
How many isomers of the alkene pentene are there?
Answer
552.9k+ views
Hint: Isomers are the chemical structure with the same molecular formula but they are connected differently, these are called “structural isomers”. If we consider pentene which is an olefin it can be arranged in different ways by altering the position of double bond, sometimes positions of carbon and sometimes position of both.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let’s try to figure out that if all five carbon are arranged in a straight line having a double bond at position \[(1)\] then we get something like as we have the first structure in the diagram. So now if we move the double bond to position \[(2)\] then we will get the second isomer of pentene which is called $2 - pentene$ . $2 - pentene$ can be arranged in two types one is when both hydrogens are on same side of the plane and the second one is where two hydrogens are opposite planes. Thus we get the structure \[(2)\] and \[(4)\] . Now if we move the carbon atoms and not the double bond we will get firstly $2 - methyl - 1 - butene$ and $3 - methyl - 1 - butene$ .
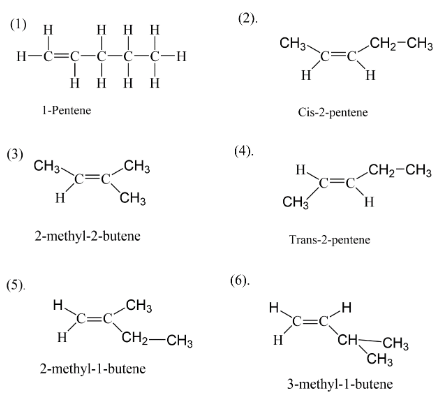
After these structures we get overall a total of five structures. At last when we move both the double bond and carbon atom we get the last isomer of pentene which is $2 - methyl - 2 - butene$ . Thus we at the end have six isomers of pentene.
$1 - pentene$
$cis - 2 - pentene$
$trans - 2 - pentene$
$2 - methyl - 1 - butene$
$3 - methyl - 1 - butene$
$2 - methyl - 2 - butene$
Note: We can make different structures for any hydrocarbon it can be aliphatic (saturated and unsaturated). In both cases we just have to see the different arrangements possible for the structures. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are double bond or triple bond as we have above for pentene. Similarly we can make it for saturated hydrocarbons which have only a single bond all over the compound example propane, butane etc.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let’s try to figure out that if all five carbon are arranged in a straight line having a double bond at position \[(1)\] then we get something like as we have the first structure in the diagram. So now if we move the double bond to position \[(2)\] then we will get the second isomer of pentene which is called $2 - pentene$ . $2 - pentene$ can be arranged in two types one is when both hydrogens are on same side of the plane and the second one is where two hydrogens are opposite planes. Thus we get the structure \[(2)\] and \[(4)\] . Now if we move the carbon atoms and not the double bond we will get firstly $2 - methyl - 1 - butene$ and $3 - methyl - 1 - butene$ .

After these structures we get overall a total of five structures. At last when we move both the double bond and carbon atom we get the last isomer of pentene which is $2 - methyl - 2 - butene$ . Thus we at the end have six isomers of pentene.
$1 - pentene$
$cis - 2 - pentene$
$trans - 2 - pentene$
$2 - methyl - 1 - butene$
$3 - methyl - 1 - butene$
$2 - methyl - 2 - butene$
Note: We can make different structures for any hydrocarbon it can be aliphatic (saturated and unsaturated). In both cases we just have to see the different arrangements possible for the structures. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are double bond or triple bond as we have above for pentene. Similarly we can make it for saturated hydrocarbons which have only a single bond all over the compound example propane, butane etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




