
In which of the following molecules, all atoms are coplanar?
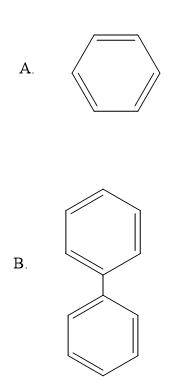
D. \[HCHO\]


Answer
514.5k+ views
Hint :Co-planar molecule can be defined as the molecule in which all the atoms, bonds, lone pairs of electrons of the compound lie in the same plane. Co-planar molecule suggests that it has taken two dimensional geometry.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
So, as we have understood the meaning of the term co-plane i.e. all the atoms of the molecules in the same plane (two dimensional).
Now, the next question arises: how to check whether the compound is co-planar or not.
So, to check this coplanarity we need to understand the Hybridisation of the molecule.
So, hybridisation is the binding of atomic orbitals to form newly hybridized orbitals.
Therefore, co-planarity is found in the unsaturated compounds.
The compounds having the \[s{p^2}\] hybridisation will be the co-planar molecule or better say that when in the compound all the atoms are in \[s{p^2}\] hybridisation, then that compound is co-planar.
So, let’s solve the given question.
From the given options we can see very clearly that the benzene molecule has all the atoms in the \[s{p^2}\] hybridized state, so it is a co-planar molecule.
Also, the option B i.e. biphenyl, also has all the atoms in the \[s{p^2}\] hybridized state only, so it is also a co-planar molecule.
Therefore we can say that the correct answer is option A and B i.e. Benzene and biphenyl.
Note :
There is a shortcut method to calculate the hybridisation of the atom of the given molecule. So for that just look at the particular atom, then count its number of atoms connected to it and not the bonds. Then count the number of lone pairs of electrons attached to it. Then add both, this will give the hybridisation of the atom.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
So, as we have understood the meaning of the term co-plane i.e. all the atoms of the molecules in the same plane (two dimensional).
Now, the next question arises: how to check whether the compound is co-planar or not.
So, to check this coplanarity we need to understand the Hybridisation of the molecule.
So, hybridisation is the binding of atomic orbitals to form newly hybridized orbitals.
Therefore, co-planarity is found in the unsaturated compounds.
The compounds having the \[s{p^2}\] hybridisation will be the co-planar molecule or better say that when in the compound all the atoms are in \[s{p^2}\] hybridisation, then that compound is co-planar.
So, let’s solve the given question.
From the given options we can see very clearly that the benzene molecule has all the atoms in the \[s{p^2}\] hybridized state, so it is a co-planar molecule.
Also, the option B i.e. biphenyl, also has all the atoms in the \[s{p^2}\] hybridized state only, so it is also a co-planar molecule.
Therefore we can say that the correct answer is option A and B i.e. Benzene and biphenyl.
Note :
There is a shortcut method to calculate the hybridisation of the atom of the given molecule. So for that just look at the particular atom, then count its number of atoms connected to it and not the bonds. Then count the number of lone pairs of electrons attached to it. Then add both, this will give the hybridisation of the atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




