
Intermolecular forces determine the state of matter for substance. All of the following substances are gases at room temperature and pressure. Which of the following compounds contains the weakest intermolecular forces?
A) Ethane $\left( {C{H_3}C{H_3}} \right)$
B) Nitrogen trifluoride.
C) Sulfur dioxide.
D) Ammonia.
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint: We know that,
Molecules in liquids are held together by intermolecular interactions, which are weaker than the intramolecular interactions that hold the atoms together within molecules and polyatomic ions. Higher the intermolecular forces are higher the melting and boiling point.
The three major types of intermolecular interactions are,
1.Dipole-dipole interactions
2.London dispersion forces
3.Hydrogen bonds
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of $N{F_3}$ is,
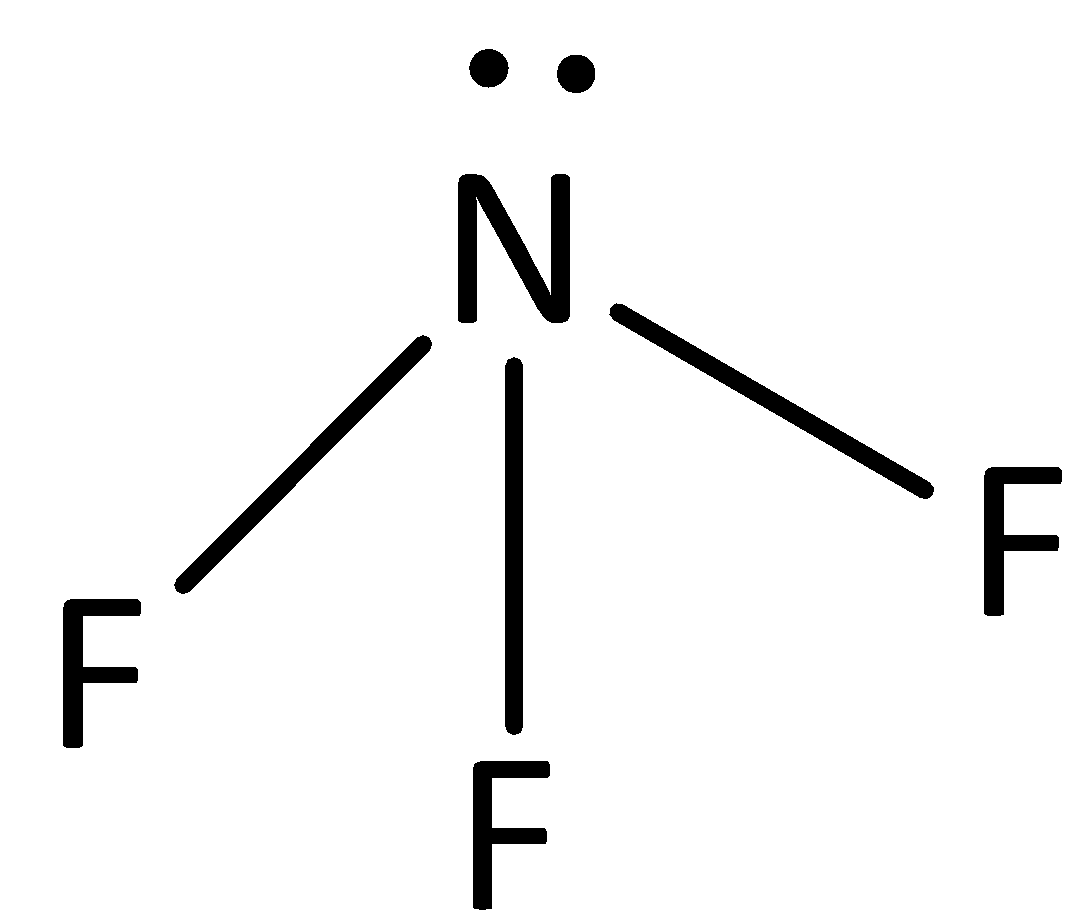
The electronegativity of fluorine is high and the nitrogen-fluorine bonds are polarized such that a partial negative charge accumulates on the fluorine atom and a partial positive charge is found on the nitrogen atom. The interaction between nitrogen and fluoride is dipole-dipole interaction.
