
Why is iodine a better leaving group than other halogen atoms?
A. Due to its small size.
B. Due to its large size.
C. Due to its least electronegativity.
D.Due to its more electro positivity.
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: There are two kinds of substitution reactions. One is a nucleophilic substitution reaction and the other is an electrophilic substitution reaction. In the case of substitution of alkyl halide, the halide ion is the leaving group for the substitution reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
The leaving ability of the halide depends upon the \[C - X\] bond strength. The higher the bond stability of the \[C - X\] bond, the lower will be the leaving ability of the halide. In the case of halogen from fluorine to iodine size increases, therefore, the bond stability with the carbon decreases as with the increasing size of the halide the overlap of orbital decreases.
Therefore, in the case of iodine due to large size, the \[C - I\] bond stability decreases, and iodine becomes a very good leaving group than other halogen atoms.
So the correct option is B.
Additional information:
In the case of nucleophilic substitution reactions, there are mainly two kinds of substitution reactions: one is \[S{N^1}\] another one is \[S{N^2}\]. Where 1 and 2 stand for the order of the reaction. Where the \[S{N^1}\] reaction rate depends upon the carbocation stability, which is formed from the alkyl halide, and \[S{N^2}\] the reaction rate depends upon the steric hindrance of the backside of the alkyl halide.
There is a graph representation of the order of rate of the reaction with the substrate of nucleophilic substitution reaction.
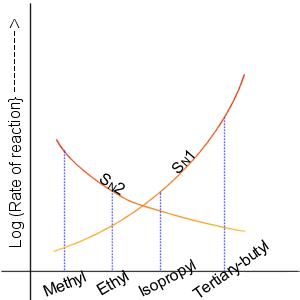
Note:
The \[S{N^2}\] reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction where one bond is broken, and another is formed simultaneously. The two reacting species are involved in the rate-determining step of the reaction. In the case of \[S{N^1}\] in the rate-determining step, carbocation is formed. only one reacting species is involved in the rate-determining step that is why it is a 1st order reaction. Substitution nucleophilic by the molecular reaction is also referred to as associative substitution and interchange mechanism.
Complete step by step answer:
The leaving ability of the halide depends upon the \[C - X\] bond strength. The higher the bond stability of the \[C - X\] bond, the lower will be the leaving ability of the halide. In the case of halogen from fluorine to iodine size increases, therefore, the bond stability with the carbon decreases as with the increasing size of the halide the overlap of orbital decreases.
Therefore, in the case of iodine due to large size, the \[C - I\] bond stability decreases, and iodine becomes a very good leaving group than other halogen atoms.
So the correct option is B.
Additional information:
In the case of nucleophilic substitution reactions, there are mainly two kinds of substitution reactions: one is \[S{N^1}\] another one is \[S{N^2}\]. Where 1 and 2 stand for the order of the reaction. Where the \[S{N^1}\] reaction rate depends upon the carbocation stability, which is formed from the alkyl halide, and \[S{N^2}\] the reaction rate depends upon the steric hindrance of the backside of the alkyl halide.
There is a graph representation of the order of rate of the reaction with the substrate of nucleophilic substitution reaction.

Note:
The \[S{N^2}\] reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction where one bond is broken, and another is formed simultaneously. The two reacting species are involved in the rate-determining step of the reaction. In the case of \[S{N^1}\] in the rate-determining step, carbocation is formed. only one reacting species is involved in the rate-determining step that is why it is a 1st order reaction. Substitution nucleophilic by the molecular reaction is also referred to as associative substitution and interchange mechanism.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




