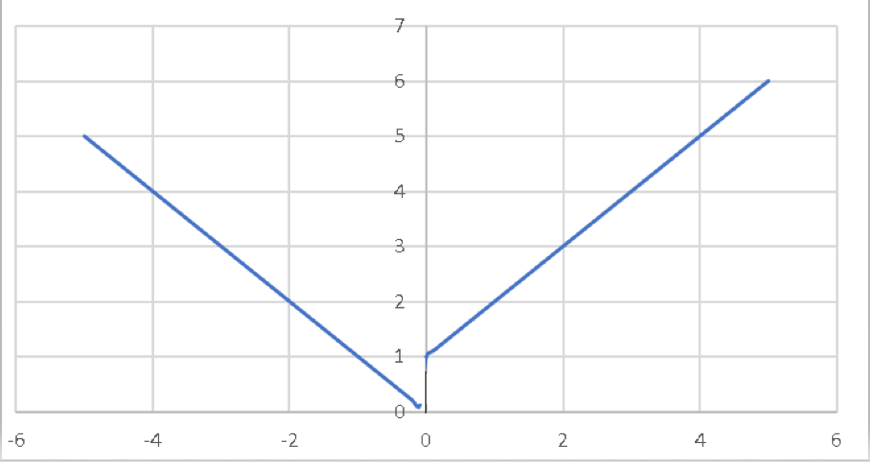
Now we can see from the graph clearly that there is a jump in the limit of the function from the left side and the right side. The jump from 0 to 1 can be clearly seen and hence we can conclude what is the jump discontinuity.
Note: Here in the function, the discontinuity appears when the left hand limit and right hand limits are not equal, other types of discontinuity may occur when the function is not defined at that point, in that case do not mix the two definitions.
Complete step by step solution:
In this question we will find the limits of the given function. Now by limits we mean that we will find the left-hand limit and right-hand limit of the function and then we will compare the limits. We say that it is a jump discontinuity in maths if we see that after finding the left-hand limit and right-hand limit of the function that they are not equal. When this case appears then we say that it is a jump discontinuity.
We can see jump discontinuity from the graph of the function given below:
\[f\left(x\right) = \begin{cases}
x+1 & x> 0 \\
-x & x\leq 0
\end{cases}\]
The graph of the function is as follows, and the jump discontinuity can clearly be seen here:

Now we can see from the graph clearly that there is a jump in the limit of the function from the left side and the right side. The jump from 0 to 1 can be clearly seen and hence we can conclude what is the jump discontinuity.
Note: Here in the function, the discontinuity appears when the left hand limit and right hand limits are not equal, other types of discontinuity may occur when the function is not defined at that point, in that case do not mix the two definitions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




