
Is respiration exergonic or endergonic?
Answer
496.5k+ views
Hint: A type of reaction in which free energy is released is termed as exergonic reaction and indicate that the energy is released in the system and do not require energy to begin while a type of reaction in which free energy is absorbed is termed as endergonic reaction and indicates that the energy is absorbed by the system and require energy to begin.
Complete answer:
Exergonic reaction is a downhill reaction. Some examples areFatty acid catabolism, cellular respiration, and glycolysis.
Endergonic is an uphill reaction. Some examples are DNA/RNA synthesis, protein synthesis, fatty acid synthesis.
Now let us discuss respiration. The word respiration came from the Latin word respirare which means to breath. An energy releasing, enzymatically controlled, catabolic process which involves oxidative breakdown of organic substances in a stepwise manner inside living cells is called cellular respiration. The energy needed by the cells is obtained through cellular respiration. About Kcal or 204 KJ of energy is released for each molecule of oxygen, used in respiration. This energy is then used to synthesize 6 molecules of ATP. It releases energy in steps, each step is coupled with the synthesis of ATP. Only a small amount of energy dissipates as heat.
Therefore, we say that the cellular respiration is an exergonic process because in this the energy is released.
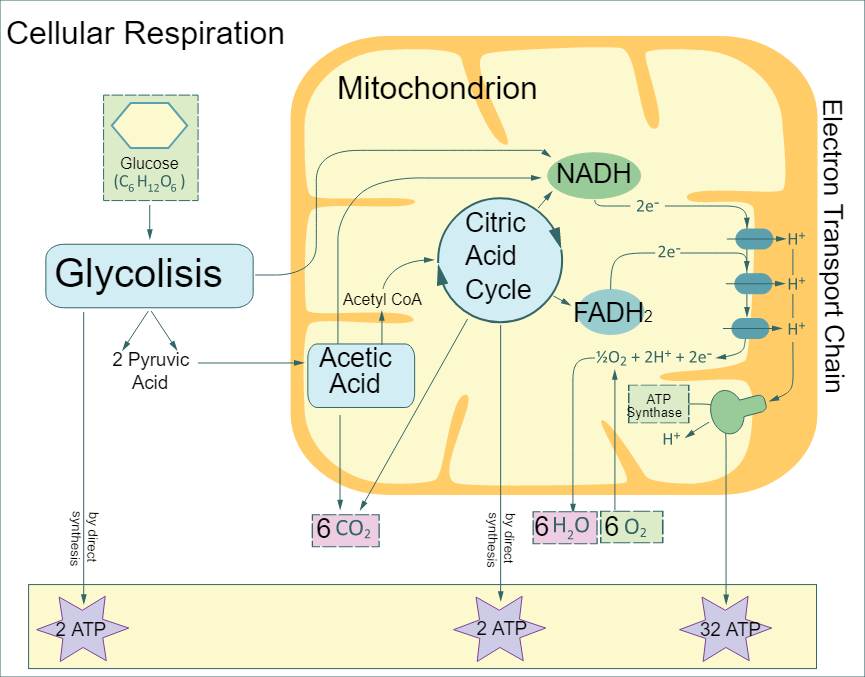
The process of respiration can be seen in the below figure.
Note:
Cellular respiration are of two types:
1. Aerobic respiration: The organic food is completely oxidized with the help of oxygen into carbon dioxide and water. It occurs in mitochondria.
2. Anaerobic respiration: The organic food is not completely oxidized without oxygen being used as an oxidant. It occurs in cytoplasm and releases a small amount of energy.
Complete answer:
Exergonic reaction is a downhill reaction. Some examples areFatty acid catabolism, cellular respiration, and glycolysis.
Endergonic is an uphill reaction. Some examples are DNA/RNA synthesis, protein synthesis, fatty acid synthesis.
Now let us discuss respiration. The word respiration came from the Latin word respirare which means to breath. An energy releasing, enzymatically controlled, catabolic process which involves oxidative breakdown of organic substances in a stepwise manner inside living cells is called cellular respiration. The energy needed by the cells is obtained through cellular respiration. About Kcal or 204 KJ of energy is released for each molecule of oxygen, used in respiration. This energy is then used to synthesize 6 molecules of ATP. It releases energy in steps, each step is coupled with the synthesis of ATP. Only a small amount of energy dissipates as heat.
Therefore, we say that the cellular respiration is an exergonic process because in this the energy is released.
The process of respiration can be seen in the below figure.

Note:
Cellular respiration are of two types:
1. Aerobic respiration: The organic food is completely oxidized with the help of oxygen into carbon dioxide and water. It occurs in mitochondria.
2. Anaerobic respiration: The organic food is not completely oxidized without oxygen being used as an oxidant. It occurs in cytoplasm and releases a small amount of energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




