
What is Inorganic Benzene? Why is it so called? How will you get it from Diborane?
Answer
512.4k+ views
Hint: Let us get some idea about the inorganic compound. In chemistry, an inorganic compound is a chemical compound that does not contain carbon–hydrogen bonds, i.e., one that is not an organic compound. The distinction, however, is not well defined, and authorities have various opinions on the matter. Inorganic chemistry is a branch of science that studies inorganic substances.
Complete answer:
Inorganic benzene is borazole ( $ {B_3}{N_3}{H_6} $ ) or borazine ( $ {B_3}{N_3}{H_6} $ ). Because the structure of borazine is similar to that of benzene, it is also known as. With benzene, it is also isoelectronic and isosteric.
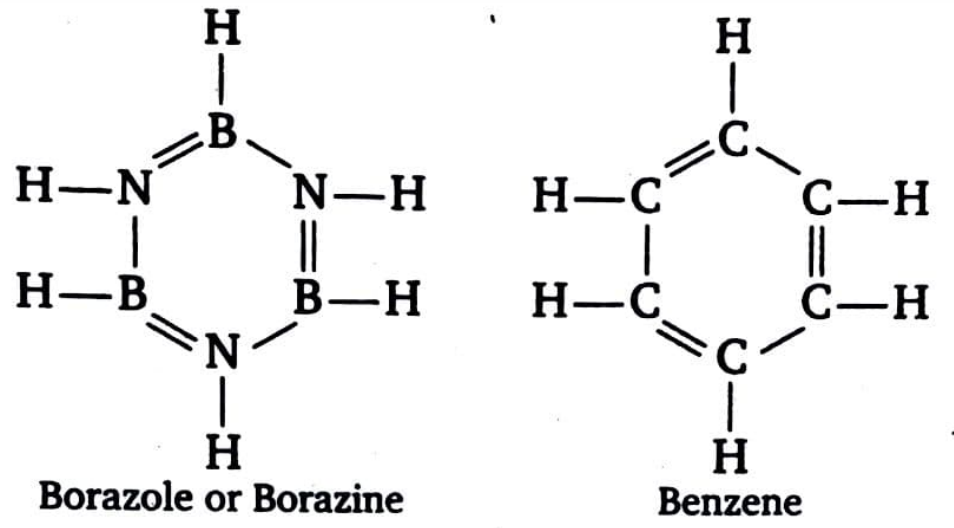
Both N and B in borazine are $ s{p^2} $ hybridised, just as carbon in benzene. Each N has a p-orbital with a lone pair of electrons that is perpendicular to the a-bonding orbitals. Each B, on the other hand, has an empty p-orbitals that is also perpendicular to the ring plane. As a result, borazine's x-bonding is dative, arising from the lateral overlap of fully filled N orbitals and vacant p-orbitals of B.
Borazine is made by combining diborane with ammonia at low temperatures to generate an additional product. When heated to $ 473{\text{ }}K $ , this additional compound decomposes into the volatile chemical borazine.
$ 3{B_2}{H_6} \cdot 2N{H_3}\xrightarrow{{473K}}2{B_3}{N_3}{H_6} + 12{H_2} $
Note:
The main distinction between borazine and benzene is that the ring structure of borazine has three boron atoms and three nitrogen atoms, whereas the ring structure of benzene has six carbon atoms. That is, borazine and benzene have the same number of electrons or electronic structure.
Complete answer:
Inorganic benzene is borazole ( $ {B_3}{N_3}{H_6} $ ) or borazine ( $ {B_3}{N_3}{H_6} $ ). Because the structure of borazine is similar to that of benzene, it is also known as. With benzene, it is also isoelectronic and isosteric.

Both N and B in borazine are $ s{p^2} $ hybridised, just as carbon in benzene. Each N has a p-orbital with a lone pair of electrons that is perpendicular to the a-bonding orbitals. Each B, on the other hand, has an empty p-orbitals that is also perpendicular to the ring plane. As a result, borazine's x-bonding is dative, arising from the lateral overlap of fully filled N orbitals and vacant p-orbitals of B.
Borazine is made by combining diborane with ammonia at low temperatures to generate an additional product. When heated to $ 473{\text{ }}K $ , this additional compound decomposes into the volatile chemical borazine.
$ 3{B_2}{H_6} \cdot 2N{H_3}\xrightarrow{{473K}}2{B_3}{N_3}{H_6} + 12{H_2} $
Note:
The main distinction between borazine and benzene is that the ring structure of borazine has three boron atoms and three nitrogen atoms, whereas the ring structure of benzene has six carbon atoms. That is, borazine and benzene have the same number of electrons or electronic structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




