
Interfascicular cambium develops from the cells of
(a)Xylem parenchyma
(b)Endodermis
(c) Medullary rays
(d)None of the above
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: The cells of this part are parenchymatous and help in the lateral conduction of substances like water and minerals. They lie between vascular bundles and contribute towards secondary growth.
Complete answer:
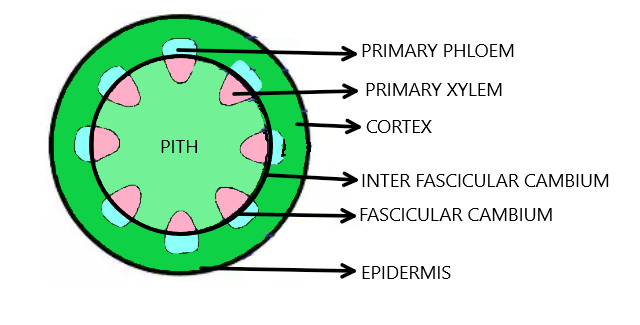
Interfascicular cambium develops from the cells of medullary rays. At the time of secondary growth, cells of medullary rays, in a line with intra-fascicular cambium become meristematic and form interfascicular cambium.
Additional Information: Intrafascicular cambium, interfascicular cambium, and cork cambium constitute primary meristem. Intrafascicular cambium is present in f dicot stem’s vascular bundle. It is present within that of the primary xylem and primary phloem. As the meristems are derived from the embryonic meristems, they are called primary meristems. It is present in the plantain the earlier stage itself and so it is named to be as the primary meristems. It produces primary xylem on the inner side and primary phloem on the outer side. When secondary growth takes place, the parenchyma cells lying in between the vascular bundles, at the level of intrafascicular cambium, undergo dedifferentiation and by divisions and divisions form interfascicular cambium ( I.e in between the intrafascicular cambia of vascular bundles ). Both inter and intrafascicular cambia join together to form a continuous ring of vascular cambium which starts showing its activity. I. e it will form a secondary phloem is formed outside making the other form inside.
So, the correct answer is, “ medullary rays.”
Note: -Fascicular cambium is derived from the pro-meristem and is present between xylem and phloem
of the vascular bundle. It is the primary meristem.
-Interfascicular cambium is derived from the permanent tissue and is present in vascular bundles. It is a secondary meristem.
Complete answer:
Interfascicular cambium develops from the cells of medullary rays. At the time of secondary growth, cells of medullary rays, in a line with intra-fascicular cambium become meristematic and form interfascicular cambium.
Additional Information: Intrafascicular cambium, interfascicular cambium, and cork cambium constitute primary meristem. Intrafascicular cambium is present in f dicot stem’s vascular bundle. It is present within that of the primary xylem and primary phloem. As the meristems are derived from the embryonic meristems, they are called primary meristems. It is present in the plantain the earlier stage itself and so it is named to be as the primary meristems. It produces primary xylem on the inner side and primary phloem on the outer side. When secondary growth takes place, the parenchyma cells lying in between the vascular bundles, at the level of intrafascicular cambium, undergo dedifferentiation and by divisions and divisions form interfascicular cambium ( I.e in between the intrafascicular cambia of vascular bundles ). Both inter and intrafascicular cambia join together to form a continuous ring of vascular cambium which starts showing its activity. I. e it will form a secondary phloem is formed outside making the other form inside.
So, the correct answer is, “ medullary rays.”
Note: -Fascicular cambium is derived from the pro-meristem and is present between xylem and phloem
of the vascular bundle. It is the primary meristem.
-Interfascicular cambium is derived from the permanent tissue and is present in vascular bundles. It is a secondary meristem.

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