Therefore, the option B is incorrect.
The structure of ammonia is,
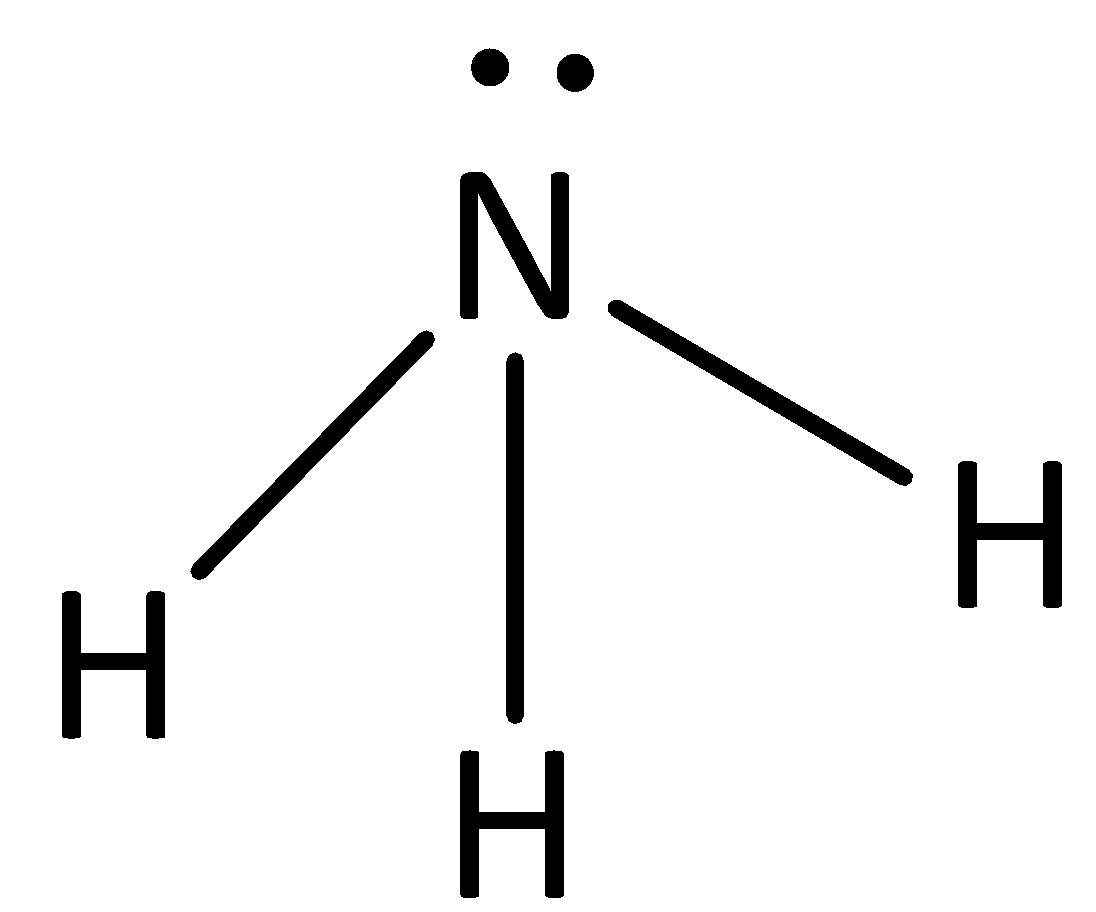
In ammonia there is a hydrogen bond between nitrogen and hydrogen.
Therefore, option D is incorrect.
Sulfur Dioxide is a nonpolar molecule. Therefore it will hold weak London Dispersion forces in which immediate dipoles are formed in the atoms and between the molecules due to the amount of electrons.
