
In triangle ABC, base BC and area of triangle are fixed. The locus of the centroid of triangle ABC is a straight line that is:
(a) parallel to side BC
(b) right bisector of side BC
(c) right angle of BC
(d) inclined at an angle ${{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{\Delta }}{BC} \right)$ to side BC
Answer
543.6k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we need to use the formula for the area of a triangle which is given by $\Delta =\dfrac{1}{2}bh$, where b and h are respectively the base length and the height of the triangle. From this, we can prove the height of the triangle to be a constant. Then using the property of the centroid that it divides the median into the ratio of $2:1$, we can arrive at the correct result.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the information given in the question, we can consider the figure of the given triangle ABC as shown below.
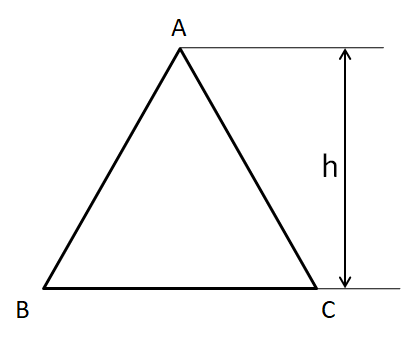
Let the height of the triangle be h, as shown in the above figure.
Now, we know that the area of a triangle is given by
$\Rightarrow \Delta =\dfrac{1}{2}bh$
In the above figure, we can see that the base is BC. Therefore, substituting $b-BC$ we get
$\Rightarrow \Delta =\dfrac{1}{2}\left( BC \right)h$
Multiplying both the sides by $\dfrac{2}{BC}$ we ge
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{BC}\times \Delta =\dfrac{2}{BC}\times \dfrac{1}{2}\left( BC \right)h \\
& \Rightarrow h=\dfrac{2\Delta }{BC} \\
\end{align}\]
According to the question, the base and the area of the triangle ABC are fixed. Therefore, $\Delta $ and $BC$ will be constant and thus from the above equation we can say that the height, h of the triangle will also be constant. From the above figure, this means that the distance of the vertex A from the base BC will be fixed. Now, let us consider the median AM passing through the vertex A as shown below.
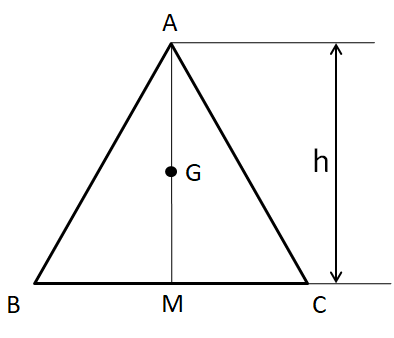
Since the centroid lies on the median, the centroid G of the triangle ABC will lie on the median AM. Now, we know that the centroid divides the median in the ratio of $2:1$. This means we can write
\[\Rightarrow AG=\dfrac{GM}{2}.......\left( i \right)\]
Also, from the above figure we can write
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow AG+GM=AM \\
& \Rightarrow AG+GM=h \\
\end{align}$
Substituting (i) in the above equation we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{GM}{2}+GM=h \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{2}GM=h \\
\end{align}$
Multiplying both the sides by $\dfrac{2}{3}$ we get
$\Rightarrow GM=\dfrac{2}{3}h$
Since we proved h to be a constant, from the above equation GM is also a constant. This means that the distance of the centroid from the base is a constant. This in turn means that the locus of the centroid has to be parallel to BC, so that its distance from BC remains constant.
Hence, the correct answer is option (a).
Note: We can also assume the coordinates of the vertices of the given triangle as $A\left( a,0 \right);B\left( b,0 \right);C\left( c,h \right)$ and using the formula for the coordinates of the centroid, we will get ${{x}_{C}}=\dfrac{a+b+c}{3}$ and ${{y}_{C}}=\dfrac{h}{3}$. Since h is a constant, the y-coordinate of the centroid will be a constant, which in turn means that the locus of the centroid must be a line parallel to the x-axis, on which the base BC lies.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the information given in the question, we can consider the figure of the given triangle ABC as shown below.

Let the height of the triangle be h, as shown in the above figure.
Now, we know that the area of a triangle is given by
$\Rightarrow \Delta =\dfrac{1}{2}bh$
In the above figure, we can see that the base is BC. Therefore, substituting $b-BC$ we get
$\Rightarrow \Delta =\dfrac{1}{2}\left( BC \right)h$
Multiplying both the sides by $\dfrac{2}{BC}$ we ge
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{BC}\times \Delta =\dfrac{2}{BC}\times \dfrac{1}{2}\left( BC \right)h \\
& \Rightarrow h=\dfrac{2\Delta }{BC} \\
\end{align}\]
According to the question, the base and the area of the triangle ABC are fixed. Therefore, $\Delta $ and $BC$ will be constant and thus from the above equation we can say that the height, h of the triangle will also be constant. From the above figure, this means that the distance of the vertex A from the base BC will be fixed. Now, let us consider the median AM passing through the vertex A as shown below.

Since the centroid lies on the median, the centroid G of the triangle ABC will lie on the median AM. Now, we know that the centroid divides the median in the ratio of $2:1$. This means we can write
\[\Rightarrow AG=\dfrac{GM}{2}.......\left( i \right)\]
Also, from the above figure we can write
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow AG+GM=AM \\
& \Rightarrow AG+GM=h \\
\end{align}$
Substituting (i) in the above equation we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{GM}{2}+GM=h \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{2}GM=h \\
\end{align}$
Multiplying both the sides by $\dfrac{2}{3}$ we get
$\Rightarrow GM=\dfrac{2}{3}h$
Since we proved h to be a constant, from the above equation GM is also a constant. This means that the distance of the centroid from the base is a constant. This in turn means that the locus of the centroid has to be parallel to BC, so that its distance from BC remains constant.
Hence, the correct answer is option (a).
Note: We can also assume the coordinates of the vertices of the given triangle as $A\left( a,0 \right);B\left( b,0 \right);C\left( c,h \right)$ and using the formula for the coordinates of the centroid, we will get ${{x}_{C}}=\dfrac{a+b+c}{3}$ and ${{y}_{C}}=\dfrac{h}{3}$. Since h is a constant, the y-coordinate of the centroid will be a constant, which in turn means that the locus of the centroid must be a line parallel to the x-axis, on which the base BC lies.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which country won the ICC Men's ODI World Cup in 2023?

In cricket, how many legal balls are there in a standard over?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

What does "powerplay" mean in limited-overs cricket?

What is the "Powerplay" in T20 cricket?




