
In the thiocyanate ion, \[{\text{SC}}{{\text{N}}^ - }\] , three resonance structures are consistent with the electron-dot method. Structure A has only one negative formal charge on the nitrogen atom, the most electron negative atom in the ion. Structure B has a single negative charge on the S, which is less electronegative than N. Structure C has charges of −2 on N and +1 on S, consistent with the relative electronegativities of the atom s but with a larger charger and greater charge separation than the first.
Predict the hybridization of an atom which is bonded with H in the structure of \[{\text{HNCS}}\] .
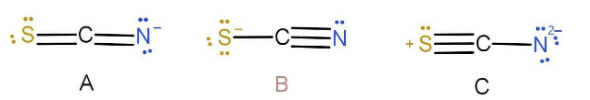
A.\[{\text{sp}}\]
B.\[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\]
C.\[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}\]
D.No hybridization

Answer
545.7k+ views
Hint: If the hydrogen gets attached to the double bond then the hybridisation will be \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\] hybridisation. If the hydrogen gets attached to an atom which is under resonance then also the hybridisation of that atom will be \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\] .
Complete step-by-step answer:Hydrogen has the atomic number 1. It requires one more electron to complete its out electronic configuration. So it will attach to that carbon which is electron rich and has more electron density in order to gain stability.
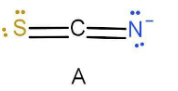
In case A as we can see that nitrogen has a negative charge and sulphur has only lone pair of electron. A negative charge has more tendencies to donate electron and hence the hydrogen will attach to the nitrogen instead of sulphur. The valency of carbon is satisfied and hence hydrogen will not attach there. Also the nitrogen is attached with double bond and hence the hybridisation will be \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\] .
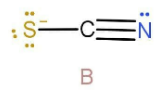
In case B the hydrogen will attach to the sulphur due to the presence of negative charge. As we can see that lone pair is in resonance with the double bond. So the hybridisation will also be \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\] .

In case C, sulphur has a positive charge and hence can never attract hydrogen. The hydrogen will go towards the nitrogen. The nitrogen has adjacent pi bonds and has lone pairs of electrons too. The nitrogen is in resonance and so the hybridisation will be \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\] .
Thus, the correct option is B.
Note:When a single Lewis structure cannot explain all the properties of an element then we have to draw various structures to explain all the properties. These various structures are known as resonating structures.
Complete step-by-step answer:Hydrogen has the atomic number 1. It requires one more electron to complete its out electronic configuration. So it will attach to that carbon which is electron rich and has more electron density in order to gain stability.

In case A as we can see that nitrogen has a negative charge and sulphur has only lone pair of electron. A negative charge has more tendencies to donate electron and hence the hydrogen will attach to the nitrogen instead of sulphur. The valency of carbon is satisfied and hence hydrogen will not attach there. Also the nitrogen is attached with double bond and hence the hybridisation will be \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\] .

In case B the hydrogen will attach to the sulphur due to the presence of negative charge. As we can see that lone pair is in resonance with the double bond. So the hybridisation will also be \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\] .

In case C, sulphur has a positive charge and hence can never attract hydrogen. The hydrogen will go towards the nitrogen. The nitrogen has adjacent pi bonds and has lone pairs of electrons too. The nitrogen is in resonance and so the hybridisation will be \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\] .
Thus, the correct option is B.
Note:When a single Lewis structure cannot explain all the properties of an element then we have to draw various structures to explain all the properties. These various structures are known as resonating structures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




