
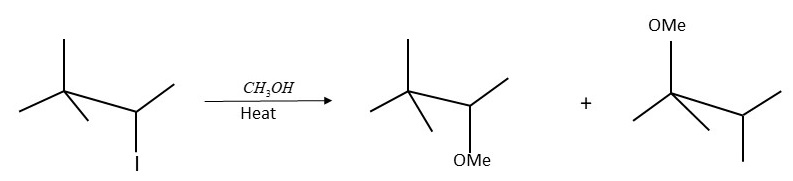
Is the above reaction an example of solvolysis reaction? Give the reason for your answer.

Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Solvolytic reactions are usually substitution reactions - that is, reactions in which one molecule or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms. Solvents form or form electron-rich atoms or groups of atoms (nucleophiles) that displace an atom or group in the substrate molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
-Solvolysis is a type of nucleophilic substitution or elimination where the nucleophile is a solvent molecule. Characterization of $SN_1$ reactions, solvolysis of a chiral reactant, affects the runner.
-Sometimes, however, the stereochemical course is complicated by intimate ion pairs, causing the leaving ion to remain close to carbocation, effectively protecting it from attack by nucleophiles. -Particularly rapid responses may occur by neighboring group participation.
-Solvolysis reactions of the organotin compounds ${R_3}{S_n}Cl$ , where R is ethyl, isopropyl, t-butyl or phenyl groups, have been studied in ethanol, propane-$2$ -ol, and water dioxin solvents.
-In this reaction, the solvent behaves as a nucleophile. Because in this reaction, $C{H_3}OH$ both behave as an atom and a solvent, so it is a solvicesis reaction. Method
-Formation of carbocation.
-Nucleophilic attack
-Deprotonation.
The above example is the Solvolysis reaction in the form of $C{H_3}OH$ acts as both a solvent and a nucleus.
Note: Solvolysis of tri-isopropyl chloride with propane-$2$- ol occurs at a moderate rate, but is much faster than that established for conventional rate measurements in the dioxane and ethanol equilibria in water, and is characterized by trivalent ethyl and trivalent phenyl. Is also true compounds studied in all solvents.
Complete step by step answer:
-Solvolysis is a type of nucleophilic substitution or elimination where the nucleophile is a solvent molecule. Characterization of $SN_1$ reactions, solvolysis of a chiral reactant, affects the runner.
-Sometimes, however, the stereochemical course is complicated by intimate ion pairs, causing the leaving ion to remain close to carbocation, effectively protecting it from attack by nucleophiles. -Particularly rapid responses may occur by neighboring group participation.
-Solvolysis reactions of the organotin compounds ${R_3}{S_n}Cl$ , where R is ethyl, isopropyl, t-butyl or phenyl groups, have been studied in ethanol, propane-$2$ -ol, and water dioxin solvents.
-In this reaction, the solvent behaves as a nucleophile. Because in this reaction, $C{H_3}OH$ both behave as an atom and a solvent, so it is a solvicesis reaction. Method
-Formation of carbocation.
-Nucleophilic attack
-Deprotonation.
The above example is the Solvolysis reaction in the form of $C{H_3}OH$ acts as both a solvent and a nucleus.
Note: Solvolysis of tri-isopropyl chloride with propane-$2$- ol occurs at a moderate rate, but is much faster than that established for conventional rate measurements in the dioxane and ethanol equilibria in water, and is characterized by trivalent ethyl and trivalent phenyl. Is also true compounds studied in all solvents.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




