
Is Yeast a Prokaryote?
Answer
489.6k+ views
Hint: Yeast is single celled organism but having higher organisms’ similarity including human’s cell. Yeast has a cell wall and unlike bacteria they do not lack nucleus. Bacteria are being considered as prokaryotes as they lack nucleus. Yeast is a fungi which is a helpful organism especially in the field of baking, wine making, brewing etc.
Complete answer-
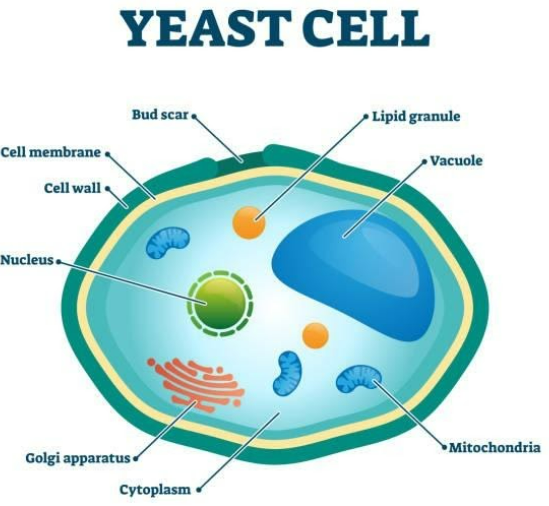
Yeast is- molds. Belonging to the kingdom fungi. Since it has a cell wall and membrane bound organelle hence, it is eukaryote. Yeasts have separate kingdoms called fungi and examples are- sac fungi Basidiomycota and Ascomycota.
Saccharomycetales have ascospores and colonies as well as cellular physiology. Some are single celled and organized to higher organisms. Their genetic content is filled with nuclei. Some single-celled counterparts have bacteria.
Naturally yeasts have habitat in growing soil, and fruits and plant leaves. They are dispersed in nature and also found on the skin surface of some animals. Some species of yeasts are found inside the body of warm-blooded animals. Some may live with a symbiotic relationship with yeasts. Example- Candida albicans. Candida albicans are the major organism for causing vaginal yeast infections.
$31\% $ of yeasts have human genes and rest can cause human diseases from yeast. Yeast cells have either one set of chromosomes and two set of chromosomes which efficiently breaks and join with DNA strands of the mutant.
Note:
Studying yeasts can be beneficial as yeasts grow quickly and DNA being manipulative and possesses a human biological process. Researchers have $50,000$ discovered a species which describes yeasts characteristics in detail. Yeasts grow about $90$ minutes and based on genes the baker’s yeast genome. It is smaller and has $3$ billion base pairs of DNA.
Complete answer-
Yeast is- molds. Belonging to the kingdom fungi. Since it has a cell wall and membrane bound organelle hence, it is eukaryote. Yeasts have separate kingdoms called fungi and examples are- sac fungi Basidiomycota and Ascomycota.
Saccharomycetales have ascospores and colonies as well as cellular physiology. Some are single celled and organized to higher organisms. Their genetic content is filled with nuclei. Some single-celled counterparts have bacteria.
Naturally yeasts have habitat in growing soil, and fruits and plant leaves. They are dispersed in nature and also found on the skin surface of some animals. Some species of yeasts are found inside the body of warm-blooded animals. Some may live with a symbiotic relationship with yeasts. Example- Candida albicans. Candida albicans are the major organism for causing vaginal yeast infections.
$31\% $ of yeasts have human genes and rest can cause human diseases from yeast. Yeast cells have either one set of chromosomes and two set of chromosomes which efficiently breaks and join with DNA strands of the mutant.

Note:
Studying yeasts can be beneficial as yeasts grow quickly and DNA being manipulative and possesses a human biological process. Researchers have $50,000$ discovered a species which describes yeasts characteristics in detail. Yeasts grow about $90$ minutes and based on genes the baker’s yeast genome. It is smaller and has $3$ billion base pairs of DNA.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




