
How can inductive and hyperconjugation effects explain the stability of primary, secondary and tertiary carbocation?
Answer
486k+ views
Hint: Those species in which a carbon atom is having positive charge are known as carbocations. In these species there is a deficiency of electrons and has planar structure. Carbocations are of three types:
Primary carbocation $\left( {{1^ \circ }} \right)$
Secondary carbocation $\left( {{2^ \circ }} \right)$
Tertiary carbocation $\left( {{3^ \circ }} \right)$
Complete answer:
These compounds have positively charged carbon atoms. In other words, carbon atoms consist of a positive charge and have three bonds. In simple words, they are carbon cations. Nowadays, it is explained as any even-electron cation which has a remarkable positive charge on the carbon atom.
There are two main norms for the stability of the carbocation which are the inductive effect and the second is hyperconjugation effect.
Inductive effect $\left( { + I} \right)$: Some compounds have a tendency to donate their electrons, this tendency to donate is termed as inductive effect. Alkyl groups have positive inductive effects. Thus, in tertiary carbocations, they have three alkyl groups that apply the $ + I$ effect while secondary carbocations consist of two alkyl groups. Therefore tertiary is more stable than secondary and secondary is more stable than primary.
${3^ \circ }\,carbocation \succ {2^ \circ }\,carbocation \succ {1^ \circ }\;carbocation$
Hyperconjugation effect: in this effect, there is delocalization of electrons taking place with the participation of $\sigma $ bonds. Alternatively known as sigma bond resonance. The stability of carbocation is directly proportional to hyperconjugation. The more hyperconjugation, the more will be the stability of carbocation.
In tertiary carbocation:
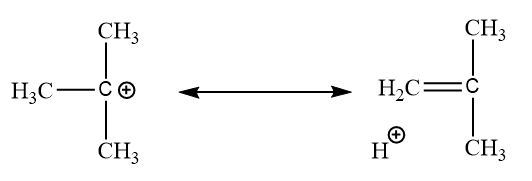
Here this type of hyperconjugation can have a total of nine structures.
In secondary carbocation:
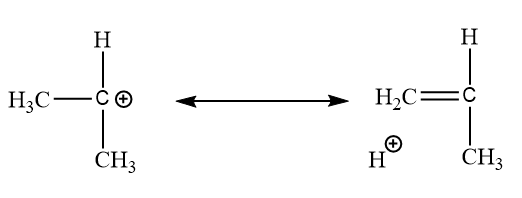
In this type of sigma bond resonance, there are only six structures.
Thus, tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary and secondary carbocation is more stable than primary.
Note:
Tertiary carbocations consist of three alkyl groups whereas secondary carbocation is those which have two alkyl groups. Primary carbocation has only one type of carbocation that is methyl carbocation which does not contain an alkyl group that can be attached to the carbocation.
Primary carbocation $\left( {{1^ \circ }} \right)$
Secondary carbocation $\left( {{2^ \circ }} \right)$
Tertiary carbocation $\left( {{3^ \circ }} \right)$
Complete answer:
These compounds have positively charged carbon atoms. In other words, carbon atoms consist of a positive charge and have three bonds. In simple words, they are carbon cations. Nowadays, it is explained as any even-electron cation which has a remarkable positive charge on the carbon atom.
There are two main norms for the stability of the carbocation which are the inductive effect and the second is hyperconjugation effect.
Inductive effect $\left( { + I} \right)$: Some compounds have a tendency to donate their electrons, this tendency to donate is termed as inductive effect. Alkyl groups have positive inductive effects. Thus, in tertiary carbocations, they have three alkyl groups that apply the $ + I$ effect while secondary carbocations consist of two alkyl groups. Therefore tertiary is more stable than secondary and secondary is more stable than primary.
${3^ \circ }\,carbocation \succ {2^ \circ }\,carbocation \succ {1^ \circ }\;carbocation$
Hyperconjugation effect: in this effect, there is delocalization of electrons taking place with the participation of $\sigma $ bonds. Alternatively known as sigma bond resonance. The stability of carbocation is directly proportional to hyperconjugation. The more hyperconjugation, the more will be the stability of carbocation.
In tertiary carbocation:

Here this type of hyperconjugation can have a total of nine structures.
In secondary carbocation:

In this type of sigma bond resonance, there are only six structures.
Thus, tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary and secondary carbocation is more stable than primary.
Note:
Tertiary carbocations consist of three alkyl groups whereas secondary carbocation is those which have two alkyl groups. Primary carbocation has only one type of carbocation that is methyl carbocation which does not contain an alkyl group that can be attached to the carbocation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




