
Is E. coli a eukaryotic?
Answer
509.4k+ views
Hint: Cells are broadly classified into two main types- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic.
A prokaryotic cell is the one which lacks most of the membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria, Golgi body, etc. and lacks a proper membrane-bound nucleus. This is a primitive type of cell common among bacteria and most unicellular organisms.
A eukaryotic cell has a well-organized membrane-bound nucleus and has advanced cell organelles like ER, Golgi body, lysosomes, etc.
Complete answer:
When we see the structure of E. coli, to identify the type of cell, we observe some identifiable features:
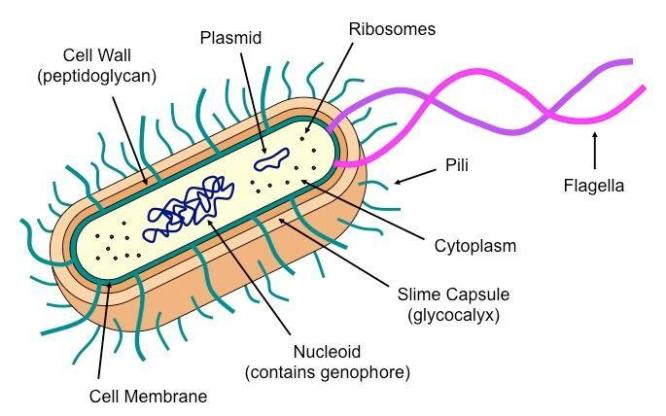
A prokaryotic cell diagram
The organism does not contain a distinct membrane-bound nucleus. Rather, the genetic material just floats over the cytoplasm of the cell.
Most of the organelles like the ER (Endoplasmic reticulum), Golgi body, mitochondria, lysosomes, etc. are absent.
This is enough to prove that E. coli is a prokaryotic cell, and not a eukaryote.
Now, the cell has some unique features too. Some of them are:
In addition to the genomic DNA, some strains of the bacterium may contain a small circular DNA called plasmid outside the DNA. The plasmid confers some special properties to the cell. The presence or absence of a plasmid does not have any effect on the activities of the cell. Like the ‘pili’ in E. coli is due to the presence of $F^+$ plasmid (fertility plasmid).
The cell locomotes with the help of flagella.
This organism is a common habitant in the human alimentary system (in the colon portion) where it acts as a symbiont; it draws nutrition from humans and as a reward synthesizes vitamin K for the body.
Note:
Nowadays, many biologists often consider E. coli as an organism in between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Some scientists even claim that the organism contains eukaryotic genes. But this research is an ongoing thing and no such fact has been established firmly. So, based on the characteristics, E. coli is a prokaryotic organism.
A prokaryotic cell is the one which lacks most of the membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria, Golgi body, etc. and lacks a proper membrane-bound nucleus. This is a primitive type of cell common among bacteria and most unicellular organisms.
A eukaryotic cell has a well-organized membrane-bound nucleus and has advanced cell organelles like ER, Golgi body, lysosomes, etc.
Complete answer:
When we see the structure of E. coli, to identify the type of cell, we observe some identifiable features:

A prokaryotic cell diagram
The organism does not contain a distinct membrane-bound nucleus. Rather, the genetic material just floats over the cytoplasm of the cell.
Most of the organelles like the ER (Endoplasmic reticulum), Golgi body, mitochondria, lysosomes, etc. are absent.
This is enough to prove that E. coli is a prokaryotic cell, and not a eukaryote.
Now, the cell has some unique features too. Some of them are:
In addition to the genomic DNA, some strains of the bacterium may contain a small circular DNA called plasmid outside the DNA. The plasmid confers some special properties to the cell. The presence or absence of a plasmid does not have any effect on the activities of the cell. Like the ‘pili’ in E. coli is due to the presence of $F^+$ plasmid (fertility plasmid).
The cell locomotes with the help of flagella.
This organism is a common habitant in the human alimentary system (in the colon portion) where it acts as a symbiont; it draws nutrition from humans and as a reward synthesizes vitamin K for the body.
Note:
Nowadays, many biologists often consider E. coli as an organism in between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Some scientists even claim that the organism contains eukaryotic genes. But this research is an ongoing thing and no such fact has been established firmly. So, based on the characteristics, E. coli is a prokaryotic organism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




