
JGA (JuxtaGlomerular Apparatus), a sensitive region, which regulates the glomerular filtration rate is present near the
A. DCT and PCT
B. DCT and efferent arteriole
C. DCT and afferent arteriole
D. Loop of Henle and DCT
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: The JGA is a very sensitive cell. This is seen near the Bowman's capsular region of the kidney where the afferent arteriole enters and the efferent arteriole exits the nephron.
Step by step answer:The juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA, also called the juxtaglomerular complex) is a structural part that is present in the kidney. It regulates the function of the nephron. The juxtaglomerular apparatus is named because it is juxta to (which means next to) the glomerulus.
The juxtaglomerular apparatus contains three types of cells:
The macula densa, which is the part of the distal convoluted tubule of the same nephron,
Juxtaglomerular cells or granular cells that secrete renin,
Extraglomerular mesangial cells.
So, the correct answer is option C. DCT and afferent arteriole.
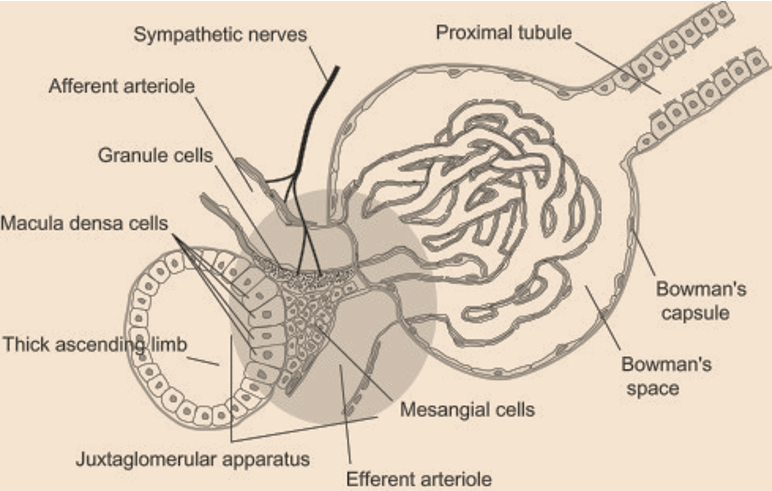
Additional Information: The functions of the cells of JGA are as follows:
-Juxtaglomerular cells: Renin is produced by juxtaglomerular cells in response to stimulation of the beta-1 adrenergic receptor, reduction in renal perfusion pressure, and decrease in the salt (NaCl) concentration at the macula densa cells, which is a result of reduced glomerular filtration rate.
-Extraglomerular mesangial cells: These cells are present in the connection between the afferent and efferent arterioles. These cells have a contractile property by which they can control the regulation of GFR or glomerular filtration rate by the alteration of the diameter of the blood vessels.
-Macula densa: These cells are seen in the junction of the afferent arterioles and the efferent arteriole. At this location, the wall of the distal convoluted tubule is attached with the afferent arteriole and some cells are modified to form the macula densa. These cells respond against the change in the sodium chloride concentration in the distal tubule of the nephron.
Note: The JGA or juxtaglomerular apparatus is a structural part present in the kidney and regulates the function of the nephron. Three different types of cells are present in JGA are- juxtaglomerular cells, extraglomerular mesangial cells, and macula densa.
Step by step answer:The juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA, also called the juxtaglomerular complex) is a structural part that is present in the kidney. It regulates the function of the nephron. The juxtaglomerular apparatus is named because it is juxta to (which means next to) the glomerulus.
The juxtaglomerular apparatus contains three types of cells:
The macula densa, which is the part of the distal convoluted tubule of the same nephron,
Juxtaglomerular cells or granular cells that secrete renin,
Extraglomerular mesangial cells.
So, the correct answer is option C. DCT and afferent arteriole.

Additional Information: The functions of the cells of JGA are as follows:
-Juxtaglomerular cells: Renin is produced by juxtaglomerular cells in response to stimulation of the beta-1 adrenergic receptor, reduction in renal perfusion pressure, and decrease in the salt (NaCl) concentration at the macula densa cells, which is a result of reduced glomerular filtration rate.
-Extraglomerular mesangial cells: These cells are present in the connection between the afferent and efferent arterioles. These cells have a contractile property by which they can control the regulation of GFR or glomerular filtration rate by the alteration of the diameter of the blood vessels.
-Macula densa: These cells are seen in the junction of the afferent arterioles and the efferent arteriole. At this location, the wall of the distal convoluted tubule is attached with the afferent arteriole and some cells are modified to form the macula densa. These cells respond against the change in the sodium chloride concentration in the distal tubule of the nephron.
Note: The JGA or juxtaglomerular apparatus is a structural part present in the kidney and regulates the function of the nephron. Three different types of cells are present in JGA are- juxtaglomerular cells, extraglomerular mesangial cells, and macula densa.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




