
Interphase is also called the resting phase because
A. Cell division is stopped
B. Cell is metabolically active
C. No visible changes occur in the nucleus
D. Cell does not grow
Answer
520.5k+ views
Hint: Interphase is a part of the cell cycle where the cell grows but there are no visible changes microscopically, this is the preparatory phase just before mitosis.
Complete answer:
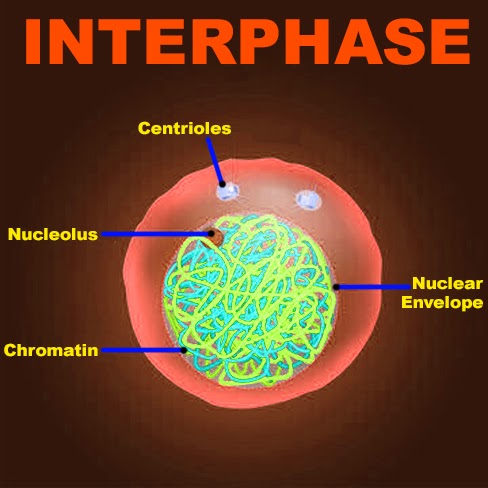
Interphase: The cell cycle is divided into two parts in the interphase and the mitotic phase. This portion of the cell cycle shows no observable changes under the microscope. The interphase is further composed of G1, S, and G2 phases. In the interphase, a cell prepares itself for mitosis by growing in size metabolically active and doing its day to day functions, since this is not an actively dividing state it is also called the resting phase of the cell.
In the interphase the cell systematically prepares itself for cell division:
G1 phase: This is also called the Gap1 phase. This phase mainly consists of protein synthesis and growth in cell size. This growth is an increase in the number of cell organelles and an increase in the volume of the cytoplasm .
S Phase: This is also called the synthesis phase. This phase concentrates all its energy on DNA doubling. Here the DNA is doubled but the number of chromosomes remains the same.
G2 Phase: This is also called the gap phase. Here the cell resumes cell growth and prepares for cell division. Mitochondria and chloroplast divide during this phase.
So, the correct answer is option c, ‘no visible changes occur in the nucleus’.
Note:
A cell in interphase is different from a cell in quiescent stage, this is also called a state of dormancy of the cells, but it is a is misleading term since a quiescent cell doesn’t halt metabolism, instead it is synthesizing proteins, transcription of DNA, engulfing extracellular material for food or defense, processing stimulus, etc. The cell is quiescent or dormant only with respect to cell division.
Complete answer:
Interphase: The cell cycle is divided into two parts in the interphase and the mitotic phase. This portion of the cell cycle shows no observable changes under the microscope. The interphase is further composed of G1, S, and G2 phases. In the interphase, a cell prepares itself for mitosis by growing in size metabolically active and doing its day to day functions, since this is not an actively dividing state it is also called the resting phase of the cell.
In the interphase the cell systematically prepares itself for cell division:
G1 phase: This is also called the Gap1 phase. This phase mainly consists of protein synthesis and growth in cell size. This growth is an increase in the number of cell organelles and an increase in the volume of the cytoplasm .
S Phase: This is also called the synthesis phase. This phase concentrates all its energy on DNA doubling. Here the DNA is doubled but the number of chromosomes remains the same.
G2 Phase: This is also called the gap phase. Here the cell resumes cell growth and prepares for cell division. Mitochondria and chloroplast divide during this phase.
So, the correct answer is option c, ‘no visible changes occur in the nucleus’.

Note:
A cell in interphase is different from a cell in quiescent stage, this is also called a state of dormancy of the cells, but it is a is misleading term since a quiescent cell doesn’t halt metabolism, instead it is synthesizing proteins, transcription of DNA, engulfing extracellular material for food or defense, processing stimulus, etc. The cell is quiescent or dormant only with respect to cell division.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




