
It’s basic strength is ${ 10 }^{ 10 }$ more than 1- dimethylamino naphthalene due to
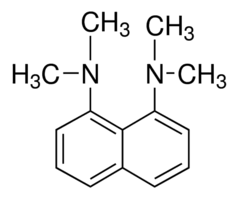
1,8-Bis (dimethylamino) naphthalene
(A) Resonance
(B) Steric inhibition of resonance
(C) Ortho effect
(D) Hyper conjugation

Answer
604.8k+ views
Hint: Give a close observation on the structure of 1,8-Bis (dimethylamino) naphthalene also keep in mind that according to the Bronsted-Lowry concept, a base is defined as a substance which accepts protons.
Complete step by step solution: In 1,8-Bis (dimethylamino) naphthalene both the dimethyl amino groups are in close vicinity to each other, that originates from the electrostatic repulsion between the unshared electron pairs of nitrogen atoms, which strongly destabilised the neutral base.
This repulsion is additionally fortified by the steric inhibition of resonance (both NMe2 groups cannot be conjugated to the aromatic system at the same time) preventing charge delocalisation. The protonation results in the formation of the N–H···N bonded cation 1 ${ H }^{ + }$ , the removal of the electro-static and steric strain and thus a considerable free energy gain.
While in the case of 1- dimethylamino naphthalene, it has only one Nitrogen group and there are no steric effects.
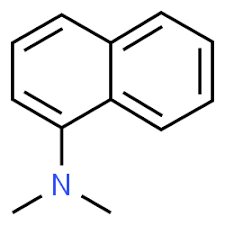
1-dimethylamino naphthalene
Here, in 1- dimethylamino naphthalene, the basicity is due to resonance only, but the steric inhibition comes in the case of 1,8-Bis (dimethylamino) naphthalene.
So, it is clear that our answer to the question is option (B) , steric inhibition due to resonance.
As we have already mentioned in the Hint section, why we are considering Bronsted- Lowry concept for basis is because of the following reaction given below:
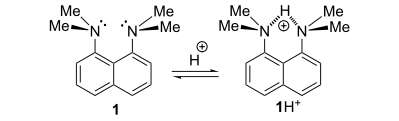
This is also a reason why the vast majority of DMAN derivatives are protonated to the internitrogen space, even if other centres of basicity are present in the molecule.
From the above , we can conclude that the answer is option (B) steric inhibition due to resonance.
Additional Information:
1,8-Bis (dimethylamino) naphthalene is classified as a peri-naphthalene, i.e. a 1,8- substituted derivative of naphthalene. Owing to its unusual structure, it exhibits exceptional basicity. It is often referred to by the trade name Proton Sponge, a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich.
In case of 1,8-Bis (dimethylamino) naphthalene, there is two types of basicity known as in-basicity and out-basicity.A possibility of non-conventional two-step protonation of 1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene (proton sponge) is there.
Unlike the generally accepted mechanism, involving relatively slow direct penetration of a proton into the cleft between the peri-${ NMe }_{ 2 }$ groups, it consists of the rapid addition of a proton to the out-inverted ${ NMe }_{ 2 }$ group with the subsequent slower rotational transfer of the proton into the inter-nitrogen space to produce a stable chelated cation.
Note: Hyperconjugation also provides a basicity feature but the steric inhibition due to resonance dominates over it and that’s why we are not considering hyperconjugation over here.
Complete step by step solution: In 1,8-Bis (dimethylamino) naphthalene both the dimethyl amino groups are in close vicinity to each other, that originates from the electrostatic repulsion between the unshared electron pairs of nitrogen atoms, which strongly destabilised the neutral base.
This repulsion is additionally fortified by the steric inhibition of resonance (both NMe2 groups cannot be conjugated to the aromatic system at the same time) preventing charge delocalisation. The protonation results in the formation of the N–H···N bonded cation 1 ${ H }^{ + }$ , the removal of the electro-static and steric strain and thus a considerable free energy gain.
While in the case of 1- dimethylamino naphthalene, it has only one Nitrogen group and there are no steric effects.

1-dimethylamino naphthalene
Here, in 1- dimethylamino naphthalene, the basicity is due to resonance only, but the steric inhibition comes in the case of 1,8-Bis (dimethylamino) naphthalene.
So, it is clear that our answer to the question is option (B) , steric inhibition due to resonance.
As we have already mentioned in the Hint section, why we are considering Bronsted- Lowry concept for basis is because of the following reaction given below:

This is also a reason why the vast majority of DMAN derivatives are protonated to the internitrogen space, even if other centres of basicity are present in the molecule.
From the above , we can conclude that the answer is option (B) steric inhibition due to resonance.
Additional Information:
1,8-Bis (dimethylamino) naphthalene is classified as a peri-naphthalene, i.e. a 1,8- substituted derivative of naphthalene. Owing to its unusual structure, it exhibits exceptional basicity. It is often referred to by the trade name Proton Sponge, a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich.
In case of 1,8-Bis (dimethylamino) naphthalene, there is two types of basicity known as in-basicity and out-basicity.A possibility of non-conventional two-step protonation of 1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene (proton sponge) is there.
Unlike the generally accepted mechanism, involving relatively slow direct penetration of a proton into the cleft between the peri-${ NMe }_{ 2 }$ groups, it consists of the rapid addition of a proton to the out-inverted ${ NMe }_{ 2 }$ group with the subsequent slower rotational transfer of the proton into the inter-nitrogen space to produce a stable chelated cation.
Note: Hyperconjugation also provides a basicity feature but the steric inhibition due to resonance dominates over it and that’s why we are not considering hyperconjugation over here.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