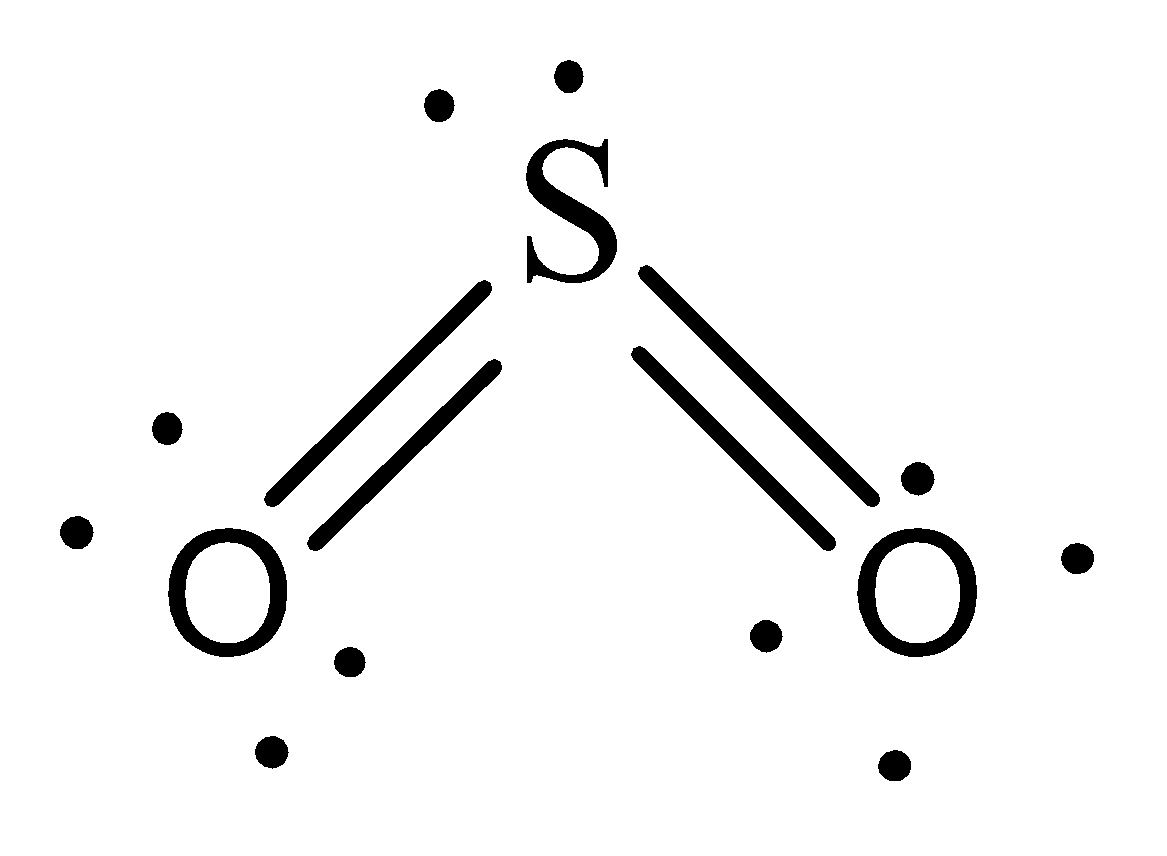
Therefore, the option C is incorrect.
Ethane has the weakest intermolecular force because it is a nonpolar molecule and has only dispersion forces.
