
Is the pith of plants ground tissue?
Answer
487.2k+ views
Hint: Ground tissue in the plants is inclusive of tissues, which are neither vascular nor dermal. The ground tissue system arises from the ground tissue meristem. Based on the nature of the cell walls, the ground tissue is divided into three types, namely, parenchyma, sclerenchyma, and collenchyma. Ground tissue surrounds the pericycle and vascular cylinder.
Complete answer:
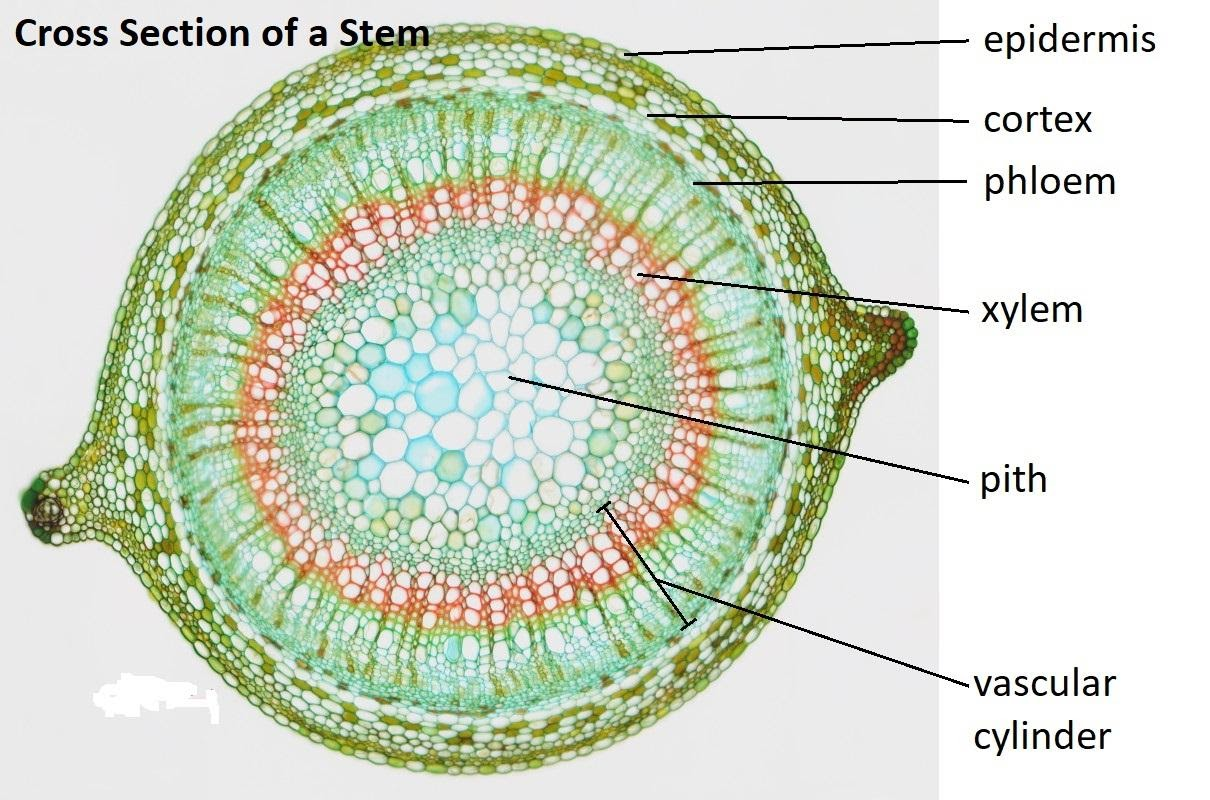
Fig: Internal Anatomy of Stem
As the pith of plants is composed of parenchyma cells, it is ground tissue.
Pith is present in the central portion of the stem. The cells of the pith are rounded in shape, with large intercellular spaces. The cells of the pith, which are present between the vascular bundles, constitute the pith rays, which are otherwise known as medullary rays. As the parenchyma cells are radially arranged in between the bundles, the arrangement provides the appearance of rays. These pith rays aid in the radial conduction of food. Pith offers structure to the stem at the center.
Pith performs storage of food. So the cells are unspecialized since storage is not an active function. The tissue exists and stores different substances. It is the central parenchyma cell in the stem and is primarily used for storage.
In the dicot root, the xylem and phloem form an X-shape at the center of the root, while in the monocot root, the phloem and the xylem form a characteristic ring around the pith. Thus, the center of the monocot root is filled with pith.
Note:
When the ground tissue is present in the root center, it is the pith. At the same time, when the ground tissue is present at the root periphery, it is the cortex. Parenchyma aids in the photosynthesis of leaves and storage in roots. Collenchyma provides support to the shoot in areas of active growth. Sclerenchyma displays support for the shoot in the areas where the growth has ceased.
Complete answer:

Fig: Internal Anatomy of Stem
As the pith of plants is composed of parenchyma cells, it is ground tissue.
Pith is present in the central portion of the stem. The cells of the pith are rounded in shape, with large intercellular spaces. The cells of the pith, which are present between the vascular bundles, constitute the pith rays, which are otherwise known as medullary rays. As the parenchyma cells are radially arranged in between the bundles, the arrangement provides the appearance of rays. These pith rays aid in the radial conduction of food. Pith offers structure to the stem at the center.
Pith performs storage of food. So the cells are unspecialized since storage is not an active function. The tissue exists and stores different substances. It is the central parenchyma cell in the stem and is primarily used for storage.
In the dicot root, the xylem and phloem form an X-shape at the center of the root, while in the monocot root, the phloem and the xylem form a characteristic ring around the pith. Thus, the center of the monocot root is filled with pith.
Note:
When the ground tissue is present in the root center, it is the pith. At the same time, when the ground tissue is present at the root periphery, it is the cortex. Parenchyma aids in the photosynthesis of leaves and storage in roots. Collenchyma provides support to the shoot in areas of active growth. Sclerenchyma displays support for the shoot in the areas where the growth has ceased.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




