
_______is the control centre of the cell.
A. Nucleus
B. Mitochondria
C. Lysosome
D. All of the above
Answer
603k+ views
Hint: It is a membrane-enclosed organelle that contains the majority of the cell’s genetic material.
Complete answer:
The nucleus is known as the control center of the cell because it controls gene expression and facilitates the replication of DNA during the cell cycle. The nucleus is the largest structure of animal cells with an average diameter of 6µm. The nuclear membrane completely encloses the nucleus and is made up of two cellular membranes, an inner and outer membrane. The outer membrane is continuous with the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. The inner membrane is attached to proteins that are precise to the nucleus. The nuclear lamina is a mesh structure that is present on the internal structure of the nucleus. It provides mechanical strength to the nucleus.
The functions of the cell nucleus:
> The nucleus is the important structure of cells that controls all the cellular activities by regulating the enzymes required for cellular processes.
> The nucleus provides a site for transcription of the mRNA to protein.
> In the cell nucleus, genetic material is organized as DNA molecules, along with various proteins to form chromosomes.
> It serves for the storage of DNA, RNA, and ribosomes.
> Post-transcriptional modifications in pre mRNA take place in the cell nucleus, where molecules are added or removed from the mRNA.
> Nuclear envelope separates the genetic material of the cell nucleus from the cytoplasm.
So, the correct answer is ‘nucleus’.
Note:
- The nucleolus is an important part of the nucleus because it is the site of ribosomal RNA production.
- Most of the human cells contain a single nucleus, while there are several cells that have multiple nuclei like osteoclasts.
- Some cells don’t have a nucleus such as erythrocytes.
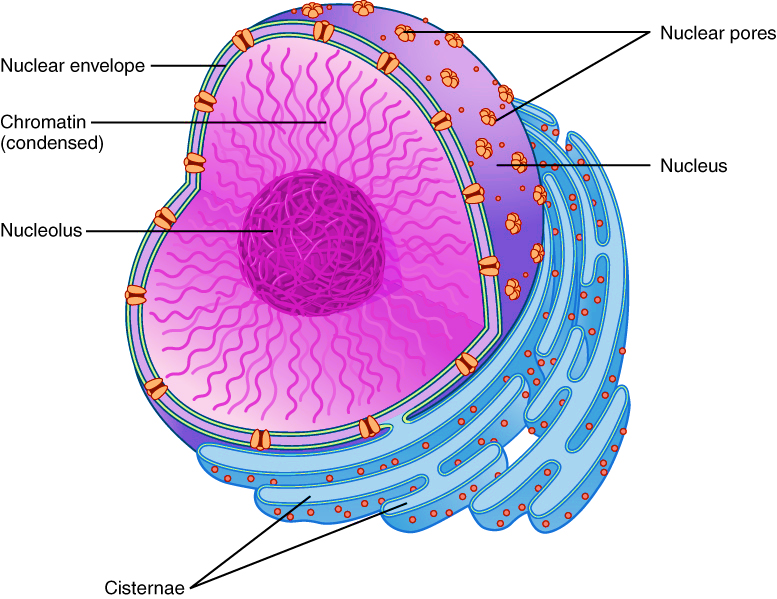
Figure: Structure of the nucleus
Complete answer:
The nucleus is known as the control center of the cell because it controls gene expression and facilitates the replication of DNA during the cell cycle. The nucleus is the largest structure of animal cells with an average diameter of 6µm. The nuclear membrane completely encloses the nucleus and is made up of two cellular membranes, an inner and outer membrane. The outer membrane is continuous with the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. The inner membrane is attached to proteins that are precise to the nucleus. The nuclear lamina is a mesh structure that is present on the internal structure of the nucleus. It provides mechanical strength to the nucleus.
The functions of the cell nucleus:
> The nucleus is the important structure of cells that controls all the cellular activities by regulating the enzymes required for cellular processes.
> The nucleus provides a site for transcription of the mRNA to protein.
> In the cell nucleus, genetic material is organized as DNA molecules, along with various proteins to form chromosomes.
> It serves for the storage of DNA, RNA, and ribosomes.
> Post-transcriptional modifications in pre mRNA take place in the cell nucleus, where molecules are added or removed from the mRNA.
> Nuclear envelope separates the genetic material of the cell nucleus from the cytoplasm.
So, the correct answer is ‘nucleus’.
Note:
- The nucleolus is an important part of the nucleus because it is the site of ribosomal RNA production.
- Most of the human cells contain a single nucleus, while there are several cells that have multiple nuclei like osteoclasts.
- Some cells don’t have a nucleus such as erythrocytes.

Figure: Structure of the nucleus
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