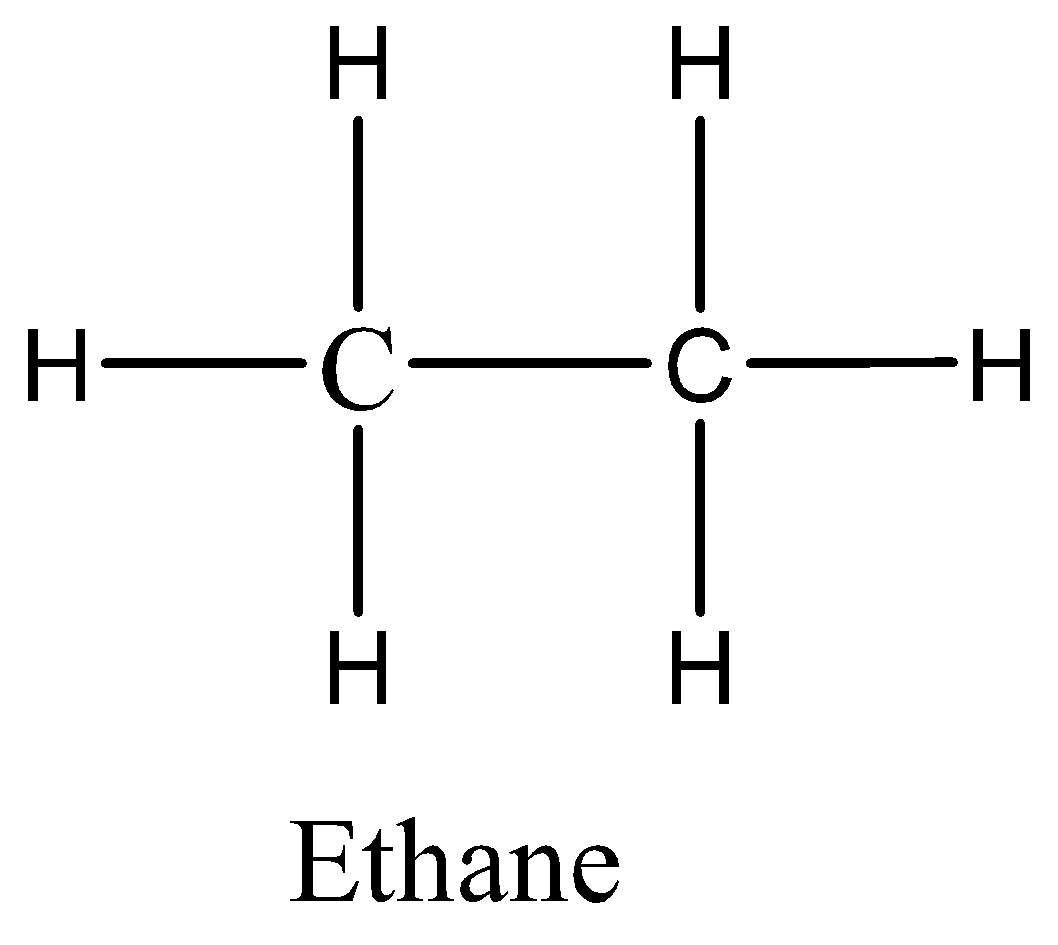
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Note: Let us discuss the hydrogen bond in detail.
In a molecule, when an atom is linked to a highly electronegative atom, it attracts the shared pair of electrons more so it becomes a slightly negative end while the opposite end becomes slightly positive. The negative end of the molecule attracts the positive end of the opposite and as a result, a weak bond is made between them. This bond is named a hydrogen bond.
There are two types of the hydrogen bond. They are,
1.Intermolecular hydrogen bond.
2.Intramolecular Hydrogen bond.
Molecules in liquids are held together by intermolecular interactions, which are weaker than the intramolecular interactions that hold the atoms together within molecules and polyatomic ions. Higher the intermolecular forces are higher the melting and boiling point.
The three major types of intermolecular interactions are,
1.Dipole-dipole interactions
2.London dispersion forces
3.Hydrogen bonds
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of $N{F_3}$ is,

The electronegativity of fluorine is high and the nitrogen-fluorine bonds are polarized such that a partial negative charge accumulates on the fluorine atom and a partial positive charge is found on the nitrogen atom. The interaction between nitrogen and fluoride is dipole-dipole interaction.
Therefore, the option B is incorrect.
The structure of ammonia is,

In ammonia there is a hydrogen bond between nitrogen and hydrogen.
Therefore, option D is incorrect.
Sulfur Dioxide is a nonpolar molecule. Therefore it will hold weak London Dispersion forces in which immediate dipoles are formed in the atoms and between the molecules due to the amount of electrons.

Therefore, the option C is incorrect.
Ethane has the weakest intermolecular force because it is a nonpolar molecule and has only dispersion forces.

Therefore, the correct option is A.
Note: Let us discuss the hydrogen bond in detail.
In a molecule, when an atom is linked to a highly electronegative atom, it attracts the shared pair of electrons more so it becomes a slightly negative end while the opposite end becomes slightly positive. The negative end of the molecule attracts the positive end of the opposite and as a result, a weak bond is made between them. This bond is named a hydrogen bond.
There are two types of the hydrogen bond. They are,
1.Intermolecular hydrogen bond.
2.Intramolecular Hydrogen bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




