
In YDSC there is a point P on the screen. What is path difference at point P. Given $d = 1mm, y = 2mm, D = 1m$
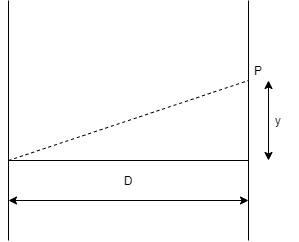

Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: The path difference is defined as the difference in the distance traveled by the two waves from their source to a given point. In this figure, if we consider O as the point of origin for the two waves, the path difference is given by,
$P.D = OP - D$
Complete step by step answer:
Consider Young’s double-slit experiment as shown in the above figure
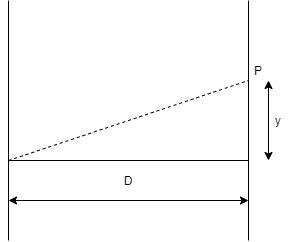
We see in this given figure that there is no presence of the slits as the dotted line at P actually, represents the path difference. By writing the actual figure denoting the two slits and the two wavefronts individually, we get a modified diagram like this,
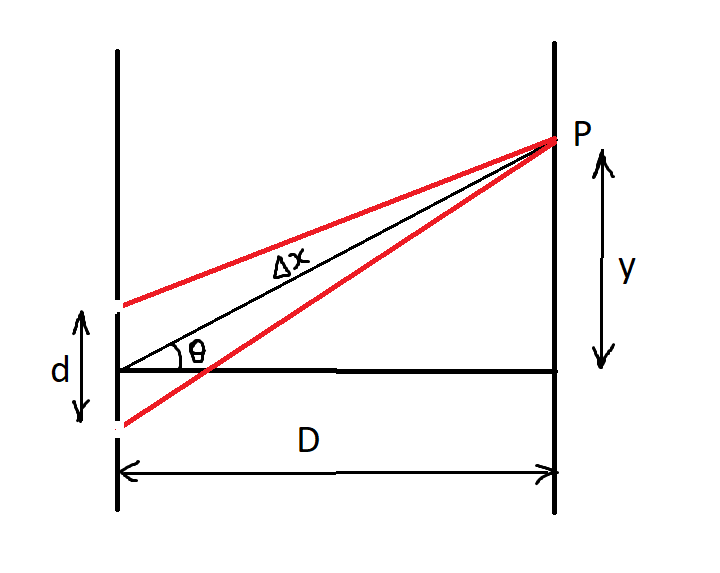
$\theta $ is the angle between the path difference and the horizontal reference line as shown.
The path difference, $\Delta x = d\sin \theta $
Since the angle $\theta $ is very small, we can say that, $\sin \theta = \tan \theta $
Substituting, we get,
$\Delta x = d\tan \theta $
From the figure, $\tan \theta = \dfrac{y}{D}$
Thus, substituting the value of $\tan \theta $, we get,
$
\Delta x = d\tan \theta \\
\Rightarrow \Delta x = d \times \dfrac{y}{D} \\
$
Substituting the values, we get
$
\Delta x = d \times \dfrac{y}{D} \\
\Rightarrow \Delta x = 1 \times \dfrac{2}{{1000}} \\
\Rightarrow \Delta x = 2 \times {10^{ - 3}}mm \\
\Rightarrow \Delta x = 2\mu m \\
$
Hence, the path difference, $\Delta x = 2\mu m$
Note:
At point P, there are two things that could happen. Either a bright fringe can be formed at the point of a dark fringe that can be formed at the point. The criteria for deciding this is solely, based on the path difference at that point.
If the path difference is equal to even multiples of $\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$ such as $\lambda, 2\lambda, 3\lambda ...2n\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$, there is a constructive interference at this point and we obtain a bright fringe.
If the path difference is equal to odd multiples of $\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$ such as $\dfrac{\lambda }{2},\dfrac{{3\lambda }}{2},\dfrac{{5\lambda }}{2}...\left( {2n + 1} \right)\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$, there is a destructive interference at this point and we obtain a dark fringe.
$P.D = OP - D$
Complete step by step answer:
Consider Young’s double-slit experiment as shown in the above figure

We see in this given figure that there is no presence of the slits as the dotted line at P actually, represents the path difference. By writing the actual figure denoting the two slits and the two wavefronts individually, we get a modified diagram like this,

$\theta $ is the angle between the path difference and the horizontal reference line as shown.
The path difference, $\Delta x = d\sin \theta $
Since the angle $\theta $ is very small, we can say that, $\sin \theta = \tan \theta $
Substituting, we get,
$\Delta x = d\tan \theta $
From the figure, $\tan \theta = \dfrac{y}{D}$
Thus, substituting the value of $\tan \theta $, we get,
$
\Delta x = d\tan \theta \\
\Rightarrow \Delta x = d \times \dfrac{y}{D} \\
$
Substituting the values, we get
$
\Delta x = d \times \dfrac{y}{D} \\
\Rightarrow \Delta x = 1 \times \dfrac{2}{{1000}} \\
\Rightarrow \Delta x = 2 \times {10^{ - 3}}mm \\
\Rightarrow \Delta x = 2\mu m \\
$
Hence, the path difference, $\Delta x = 2\mu m$
Note:
At point P, there are two things that could happen. Either a bright fringe can be formed at the point of a dark fringe that can be formed at the point. The criteria for deciding this is solely, based on the path difference at that point.
If the path difference is equal to even multiples of $\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$ such as $\lambda, 2\lambda, 3\lambda ...2n\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$, there is a constructive interference at this point and we obtain a bright fringe.
If the path difference is equal to odd multiples of $\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$ such as $\dfrac{\lambda }{2},\dfrac{{3\lambda }}{2},\dfrac{{5\lambda }}{2}...\left( {2n + 1} \right)\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$, there is a destructive interference at this point and we obtain a dark fringe.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




