
What intermolecular forces are present in $ C{H_4} $ ?
Answer
532.2k+ views
Hint :Intermolecular forces refer to those forces that mediate interaction between the molecules and they include forces of attraction and repulsion which are supposed to act between the atoms or other neighbouring particles like atoms or ions. Different types of intermolecular forces include ionic bonds, Vander Waals dipole-dipole interaction, hydrogen bonding and Vander Waals dispersion forces.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The structure of $ C{H_4} $ is demonstrated below:
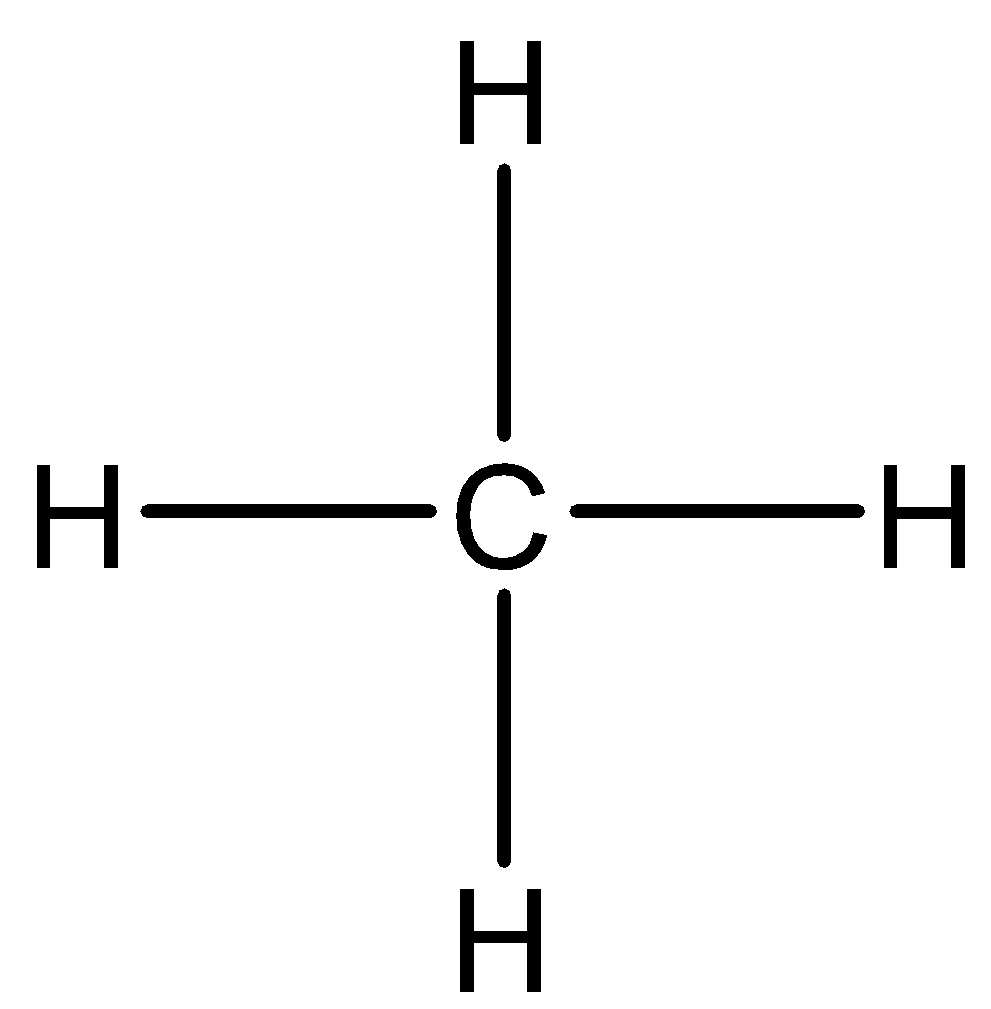
Let us look at different intermolecular forces one by one and find out which kind of forces are present in $ C{H_4} $ .
The weakest kind of intermolecular forces are Van Der Waals dispersion forces (temporary attractive forces) in which positive charge attracts electrons in an adjacent molecule. As we already know that when atoms or molecules are polarizable to a certain degree, some interactions (Vander Waals dispersion forces) occur from them when they are brought together as electrons are pushed about. All atoms and molecules possess these Van der Waals forces, so these forces are also present in $ C{H_4} $ .
Dipole-dipole interactions are present between the polar molecules. All of the outer atoms are the same with respect to the same dipoles and thus, dipole moments are in the similar direction i.e. towards the carbon atom making the overall molecule of methane $ C{H_4} $ as non-polar. As a result, methane comprises non-polar bonds, and is considered to be non-polar. Thus, $ C{H_4} $ does not possess dipole-dipole interaction.
Hydrogen bonding occurs in those molecules where hydrogen atom is bonded to any of the three most electronegative atoms (which include $ N $ , $ O $ or $ F $ ) such that hydrogen atom possess partial positive charge, and also a lone pair of electron must be present on the electronegative atom. Although $ C{H_4} $ contains four $ H $ atoms, hydrogen bonding is not present in $ C{H_4} $ as hydrogen is not bonded to $ N $ , $ O $ or $ F $ . The electronegativity of $ C $ ( $ 2.6 $ ) and $ H $ ( $ 2.2 $ ) are so close that $ C - H $ bonds are nonpolar and thus, no hydrogen bonding is observed in $ C{H_4} $ .
Hence, Vander Waals dispersion forces are found in $ C{H_4} $ .
Note :
Vander Waals dispersion forces are stronger in molecules which are not compact, but possess long chains of elements. The reason is that it is more convenient and easier to displace the electrons as the forces of attraction between electrons and the protons in the nucleus are weaker.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The structure of $ C{H_4} $ is demonstrated below:

Let us look at different intermolecular forces one by one and find out which kind of forces are present in $ C{H_4} $ .
The weakest kind of intermolecular forces are Van Der Waals dispersion forces (temporary attractive forces) in which positive charge attracts electrons in an adjacent molecule. As we already know that when atoms or molecules are polarizable to a certain degree, some interactions (Vander Waals dispersion forces) occur from them when they are brought together as electrons are pushed about. All atoms and molecules possess these Van der Waals forces, so these forces are also present in $ C{H_4} $ .
Dipole-dipole interactions are present between the polar molecules. All of the outer atoms are the same with respect to the same dipoles and thus, dipole moments are in the similar direction i.e. towards the carbon atom making the overall molecule of methane $ C{H_4} $ as non-polar. As a result, methane comprises non-polar bonds, and is considered to be non-polar. Thus, $ C{H_4} $ does not possess dipole-dipole interaction.
Hydrogen bonding occurs in those molecules where hydrogen atom is bonded to any of the three most electronegative atoms (which include $ N $ , $ O $ or $ F $ ) such that hydrogen atom possess partial positive charge, and also a lone pair of electron must be present on the electronegative atom. Although $ C{H_4} $ contains four $ H $ atoms, hydrogen bonding is not present in $ C{H_4} $ as hydrogen is not bonded to $ N $ , $ O $ or $ F $ . The electronegativity of $ C $ ( $ 2.6 $ ) and $ H $ ( $ 2.2 $ ) are so close that $ C - H $ bonds are nonpolar and thus, no hydrogen bonding is observed in $ C{H_4} $ .
Hence, Vander Waals dispersion forces are found in $ C{H_4} $ .
Note :
Vander Waals dispersion forces are stronger in molecules which are not compact, but possess long chains of elements. The reason is that it is more convenient and easier to displace the electrons as the forces of attraction between electrons and the protons in the nucleus are weaker.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




